Abstract
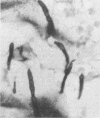
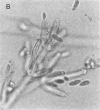
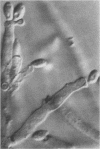
Allergic fungal sinusitis is a common disease that results from a hypersensitivity reaction mounted by the host against fungi living in the paranasal sinuses. We have recently treated a patient with allergic fungal sinusitis due to a Nodulisporium species. This is the first description of a Nodulisporium species involved in human disease. The genus Nodulisporium contains both dematiaceous and nondematiaceous members. These fungi occur worldwide in nature, often as accompanying conidial anamorphs of certain wood decay ascomycetes. Clinical mycology laboratories may encounter this new agent of phaeohyphomycosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allphin A. L., Strauss M., Abdul-Karim F. W. Allergic fungal sinusitis: problems in diagnosis and treatment. Laryngoscope. 1991 Aug;101(8):815–820. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199108000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman G. C., Hartwick R. W., Ro J. Y., Saleh G. Y., Tarrand J. J., Ayala A. G. Allergic fungal sinusitis. Report of three cases associated with dematiaceous fungi. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991 Sep;96(3):368–372. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/96.3.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. L. The role of allergy in sinusitis in adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Sep;90(3 Pt 2):518–520. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]