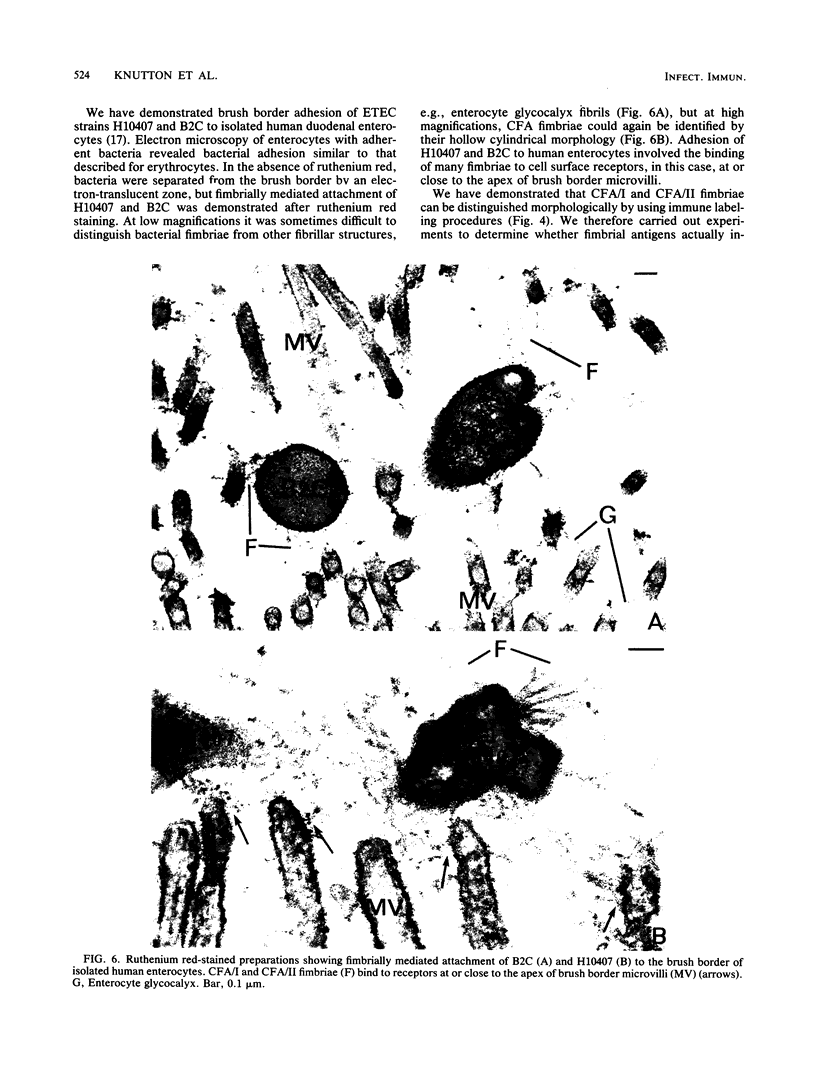
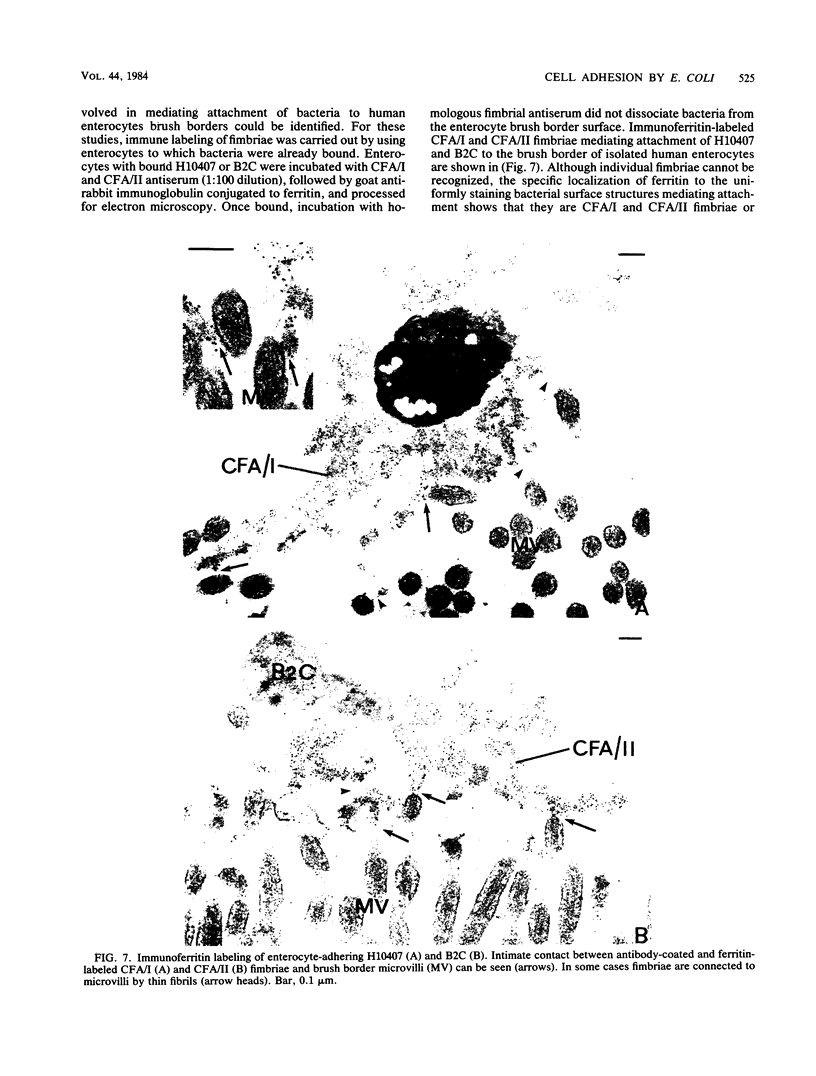
Abstract
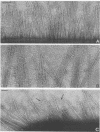
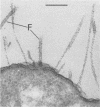
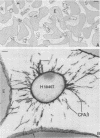
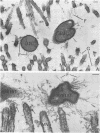
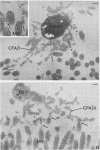
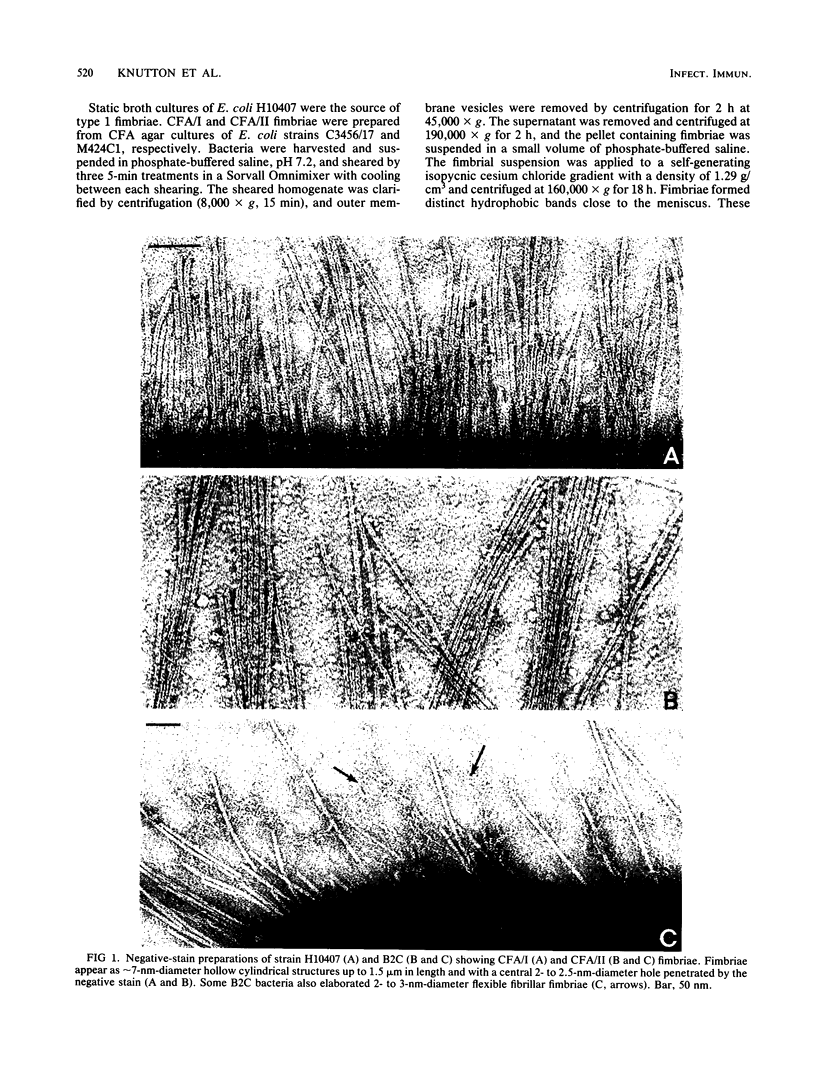
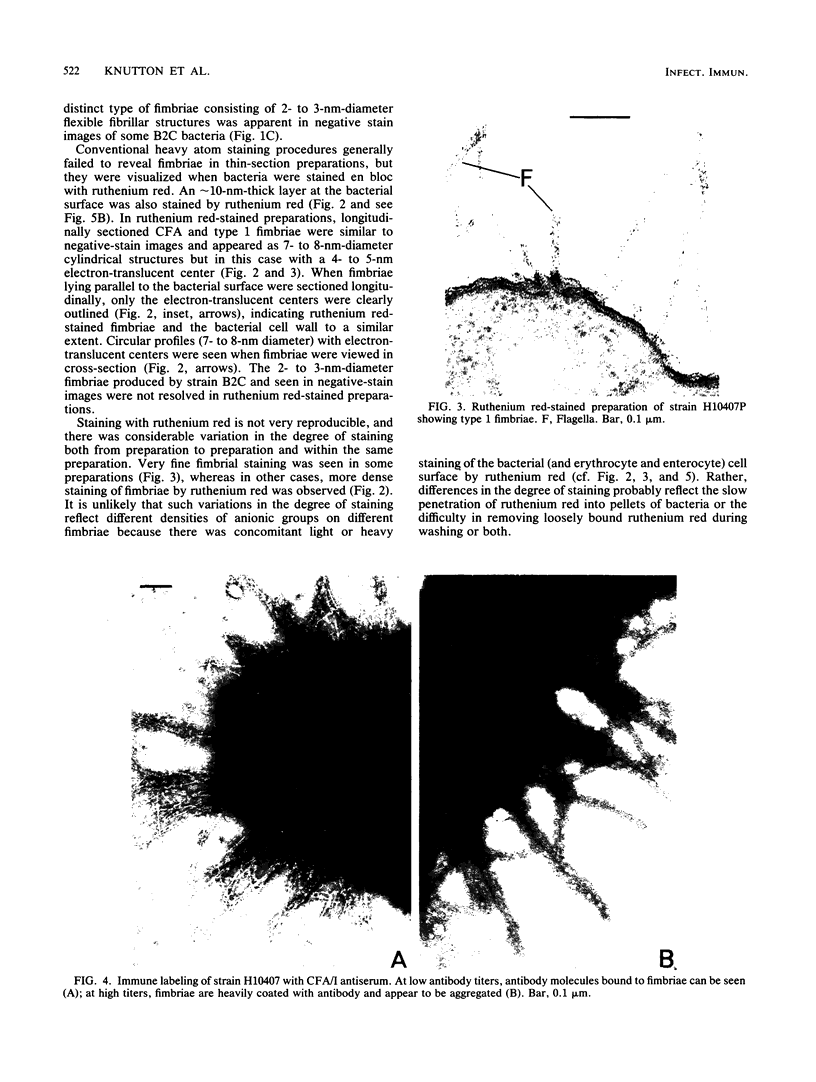
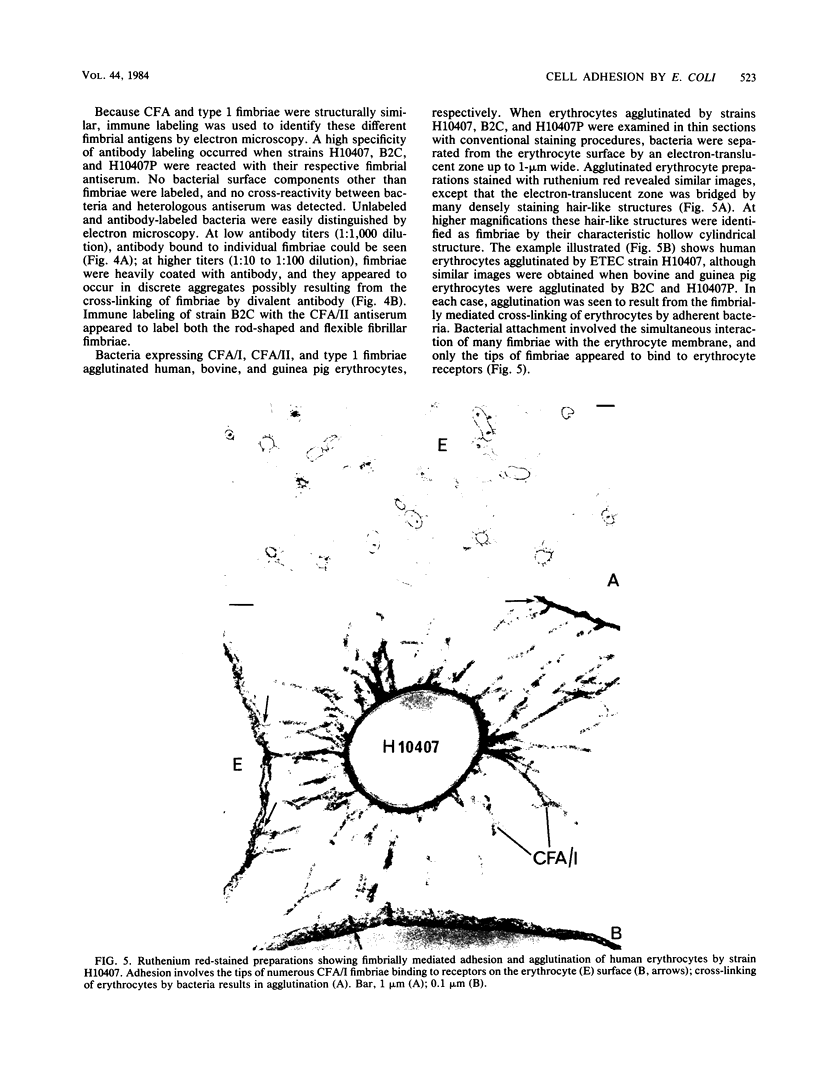
The adhesion to erythrocytes and human intestinal epithelial cells of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains H10407, B2C, and H10407P, expressing colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I), CFA/II, and type 1 fimbriae, respectively, was examined by electron microscopy. CFA and type 1 fimbriae were visualized by negative staining in thin sections after en bloc staining with ruthenium red and by immune labeling with antisera raised against purified fimbriae. By negative and ruthenium red staining, CFA/I, CFA/II, and type 1 fimbriae were indistinguishable and appeared as approximately 7-nm-diameter hollow cylindrical structures up to 1.5 micron in length; strain B2C also produced 2- to 3-nm-diameter flexible fibrillar fimbriae. Bacteria producing CFA/I, CFA/II, and type 1 fimbriae adhered to and agglutinated human, bovine, and guinea pig erythrocytes, respectively; CFA/I and CFA/II also mediated attachment of bacteria to the brush border of isolated human duodenal enterocytes. Electron microscopy of agglutinated erythrocytes and enterocytes with adherent bacteria showed, in each case, that bacterial adhesion involved the formation of many interactions between the tips of fimbriae and receptors on the erythrocyte or enterocyte brush border membrane. Immune labeling allowed different fimbrial antigens mediating bacterial attachment to human enterocytes to be identified.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Acres S. D., Costerton J. W. Use of specific antibody to demonstrate glycocalyx, K99 pili, and the spatial relationships of K99+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the ileum of colostrum-fed calves. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1170–1180. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1170-1180.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C. Adherence of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain, serotype O78:H11, to purified human intestinal brush borders. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1280–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1280-1284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cravioto A., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Hemagglutination activity and colonization factor antigens I and II in enterotoxigenic and non-enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):189–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.189-197.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Gorbach S. L. Attachment pili from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):362–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.362-368.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S., Pauley J. A. Purification and characterization of the CFA/I antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.738-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., Wilson M. R. Adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to intestinal epithelium in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):866–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.866-880.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. In vitro adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal epithelial cells from mucosal biopsies. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.514-518.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. Simple immunological labelling method for electron microscopy and its application to the study of filamentous appendages of bacteria. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1151–1152. doi: 10.1038/2141151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans and animals. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:142–160. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Ristaino P., Sack R. B., Kaper J. B., Orskov F., Orskov I. Colonization factor antigens I and II and type 1 somatic pili in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: relation to enterotoxin type. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):889–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.889-897.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Special O:K:H serotypes among enterotoxigenic E. coli strains from diarrhea in adults and children. Occurrence of the CF (colonization factor) antigen and of hemagglutinating abilities. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Jul 18;163(2):99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF02121825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Plasmids that code for production of colonization factor antigen II and enterotoxin production in strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1236–1239. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1236-1239.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Observations on the pathogenic properties of the K88, Hly and Ent plasmids of Escherichia coli with particular reference to porcine diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):467–485. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J. Two mannose-resistant haemagglutinins on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serotype O6:K15:H16 or H-isolated from travellers' and infantile diarrhoea. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2081–2096. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. V., Cravioto A., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. New fimbrial antigenic type (E8775) that may represent a colonization factor in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1119–1124. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1119-1124.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]