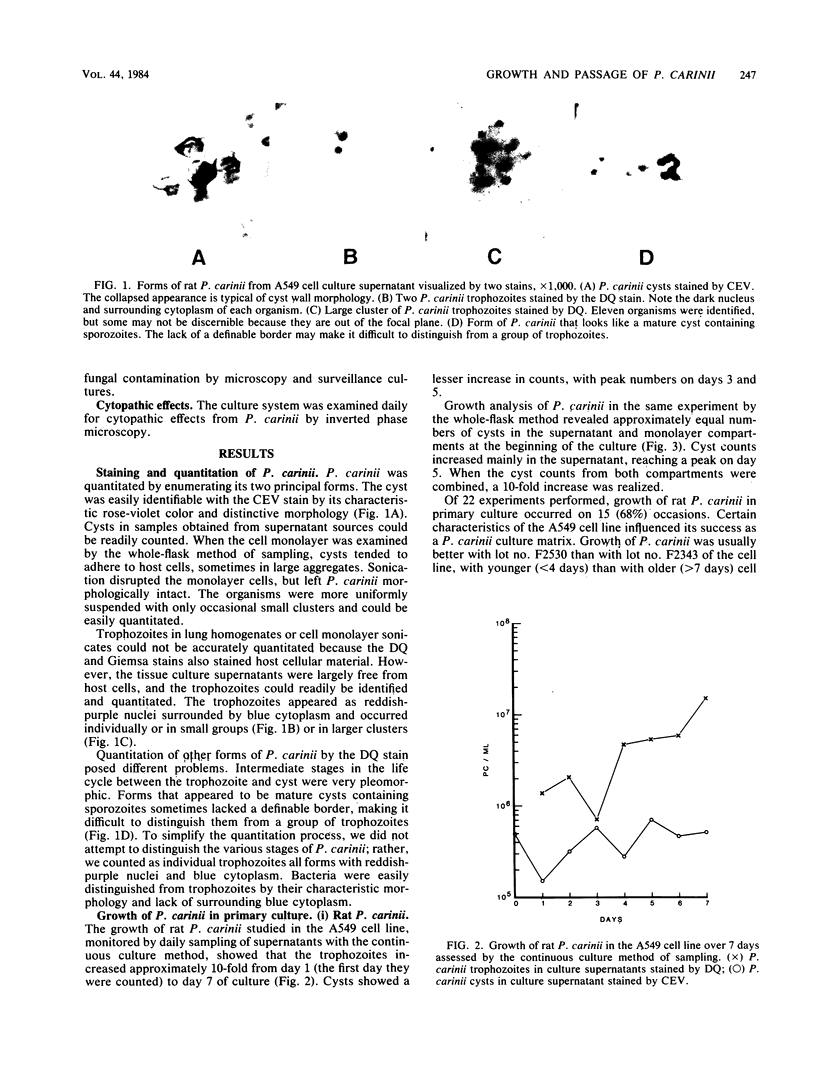
Abstract
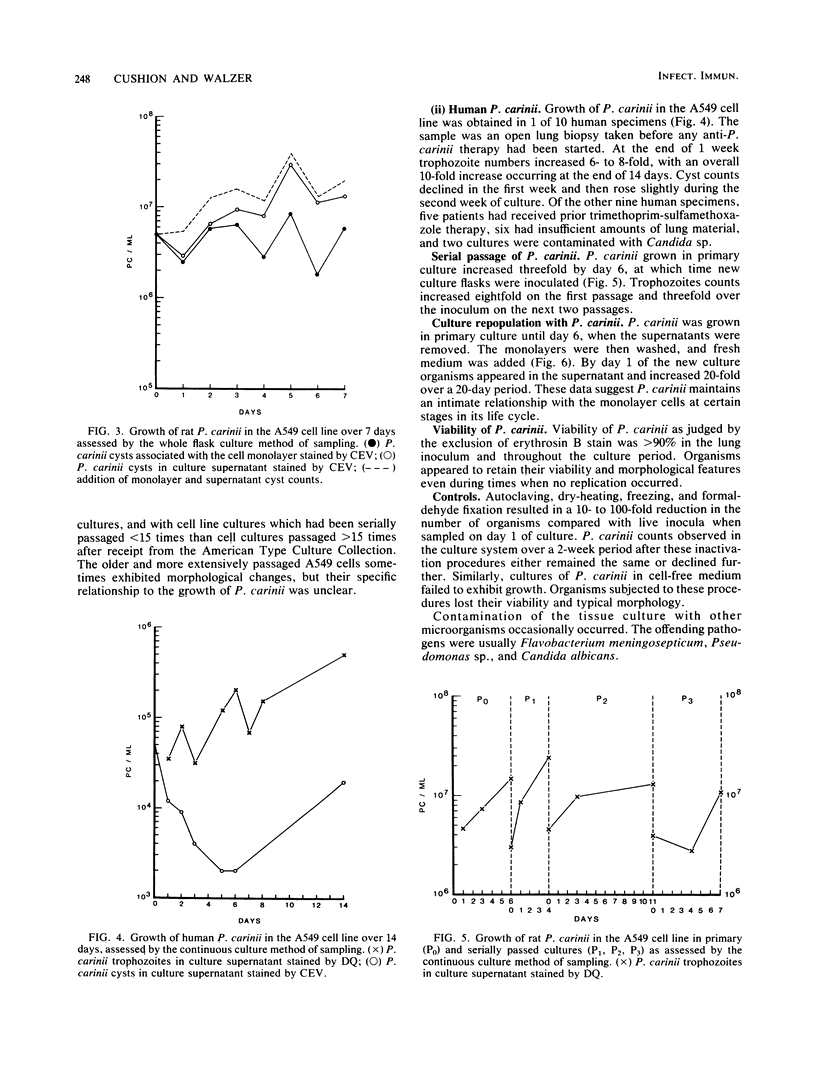
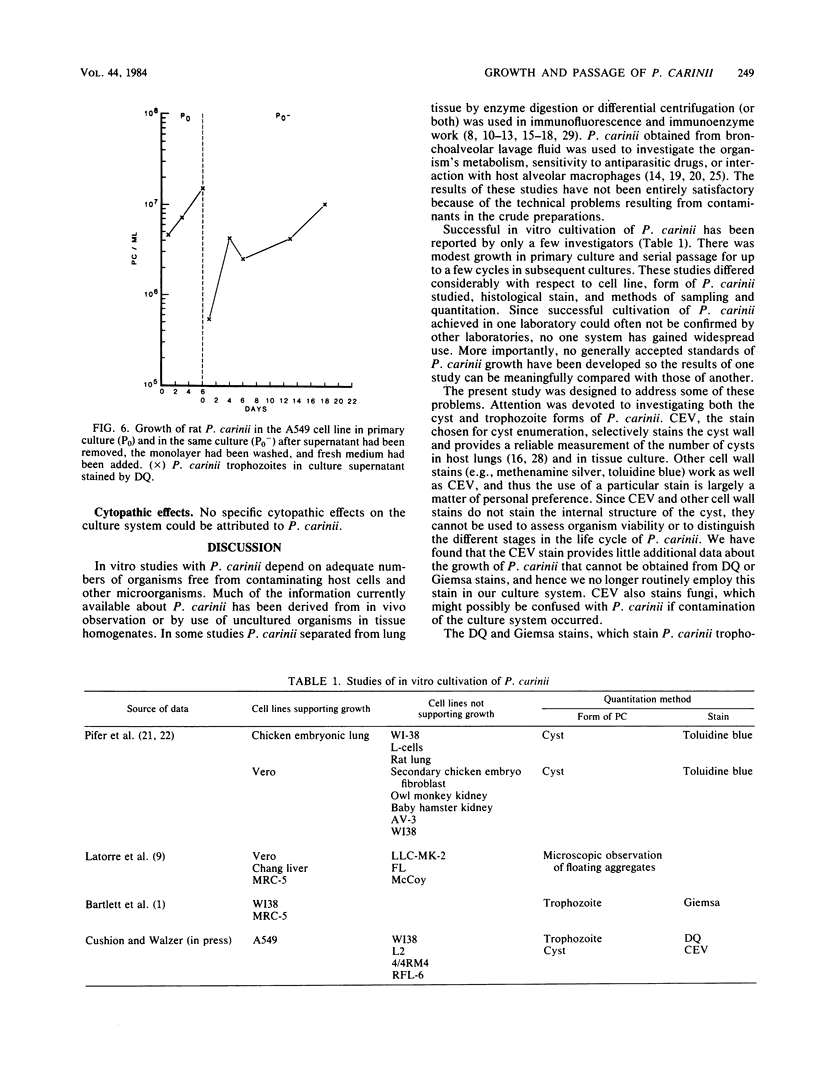
Pneumocystis carinii obtained from infected rats and patients was cultured in the A549 cell line, a presumptive alveolar type 2 cell line derived from a human lung carcinoma. Standard criteria were established for organism sampling, quantitation, and growth. The trophozoite form of P. carinii was a more sensitive indicator of growth than was the cyst. Rat P. carinii increased 10-fold in primary culture and could be serially passed three additional times to new cultures; success in growing human P. carinii was limited and appeared to be related to the quality of the specimen received for culture. Growth pattern experiments suggested that close interaction of P. carinii with the cell monolayer is an important step in the life cycle of the organism. Thus, the A549 culture system should be useful for in vitro studies of the immunobiology of P. carinii.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling M. C., Smith I. M., Wescott S. L. A rapid staining procedure for Pneumocystis carinii. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Jul;39(7):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. H., Moorman G. W., Teel R. W. The formation of histotypic structures from monodisperse fetal rat lung cells cultured on a three-dimensional substrate. In Vitro. 1976 May;12(5):373–381. doi: 10.1007/BF02796315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The syndrome of Kaposi's sarcoma and opportunistic infections: an epidemiologically restricted disorder of immunoregulation. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):777–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. J., Williams C. D., Macy M. L., Lavappa K. S. Cultured cell lines for research on pulmonary physiology available through the American type culture collection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Feb;125(2):222–232. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T., Feldman S. Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):304–309. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Development and evaluation of a direct fluorescent antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii infections in experimental animals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):666–671. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.666-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Eveland W. C., Porter R. J. Direct fluorescent-antibody method for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis from sputa or tracheal aspirates from humans. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):144–149. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.144-149.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Ivey M. H., Tsang V. C., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G. Fractionation of Pneumocystis carinii antigens used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies and in the production of antiserum for detecting Pneumocystis carinii antigenemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1029–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1029-1035.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G., Ivey M. H. Detection of specific antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and antigenemia by counterimmunoelectrophoresis in humans infected with Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1036-1043.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Leeuwenberg A. D., Heeren J., Stumpel A. New method for study of infections with Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):209–210. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder J. E., Walzer P. D., Coonrod J. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of histological and immunological techniques for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in rat bronchial lavage fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):409–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.409-417.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minielly J. A., McDuffie F. C., Holley K. E. Immunofluorescent identification of Pneumocystis carinii. Arch Pathol. 1970 Dec;90(6):561–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. A preliminary report of an indirect fluorescent antibody test for detecting antibodies to cysts of Pneumocystis carinii in human sera. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;58(2):170–176. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L., Cox C. Metabolic and synthetic activities of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):908–914. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.908-914.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. T. Cell line A549: a model system for the study of alveolar type II cell function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Feb;115(2):285–293. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. D., Harris C. C., Autrup H., Trump B. F., Kingsbury E. W., Myers G. A. Explant culture of human peripheral lung. I. Metabolism of benzo[alpha]pyrene. Lab Invest. 1978 Jun;38(6):685–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Behren L. A., Pesanti E. L. Uptake and degradation of Pneumocystis carinii by macrophages in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Dec;118(6):1051–1059. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K., Rutledge M. E., Milder J. E. Growth characteristics and pathogenesis of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):928–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.928-937.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to type I alveolar cells studied by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):812–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.812-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Interaction of Pneumocystis carinii with host lungs: an ultrastructural study. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):692–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.692-703.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]