Abstract
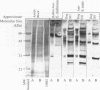
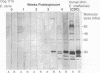
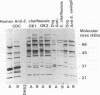
Ehrlichia chaffeensis, E. canis, and E. ewingii are genetically closely related, as determined by 16S rRNA gene base sequence comparison, but they exhibit biologic differences. E. chaffeensis is the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis. E. canis and E. ewingii cause two distinctly different forms of canine ehrlichiosis and infect different types of leukocytes, monocytes and granulocytes, respectively. E. chaffeensis can also infect dogs. In the study, Western immunoblot analysis of sera from dogs inoculated with E. chaffeensis, E. canis, or E. ewingii was performed to determine antigenic specificity and the intensities of the reactions to purified E. chaffeensis and E. canis antigens. At 2 to 3 weeks postexposure, antisera from four dogs inoculated with E. chaffeensis reacted with 64-, 47-, 31-, and 29-kDa proteins of E. chaffeensis but reacted poorly with E. canis antigen. In contrast, at 2 to 3 weeks postexposure, antisera from four E. canis-inoculated dogs reacted strongly with the 30-kDa major antigen of E. canis but reacted poorly with proteins from E. chaffeensis. At 4 weeks postexposure, the sera from three E. ewingii-inoculated dogs showed weak binding to 64- and 47-kDa proteins of both E. chaffeensis and E. canis. Convalescent-phase sera from human ehrlichiosis patients and sera from dogs chronically infected with E. ewingii strongly reacted with similar sets of proteins of E. chaffeensis and E. canis with similar intensities. However, sera from dogs chronically infected with E. canis reacted more strongly with a greater number of E. canis proteins than with E. chaffeensis proteins. The protein specificity described in the report suggests that dogs with E. canis infections can be distinguished from E. chaffeensis-infected animals by Western immunoblot analysis with both E. canis and E. chaffeensis antigens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. E., Dawson J. E., Jones D. C., Wilson K. H. Ehrlichia chaffeensis, a new species associated with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2838–2842. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2838-2842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Greene C. E., Jones D. C., Dawson J. E. Ehrlichia ewingii sp. nov., the etiologic agent of canine granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):299–302. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Anderson B. E., Fishbein D. B., Sanchez J. L., Goldsmith C. S., Wilson K. H., Duntley C. W. Isolation and characterization of an Ehrlichia sp. from a patient diagnosed with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2741–2745. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2741-2745.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Ewing S. A. Susceptibility of dogs to infection with Ehrlichia chaffeensis, causative agent of human ehrlichiosis. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Aug;53(8):1322–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Rikihisa Y., Ewing S. A., Fishbein D. B. Serologic diagnosis of human ehrlichiosis using two Ehrlichia canis isolates. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):564–567. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefe T. J., Holland C. J., Salyer P. E., Ristic M. Distribution of Ehrlichia canis among military working dogs in the world and selected civilian dogs in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Aug 1;181(3):236–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Markowitz N., Hawley R. C., Ristic M., Cox D., McDade J. E. Human infection with Ehrlichia canis, a leukocytic rickettsia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):853–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E. Ehrlichiosis--a disease of animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):609–617. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y. Cross-reacting antigens between Neorickettsia helminthoeca and Ehrlichia species, shown by immunofluorescence and Western immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2024–2029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2024-2029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Ewing S. A., Fox J. C., Siregar A. G., Pasaribu F. H., Malole M. B. Analyses of Ehrlichia canis and a canine granulocytic Ehrlichia infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):143–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.143-148.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y. The tribe Ehrlichieae and ehrlichial diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jul;4(3):286–308. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.3.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Yamamoto S., Kwak I., Iqbal Z., Kociba G., Mott J., Chichanasiriwithaya W. C-reactive protein and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein levels in dogs infected with Ehrlichia canis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Apr;32(4):912–917. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.4.912-917.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockham S. L., Schmidt D. A., Curtis K. S., Schauf B. G., Tyler J. W., Simpson S. T. Evaluation of granulocytic ehrlichiosis in dogs of Missouri, including serologic status to Ehrlichia canis, Ehrlichia equi and Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Jan;53(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]