Abstract
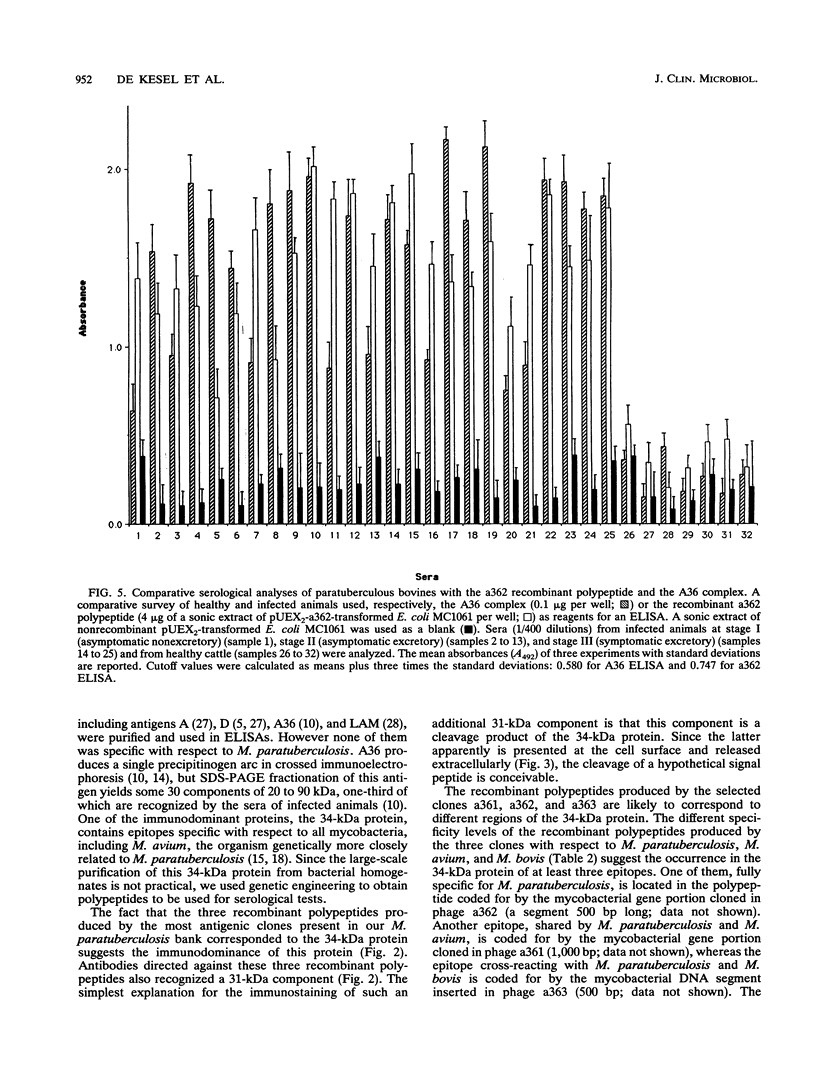
Paratuberculosis (Johne's disease), an endemic mycobacteriosis of cattle that is caused by Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, is characterized by incoercible diarrhea and fecal shedding of bacteria. The present work aimed at developing a specific serological test for this disease. We have recently shown that a 34-kDa protein belonging to the major antigen complex A36 of M. paratuberculosis is immunodominant and contains epitopes specific with respect to all mycobacteria tested, including Mycobacterium bovis and the closely related species Mycobacterium avium. From a lambda gt11 genomic library of M. paratuberculosis, three portions of the gene coding for this 34-kDa protein have been isolated. Two of them expressed cross-reacting mycobacterial epitopes. One portion (in clone a362) expressed a polypeptide which cross-reacted with all tested M. paratuberculosis strains but not with 20 other bacteria tested, including many strains of the M. avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum group. The occurrence at the M. paratuberculosis surface of epitopes corresponding to the a362 polypeptide was shown by immune electron microscopy. The recombinant a362 polypeptide was used as reagent for an enzyme-linked immunoassay for paratuberculosis. This assay correctly diagnosed all the tested blood samples from infected cattle at all stages of the disease.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas B., Riemann H. P., Lonnerdal B. Isolation of specific peptides from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis protoplasm and their use in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of paratuberculosis (Johne's disease) in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Dec;44(12):2229–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Nielsen S., Burianek L. L., Spangler E., Heider L. E., Hoffsis G. F., Dorn C. R. Characterization of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis antigenic proteins. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2418–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressan G. M., Stanley K. K. pUEX, a bacterial expression vector related to pEX with universal host specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10056–10056. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. W., Robertson R. H., Corner A. H., Samagh B. S., Garcia M. M., Turcotte C., Duncan J. R. Evaluation of the serological response of sheep in one flock to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):199–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. W., Young N. M., Watson D. C., Robertson R. H., Sugden E. A., Nielsen K. H., Becker S. A. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis antigen D: characterization and evidence that it is a bacterioferritin. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1652–1658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1652-1658.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camphausen R. T., Jones R. L., Brennan P. J. A glycolipid antigen specific to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis: structure and antigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3068–3072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., de Wergifosse P., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Identification of seven surface-exposed Brucella outer membrane proteins by use of monoclonal antibodies: immunogold labeling for electron microscopy and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3980–3987. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3980-3987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Høiby N., Jørgensen J. B., Bercovier H., Lambrecht R. S., Jørgensen E. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. APMIS. 1991 Jan;99(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kesel M., Gilot P., Coene M., Cocito C. Composition and immunological properties of the protein fraction of A36, a major antigen complex of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Aug;36(2):201–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo A., Marco R. Visualization under ultraviolet light enhances 100-fold the sensitivity of peroxidase-stained blots. Anal Biochem. 1989 Oct;182(1):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90738-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour N. J., Goudswaard J. Corynebacterium renale as a cause of reactions to the complement fixation test for Johne's disease. J Comp Pathol. 1972 Jul;82(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(72)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilot P., De Kesel M., Coene M., Cocito C. Induction of cellular immune reactions by A36, an antigen complex of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis: comparison of A36 and johnin components. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Dec;36(6):811–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson E., Fodstad F. H. Analysis of antigens in Mycobacterium paratubercuolsis. Acta Vet Scand. 1979;20(2):200–215. doi: 10.1186/BF03546612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnappa G., Jagannath C., Rao B. U. The specificity of antibody response in experimental and natural bovine paratuberculosis studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Nov;21(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körmendy B. Diagnostic value of mammalian, avian and johnin PPD tuberculins in cattle herds infected by Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Acta Vet Hung. 1988;36(3-4):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labidi A., Thoen C. O. Genetic relatedness among Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and M. avium complex. Acta Leprol. 1989;7 (Suppl 1):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie R. A., Donald B. A. Lymphadenitis in cattle associated with Corynebacterium equi: a problem in bovine tuberculosis diagnosis. J Comp Pathol. 1979 Jan;89(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(79)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie R. A., Ward W. H. Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi: a possible cause of reactions to the complement fixation test for Johne's disease of cattle. Aust Vet J. 1981 Apr;57(4):200–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1981.tb00517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Curran B. J. Growth and metabolic characteristics of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):276–279. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.276-279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeremans M., Daneels G., De Mey J. Sensitive colloidal metal (gold or silver) staining of protein blots on nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Mar;145(2):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul A., Yeganeh F. Electrophoretic identification of fusion proteins expressed in single recombinant lambda-bacteriophage plaques. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sockett D. C., Conrad T. A., Thomas C. B., Collins M. T. Evaluation of four serological tests for bovine paratuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1134–1139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1134-1139.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden E. A., Corner A. H., Samagh B. S., Brooks B. W., Turcotte C., Nielsen K. H., Stewart R. B., Duncan J. R. Serodiagnosis of ovine paratuberculosis, using lipoarabinomannan in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):850–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden E. A., Samagh B. S., Bundle D. R., Duncan J. R. Lipoarabinomannan and lipid-free arabinomannan antigens of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):762–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.762-770.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Weigand P., Murray C., Moriarty K. M. Antibody reactivities of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis infected sheep as analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and western blotting. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 1;62(2-3):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Giessen J. W., Haring R. M., Vauclare E., Eger A., Haagsma J., van der Zeijst B. A. Evaluation of the abilities of three diagnostic tests based on the polymerase chain reaction to detect Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in cattle: application in a control program. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1216–1219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1216-1219.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]