Abstract
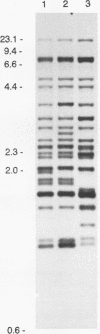
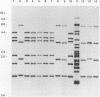
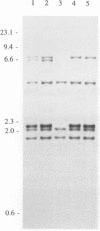
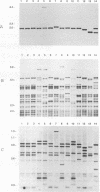
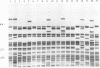
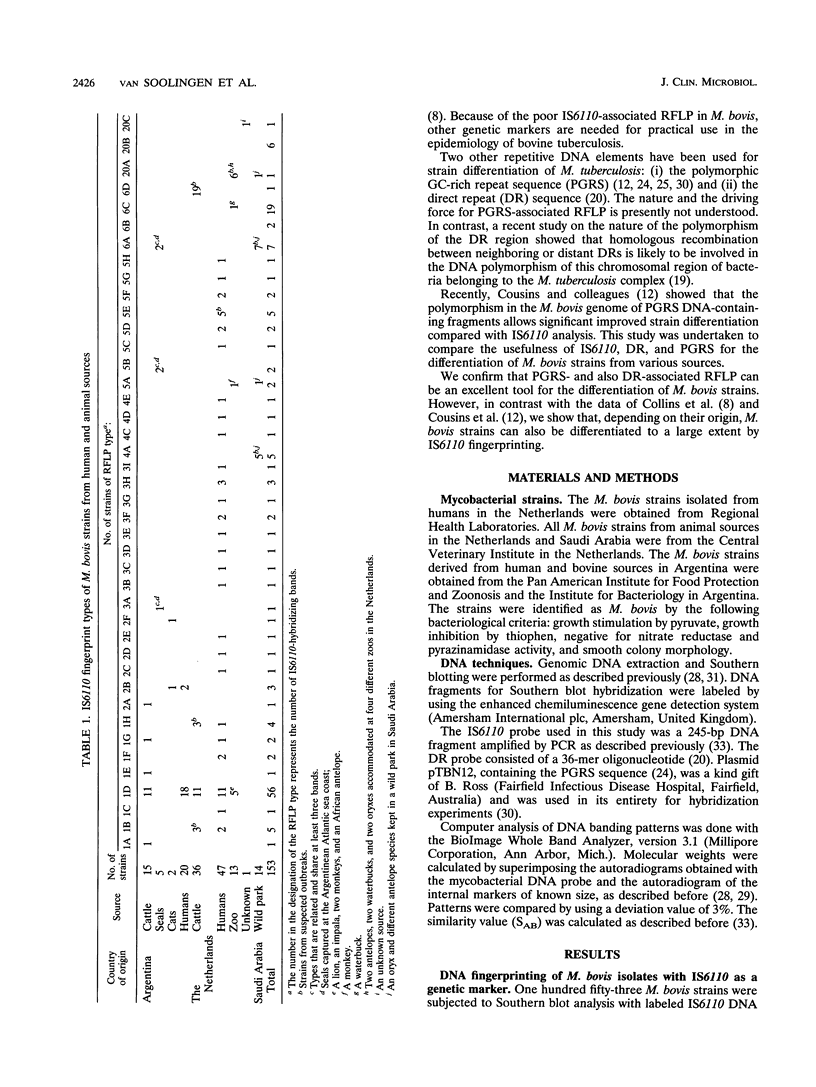
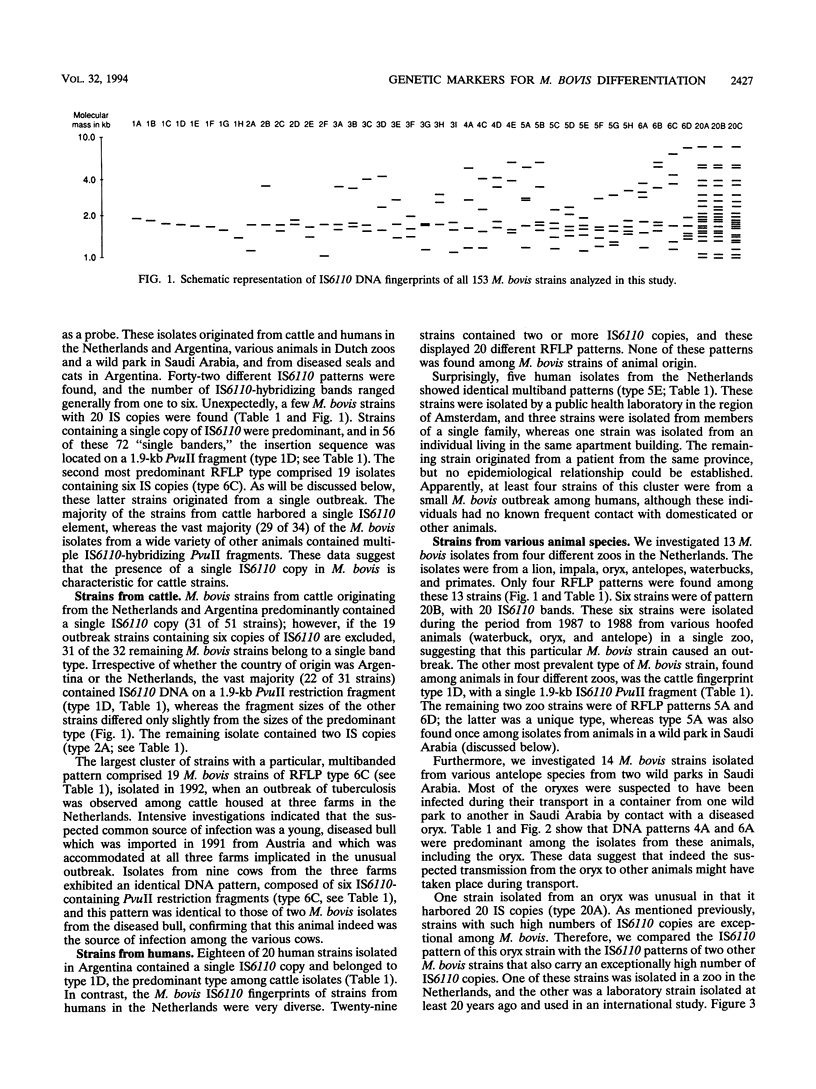
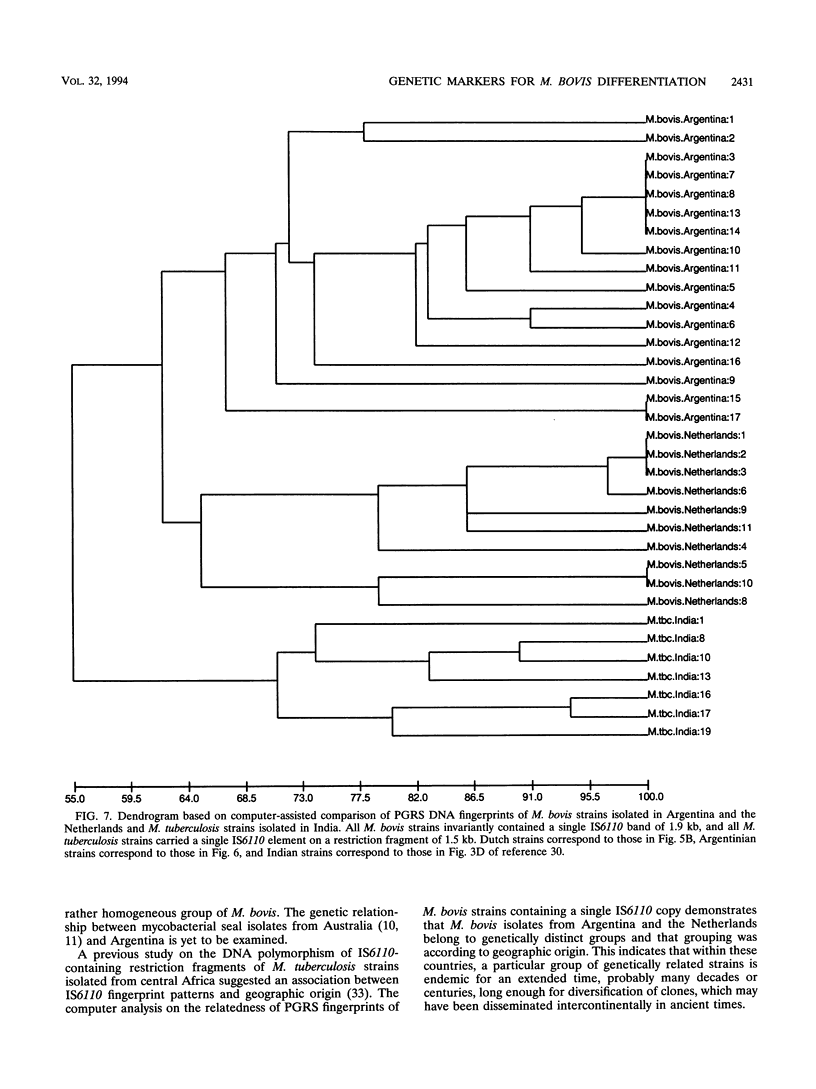
One hundred fifty-three Mycobacterium bovis strains from cattle, various animal species from zoos and wild parks, and humans were analyzed for three different genetic markers for use in the epidemiology of bovine tuberculosis. M. bovis strains isolated from cattle were found to carry a single IS6110 element, whereas the majority of strains from other animals such as antelopes, monkeys, and seals harbored multiple IS6110 elements, suggesting that the reservoirs in cattle and wild animals are separated. Because the single IS6110 element in cattle strains is located at the same chromosomal position, strain differentiation by insertion sequence fingerprinting was hampered. Therefore, we investigated the usefulness of the direct repeat and polymorphic GC-rich repeat elements for strain differentiation. Both markers allowed sufficient strain discrimination for epidemiological purposes. Evidence is presented that in Argentina, most human M. bovis infections are due to transmission from cattle, whereas M. bovis infections among humans in the Netherlands are mainly contracted from animals other than cattle. Various outbreaks of M. bovis among animals and humans are described, including a small one which likely involved transmission from human to human.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck-Sagué C., Dooley S. W., Hutton M. D., Otten J., Breeden A., Crawford J. T., Pitchenik A. E., Woodley C., Cauthen G., Jarvis W. R. Hospital outbreak of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. Factors in transmission to staff and HIV-infected patients. JAMA. 1992 Sep 9;268(10):1280–1286. doi: 10.1001/jama.1992.03490100078031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., McDermott P. F., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. IS6110: conservation of sequence in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and its utilization in DNA fingerprinting. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Feb;5(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(91)90040-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. BCG identification by DNA restriction fragment patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1431–1434. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. DNA restriction endonuclease analysis of Mycobacterium bovis and other members of the tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):562–564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.562-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. DNA restriction endonuclease analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):1019–1021. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W., Gabric D. M. Geographic distribution of restriction types of Mycobacterium bovis isolates from brush-tailed possums (Trichosurus vulpecula) in New Zealand. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Jun;96(3):431–438. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Erasmuson S. K., Stephens D. M., Yates G. F., De Lisle G. W. DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium bovis strains by restriction fragment analysis and hybridization with insertion elements IS1081 and IS6110. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1143–1147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1143-1147.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Stephens D. M. Identification of an insertion sequence, IS1081, in Mycobacterium bovis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90435-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins D. V., Francis B. R., Gow B. L., Collins D. M., McGlashan C. H., Gregory A., Mackenzie R. M. Tuberculosis in captive seals: bacteriological studies on an isolate belonging to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Res Vet Sci. 1990 Mar;48(2):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins D. V., Williams S. N., Reuter R., Forshaw D., Chadwick B., Coughran D., Collins P., Gales N. Tuberculosis in wild seals and characterisation of the seal bacillus. Aust Vet J. 1993 Mar;70(3):92–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1993.tb03284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins D. V., Williams S. N., Ross B. C., Ellis T. M. Use of a repetitive element isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in hybridization studies with Mycobacterium bovis: a new tool for epidemiological studies of bovine tuberculosis. Vet Microbiol. 1993 Oct;37(1-2):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90178-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. J., Hodgson A. L., Davies J. K., Radford A. J. Characterisation of a novel repetitive DNA sequence from Mycobacterium bovis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Sep 15;75(2-3):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90400-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer B., Jackson K., Raios K., Sievers A., Wilshire E., Ross B. DNA restriction fragment analysis to define an extended cluster of tuberculosis in homeless men and their associates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):490–494. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Tokars J. I., Grieco M. H., Crawford J. T., Williams J., Sordillo E. M., Ong K. R., Kilburn J. O., Dooley S. W., Castro K. G. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among hospitalized patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1514–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Tokars J. I., Grieco M. H., Crawford J. T., Williams J., Sordillo E. M., Ong K. R., Kilburn J. O., Dooley S. W., Castro K. G. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among hospitalized patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1514–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Uttamchandani R. B., Daikos G. L., Poblete R. B., Moreno J. N., Reyes R. R., Boota A. M., Thompson L. M., Cleary T. J., Lai S. An outbreak of tuberculosis caused by multiple-drug-resistant tubercle bacilli among patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):177–183. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomukong N. G., Dale J. W., Osborn T. W., Grange J. M. Use of gene probes based on the insertion sequence IS986 to differentiate between BCG vaccine strains. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;72(2):126–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenen P. M., Bunschoten A. E., van Soolingen D., van Embden J. D. Nature of DNA polymorphism in the direct repeat cluster of Mycobacterium tuberculosis; application for strain differentiation by a novel typing method. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):1057–1065. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Bik E. M., de Haas P. E., Dale J. W., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS987 from Mycobacterium bovis BCG is located in a hot-spot integration region for insertion elements in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2695–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2695-2705.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Dale J. W., Schuitema A. R., McAdam R. A., Catty D., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS986 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a useful tool for diagnosis and epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2051–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2051-2058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam R. A., Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Zainuddin Z. F., Catty D., van Embden J. D., Dale J. W. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence belonging to the IS3 family. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1607–1613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Dwyer B. Molecular cloning of a highly repeated DNA element from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its use as an epidemiological tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):942–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.942-946.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Sievers A., Dwyer B. Differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by use of a nonradioactive Southern blot hybridization method. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):904–907. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Brisson-Noël A., Vincent-Lévy-Frébault V., Nguyen S., Guesdon J. L., Gicquel B. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence, IS6110, and its application in diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2668–2673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2668-2673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddin Z. F., Dale J. W. Polymorphic repetitive DNA sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected with a gene probe from a Mycobacterium fortuitum plasmid. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2347–2355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lisle G. W., Collins D. M., Loveday A. S., Young W. A., Julian A. F. A report of tuberculosis in cats in New Zealand, and the examination of strains of Mycobacterium bovis by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. N Z Vet J. 1990 Apr;38(1):10–13. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1990.35606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., Cave M. D., Crawford J. T., Dale J. W., Eisenach K. D., Gicquel B., Hermans P., Martin C., McAdam R., Shinnick T. M. Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):406–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.406-409.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Soolingen D., Small P. M., Hermans P. W. Genetic markers for the epidemiology of tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 1992 May;143(4):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90051-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS1081-associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex species: a reliable tool for recognizing Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1772–1777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1772-1777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., de Haas P. E., Hermans P. W., Groenen P. M., van Embden J. D. Comparison of various repetitive DNA elements as genetic markers for strain differentiation and epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):1987–1995. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.1987-1995.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., de Haas P. E., Hermans P. W., van Embden J. D. DNA fingerprinting of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Methods Enzymol. 1994;235:196–205. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)35141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]