Abstract
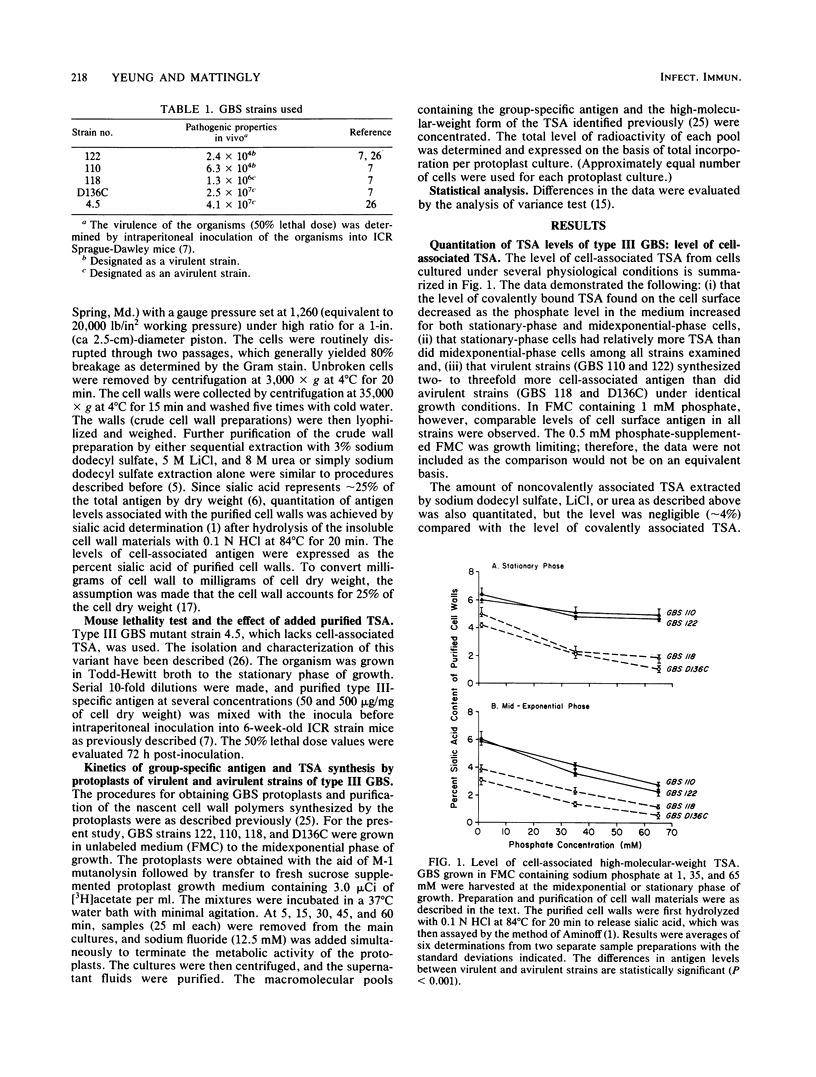
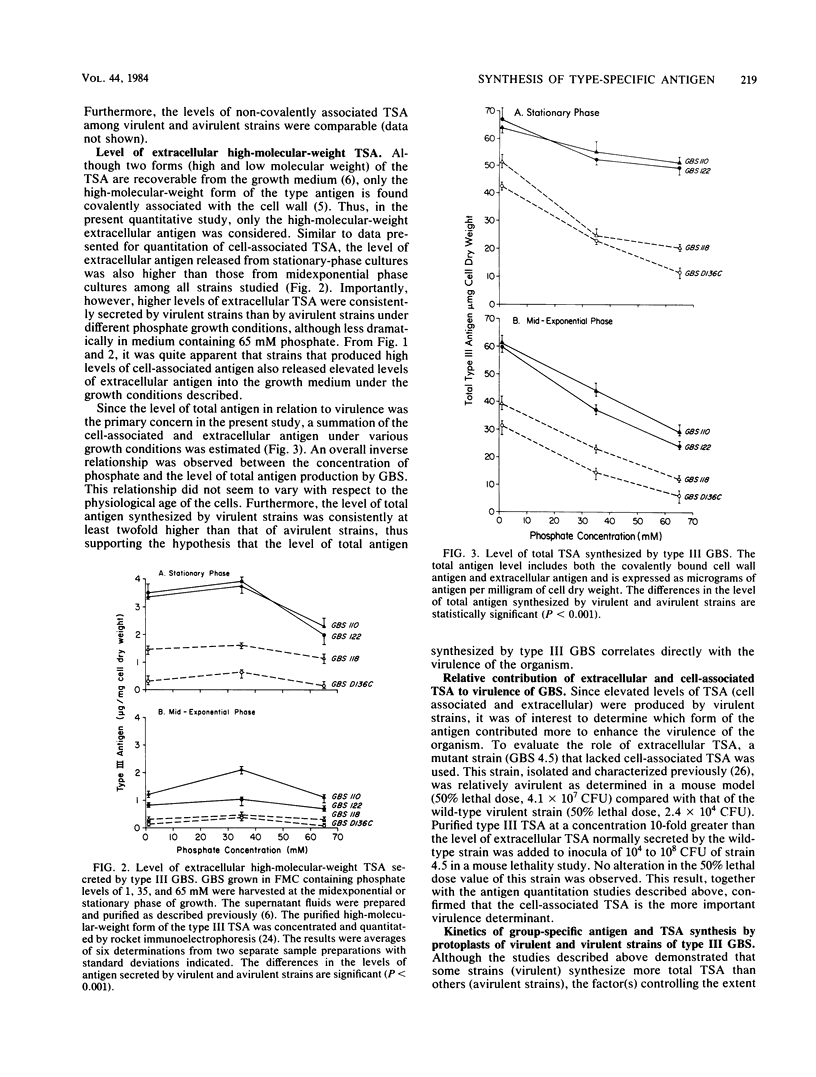
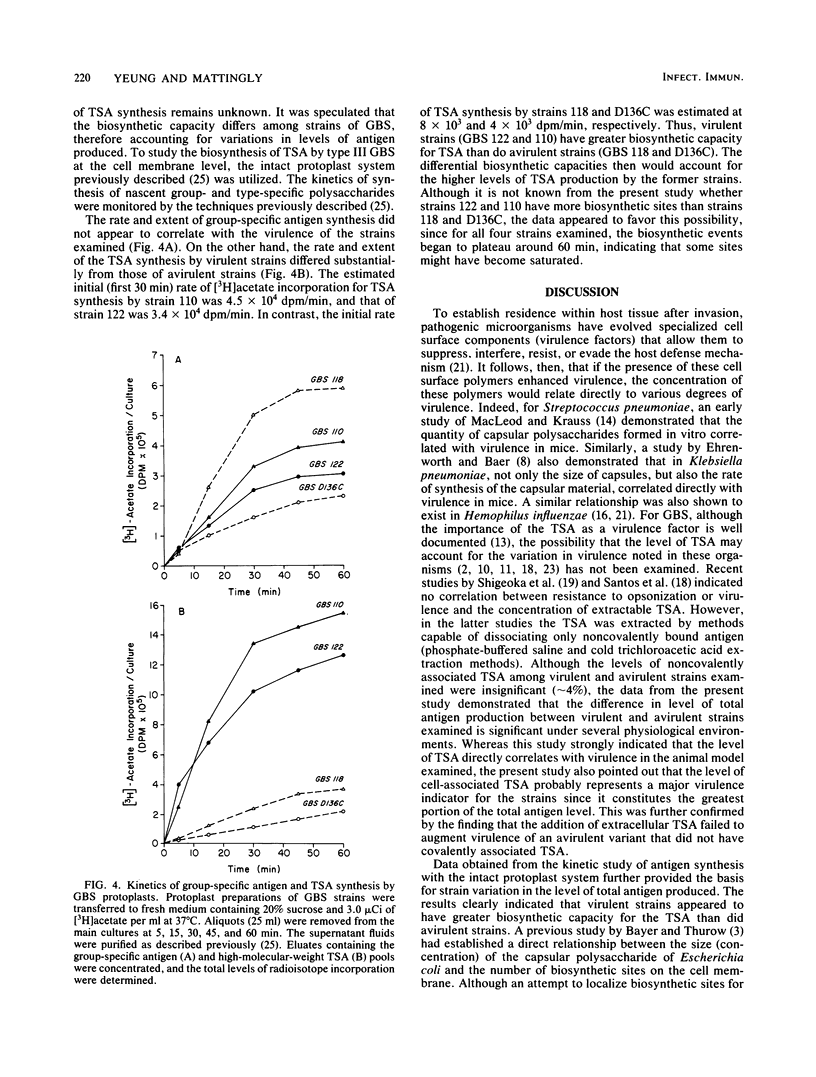
The level of type-specific antigen (that covalently associated with the cell wall peptidoglycan and that released extracellularly) synthesized by virulent and avirulent strains of type III group B streptococci was quantitated and compared. Additionally, the effect of the physiological age of the cells and the influence of the exogenous phosphate ion concentration on the level of antigen synthesis by these organisms were also examined. Approximately 4% of the total antigen synthesized by the organism is noncovalently bound to the cell surface, and the difference in level of the noncovalently associated type-specific antigen between virulent and avirulent strains was negligible. In contrast, when the cell-associated covalently bound type antigens were evaluated, virulent strains were demonstrated to have two- to threefold higher levels than those of avirulent strains during the exponential and stationary phases of growth under various growth conditions. Furthermore, virulent strains that had high levels of cell-associated type antigen also secreted more extracellular type antigen than did avirulent strains. Thus, the data were consistent with the hypothesis that an overall production of type-specific antigen correlated with virulence in mice. However, the cell-associated type-specific antigen probably represented a better indicator for virulence potential since the addition of purified extracellular type-specific antigen to a mutant strain that lacks cell surface type antigen did not alter the 50% lethality value of the organism. To account for variation in the level of type-specific antigen produced by these strains, the kinetics of both the group- and type-specific antigens synthesis was investigated at the cell membrane level by utilizing an intact protoplast system.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAER H., EHRENWORTH L. The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae for mice: the relationship to the quantity and rate of production of type-specific capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.713-717.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Vecchitto J. Mouse protection test for group B Streptococcus type III. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):81–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Group B, type III streptococcal cell wall: composition and structural aspects revealed through endo-N-acetylmuramidase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):572–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.572-581.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Mattingly S. J. Association of type- and group-specific antigens with the cell wall of serotype III group B streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1115–1122. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1115-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Factors influencing release of type III antigens by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.615-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham D. L., Mattingly S. J., Doran T. I., Milligan T. W., Straus D. C. Correlation between the production of extracellular substances by type III group B streptococcal strains and virulence in a mouse model. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):448–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.448-454.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Burke B., Nelson J. Production of bacteremia and meningitis in infant rats with group B streptococcal serotypes. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.1023-1032.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. W., Hunter K. W., Wilson S. R. Type III group B streptococcal strain differences in susceptibility to opsonization with human serum. Pediatr Res. 1981 Dec;15(12):1525–1529. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198112000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruyssen F. J., de Boer W. R., Wouters J. T. Cell wall metabolism in Bacillus subtilis subsp. niger: effects of changes in phosphate supply to the culture. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):867–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.867-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLEOD C. M., KRAUS M. R. Relation of virulence of pneumococcal strains for mice to the quantity of capsular polysaccharide formed in vitro. J Exp Med. 1950 Jul 1;92(1):1–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Anderson P., Ingram D. L., Peter G., Smith D. H. Circulating polyribophosphate in Hemophilus influenzae, type b meningitis. Correlation with clinical course and antibody response. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1012–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI108148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. I., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Strain differences in virulence of group B streptococci. Pediatr Res. 1982 May;16(5):347–350. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198205000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Hall R. T., Hill H. R. Strain specificity of opsonins for group B streptococci types II and III. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.438-445.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Schneerson R., Kendall-Morris S., Robbins J. B. Differential complement resistance mediates virulence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.95-104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieffenberg J., Vogel L., Kretschmer R. R., Padnos D., Gotoff S. P. Chicken embryo model for type III group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal septicemia. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):481–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.481-485.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. A manual of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. 1. General remarks on principles, equipment, reagents and procedures. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:15–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K., Mattingly S. J. Biosynthesis of cell wall peptidoglycan and polysaccharide antigens by protoplasts of type III group B Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.211-220.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K., Mattingly S. J. Isolation and characterization of type III group B streptococcal mutants defective in biosynthesis of the type-specific antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):141–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.141-151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


