Abstract
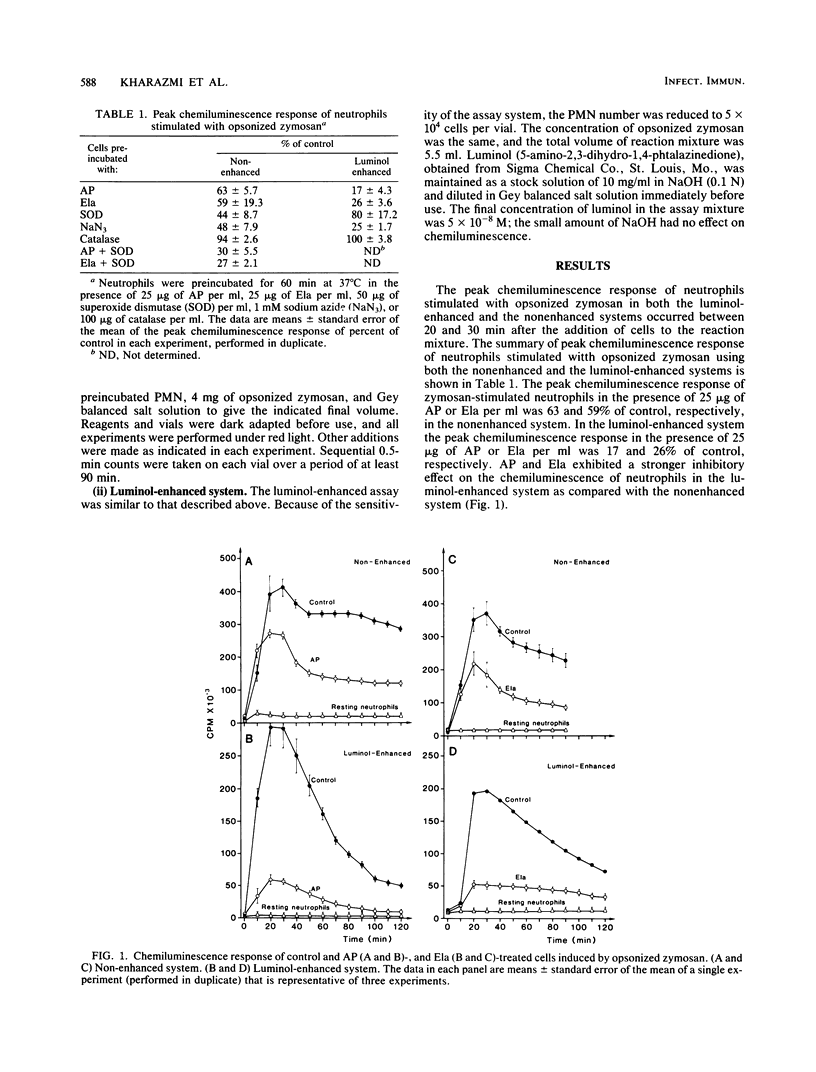
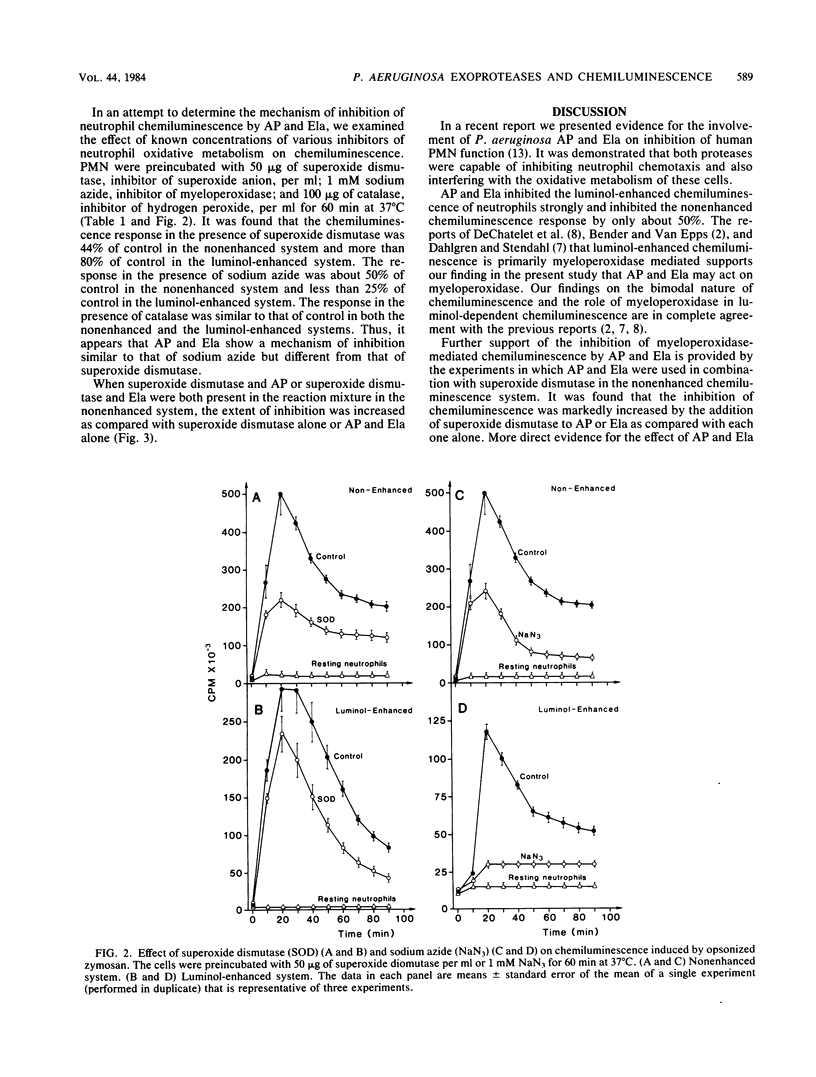
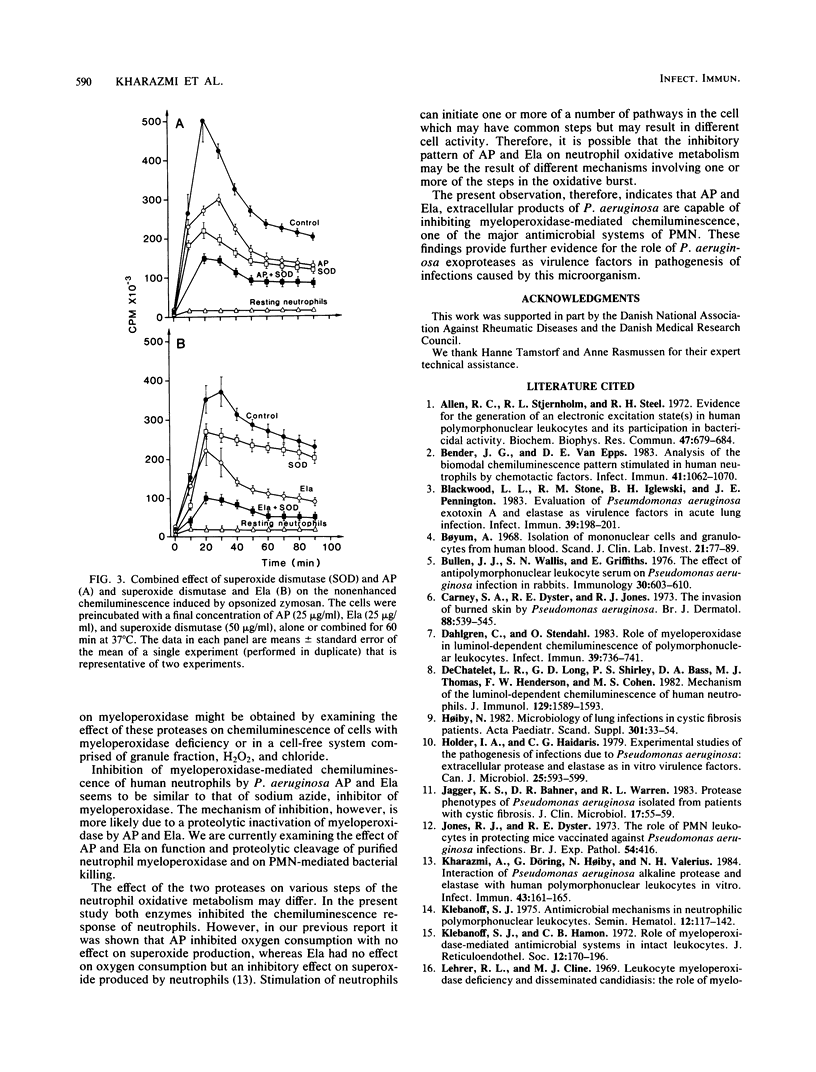
The present study was designed to examine the effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemiluminescence. Both a luminol-enhanced and a nonenhanced chemiluminescence system using opsonized zymosan were utilized. It was found that alkaline protease and elastase at concentrations of 25 micrograms/ml strongly inhibited luminol-enhanced myeloperoxidase-mediated chemiluminescence, whereas inhibition of the nonenhanced chemiluminescence response was about 50%. In an attempt to determine the mechanism of inhibition of neutrophil chemiluminescence by these proteases, we examined the effect of various inhibitors of neutrophil oxidative metabolism on chemiluminescence, namely, superoxide dismutase, sodium azide, and catalase. It was shown that the pattern of inhibition of chemiluminescence by alkaline protease and elastase was similar to that of sodium azide, inhibitor of myeloperoxidase. The present study demonstrates that alkaline protease and elastase, extracellular products of P. aeruginosa, are capable of inhibiting myeloperoxidase-mediated chemiluminescence, one of the major antimicrobial systems of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. These findings provide further evidence for the role of P. aeruginosa exoproteases as virulence factors in the pathogenesis of infections caused by this microorganism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., Van Epps D. E. Analysis of the bimodal chemiluminescence pattern stimulated in human neutrophils by chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1062–1070. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1062-1070.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Stone R. M., Iglewski B. H., Pennington J. E. Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase as virulence factors in acute lung infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):198–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.198-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Wallis S. N., Griffiths E. The effect of antipolymorphonuclear leucocyte serum on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in rabbits. Immunology. 1976 May;30(5):603–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. A., Dyster R. E., Jones R. J. The invasion of burned skin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Br J Dermatol. 1973 Jun;88(6):539–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1973.tb08016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren C., Stendahl O. Role of myeloperoxidase in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.736-741.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Long G. D., Shirley P. S., Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Henderson F. W., Cohen M. S. Mechanism of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Haidaris C. G. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: extracellular protease and elastase as in vivo virulence factors. Can J Microbiol. 1979 May;25(5):593–599. doi: 10.1139/m79-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger K. S., Bahner D. R., Warren R. L. Protease phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.55-59.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Dyster R. E. The role of polymorphonuclear leucocytes in protecting mice vaccinated against Pseudomon as aeruginosa infections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Aug;54(4):416–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Döring G., Høiby N., Valerius N. H. Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.161-165.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama S., Kojo H., Mine Y., Nishida M., Goto S., Kuwahara S. Inhibitory effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the phagocytic and killing activity of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes: mechanisms of action of a polymorphonuclear leukocyte inhibitor. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):399–403. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.399-403.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obernesser H. J., Döring G., Botzenhart K. Extrazelluläre Toxine von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Reinigung und Charakterisierung zweier Exoproteasen. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1981 Mar;249(1):76–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Wretlind B. Assessment of protease (elastase) as a Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor in experimental mouse burn infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.181-187.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Ehrie M. G. Pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia during immunosuppression. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):764–774. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Chemiluminescence and superoxide production by myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI108458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W., Jacob F., Porstendörfer J. The cytotoxic action of leucocidan from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):303–308. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: effect of exogenous amines on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.110-116.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L. S., Keele B. B., Jr, Johnston R. B., Jr Inhibition of phagocytosis-associated chemiluminescence by superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1051–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1051-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B., Nickol M. M., Jagger K. S., Saelinger C. B. Interaction of pseudomonas exoproducts with phagocytic cells. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Jun;28(6):679–685. doi: 10.1139/m82-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


