Abstract
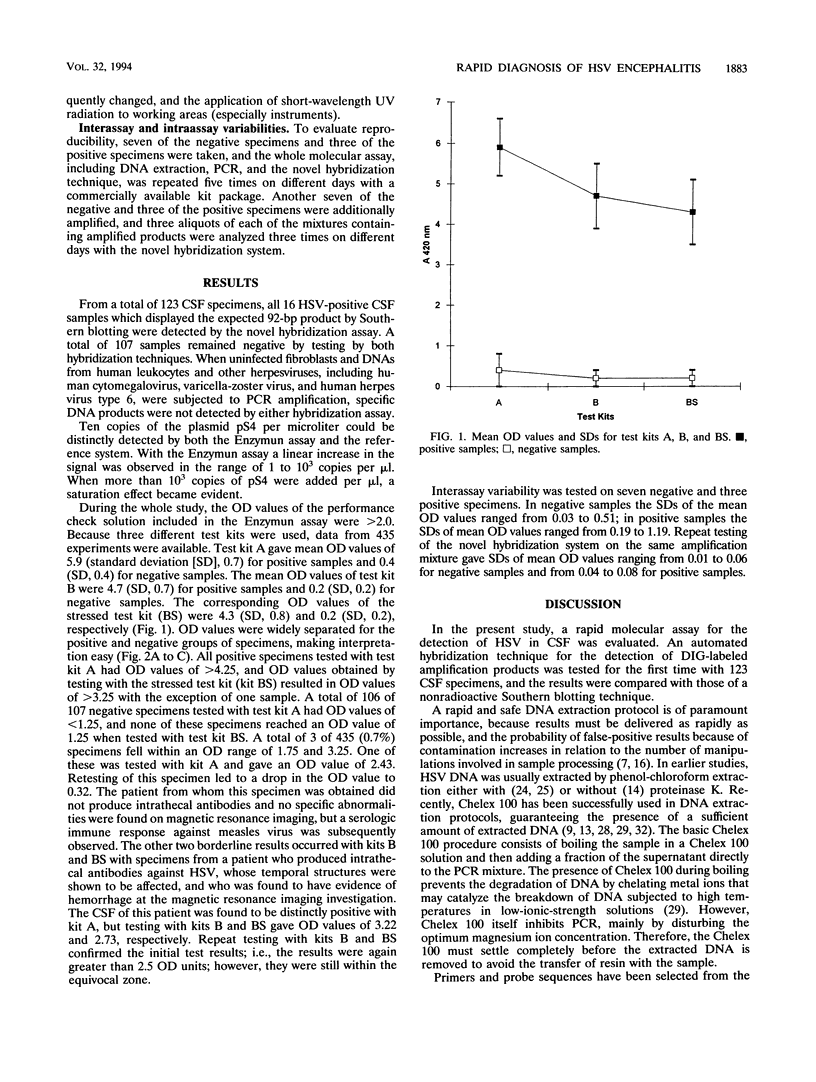
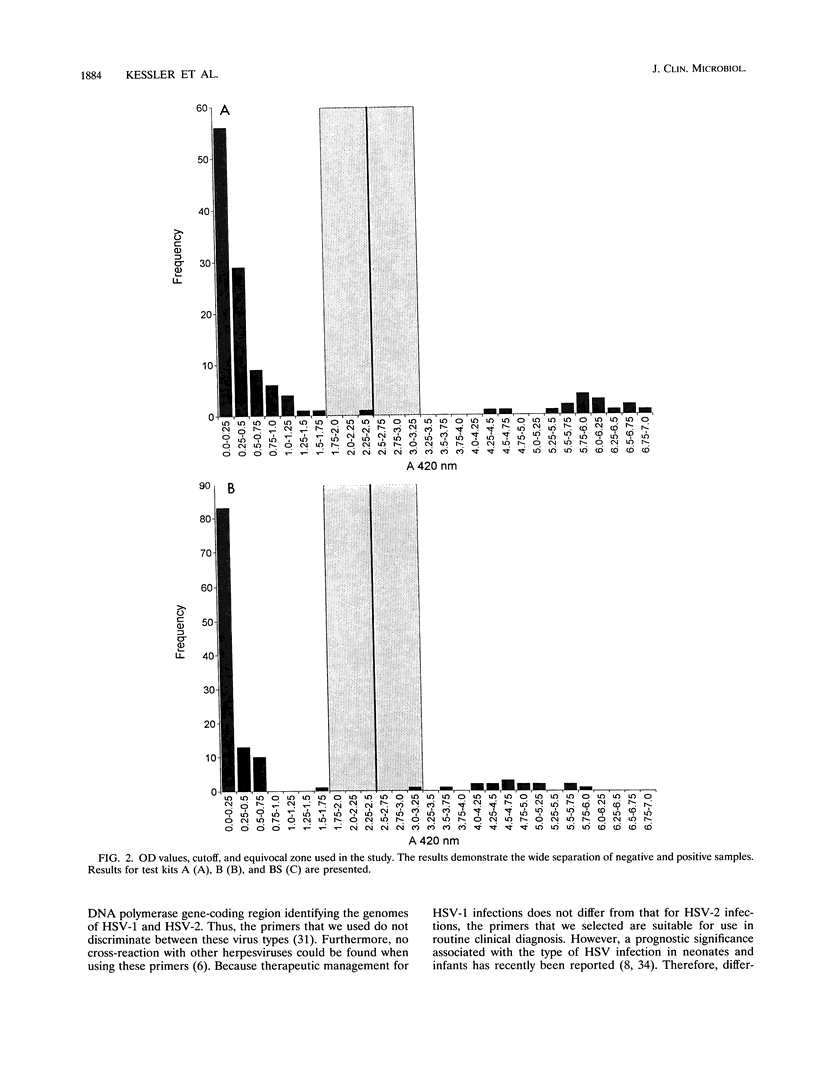
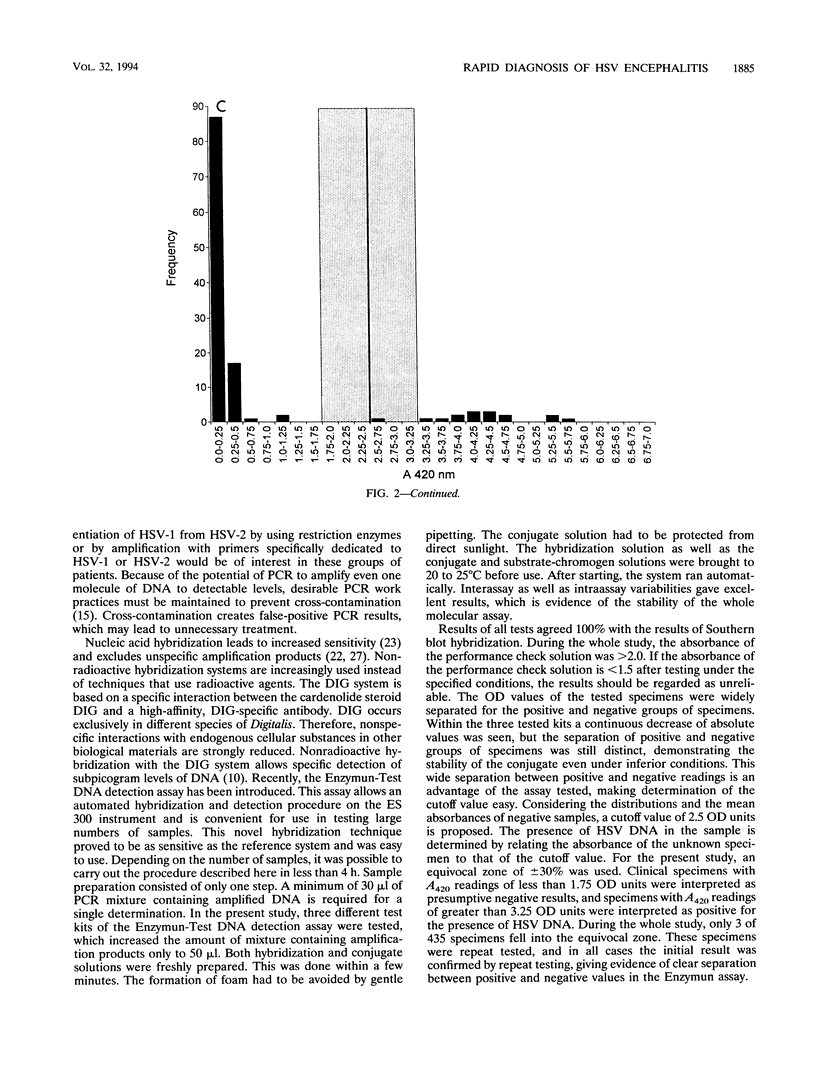
A molecular assay for the detection of herpes simplex virus (HSV), including a novel, nonradioactive hybridization technique, was evaluated with a total of 123 cerebrospinal fluid specimens. After DNA extraction, specific HSV DNA sequences were amplified with digoxigenin-labeled primers derived from the DNA polymerase gene-coding region from HSV. Amplified products were detected by the Enzymun-Test DNA detection assay (Boehringer, Mannheim, Federal Republic of Germany), which uses biotinylated probes. Amplification with nonlabeled primers and then Southern blotting and nonradioactive detection of hybrids by the digoxigenin technique was the reference system. The sensitivities of the molecular assays were determined with 10-fold dilutions of plasmid pS4 with the SalI restriction fragment of the DNA polymerase gene obtained from the HSV type 1 strain Angelotti. The Enzymun assay was able to detect all of the 16 positive samples, giving 100% agreement with the Southern blot hybridization results. Optical density values were widely separated for the positive and negative groups of specimens. Ten copies of plasmid pS4 per microliter could be distinctly detected by the Enzymun assay. The cutoff was determined for the hybridization assay, and an equivocal zone was defined. The whole molecular assay including the Enzymun-Test DNA detection proved to be sensitive and easy to use. It may contribute to the rapid and safe detection of HSV DNA in cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurelius E., Johansson B., Sköldenberg B., Forsgren M. Encephalitis in immunocompetent patients due to herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2 as determined by type-specific polymerase chain reaction and antibody assays of cerebrospinal fluid. J Med Virol. 1993 Mar;39(3):179–186. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890390302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurelius E., Johansson B., Sköldenberg B., Staland A., Forsgren M. Rapid diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by nested polymerase chain reaction assay of cerebrospinal fluid. Lancet. 1991 Jan 26;337(8735):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92155-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brice S. L., Krzemien D., Weston W. L., Huff J. C. Detection of herpes simplex virus DNA in cutaneous lesions of erythema multiforme. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jul;93(1):183–187. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao M., Xiao X., Egbert B., Darragh T. M., Yen T. S. Rapid detection of cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection with the polymerase chain reaction. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Mar;92(3):391–392. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P. The polymerase chain reaction, a review of the practical limitations for human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis. J Virol Methods. 1989 Aug;25(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Whitley R. J., Stone E. F., Mohan K. Difference between herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 neonatal encephalitis in neurological outcome. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lus P., Fields B. S., Benson R. F., Martin W. T., O'Connor S. P., Black C. M. Comparison of arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction, ribotyping, and monoclonal antibody analysis for subtyping Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1940–1942. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1940-1942.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C. The digoxigenin:anti-digoxigenin (DIG) technology--a survey on the concept and realization of a novel bioanalytical indicator system. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Jun;5(3):161–205. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(91)90041-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler H. H., Reinthaler F. F., Pschaid A., Pierer K., Kleinhappl B., Eber E., Marth E. Rapid detection of Legionella species in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids with the EnviroAmp Legionella PCR amplification and detection kit. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Dec;31(12):3325–3328. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.12.3325-3328.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper P. E., Cleator G. M., Dennett C., Lewis A. G. Diagnosis of herpes encephalitis via Southern blotting of cerebrospinal fluid DNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1990 Dec;32(4):261–264. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890320413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Darby G. Related functional domains in virus DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):169–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Whitley R. J., Visintine A. N., Takei Y., Alford C. A., Jr Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: laboratory evaluations and their diagnostic significance. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):829–836. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oommen K. J., Johnson P. C., Ray C. G. Herpes simplex type 2 virus encephalitis presenting as psychosis. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchhammer-Stöckl E., Heinz F. X., Kundi M., Popow-Kraupp T., Grimm G., Millner M. M., Kunz C. Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jan;31(1):146–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.1.146-148.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand K. H., Houck H. Taq polymerase contains bacterial DNA of unknown origin. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Dec;4(6):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90003-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. B., Josephson S. L., Mak S. K., Sweeney P. J. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of herpes simplex virus DNA from clinical samples. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Mar;79(3):464–469. doi: 10.1097/00006250-199203000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley A. H., Whitley R. J., Lakeman F. D., Wolinsky S. M. Rapid detection of herpes-simplex-virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Lancet. 1990 Feb 24;335(8687):440–441. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90667-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenberg F., Lebon P. Amplification and characterization of herpesvirus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with acute encephalitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2412–2417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2412-2417.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., Pace B., Pace N. R. Detection of DNA contamination in Taq polymerase. Biotechniques. 1991 Aug;11(2):176–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriefer M. E., Sacci J. B., Jr, Wirtz R. A., Azad A. F. Detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified malarial DNA in infected blood and individual mosquitoes. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Oct;73(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T., Maeno K., Nishiyama Y. Nucleotide sequence of the DNA polymerase gene of herpes simplex virus type 2 and comparison with the type 1 counterpart. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. S., Metzger D. A., Higuchi R. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):506–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J. Viral encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):242–250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Bayer E. A. Introduction to avidin-biotin technology. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:5–13. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84256-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


