Abstract
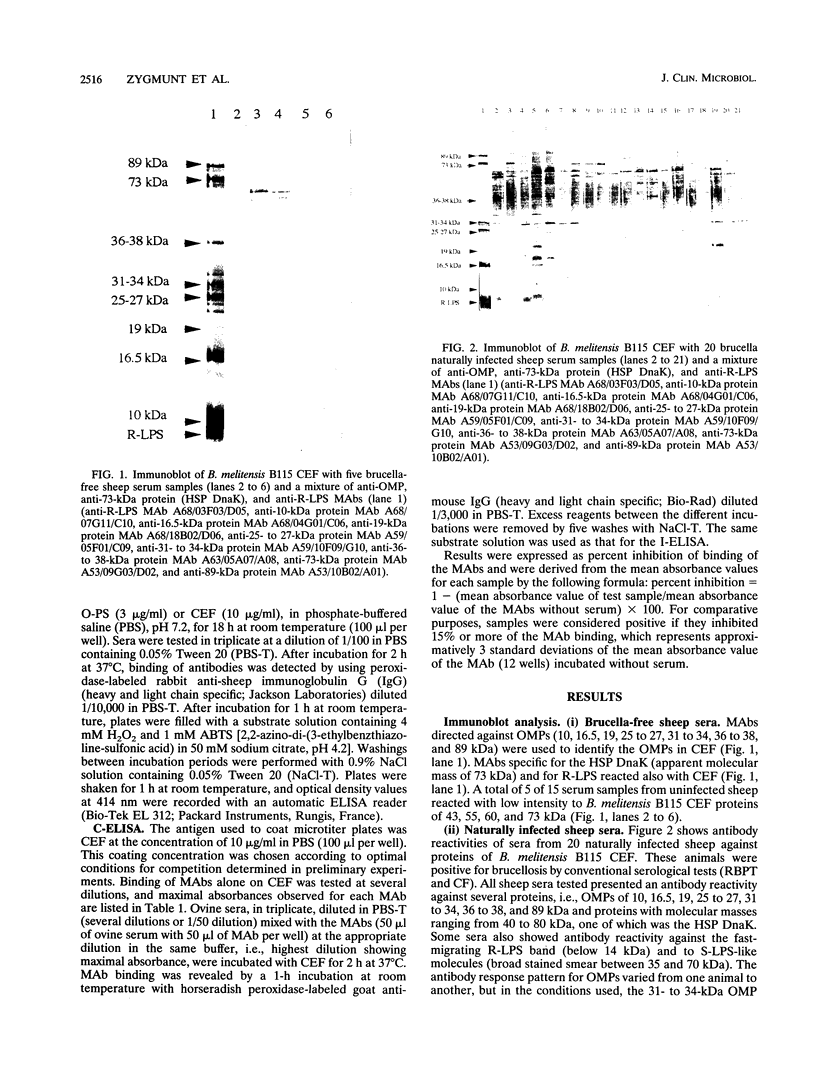
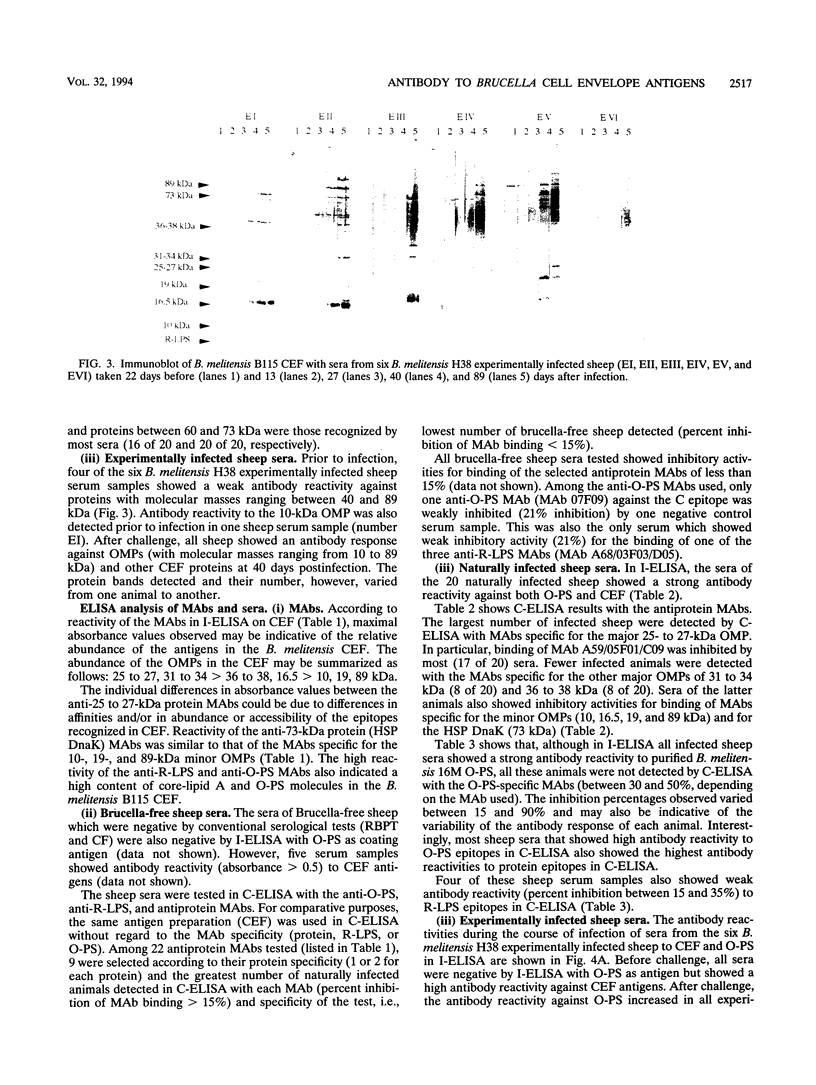
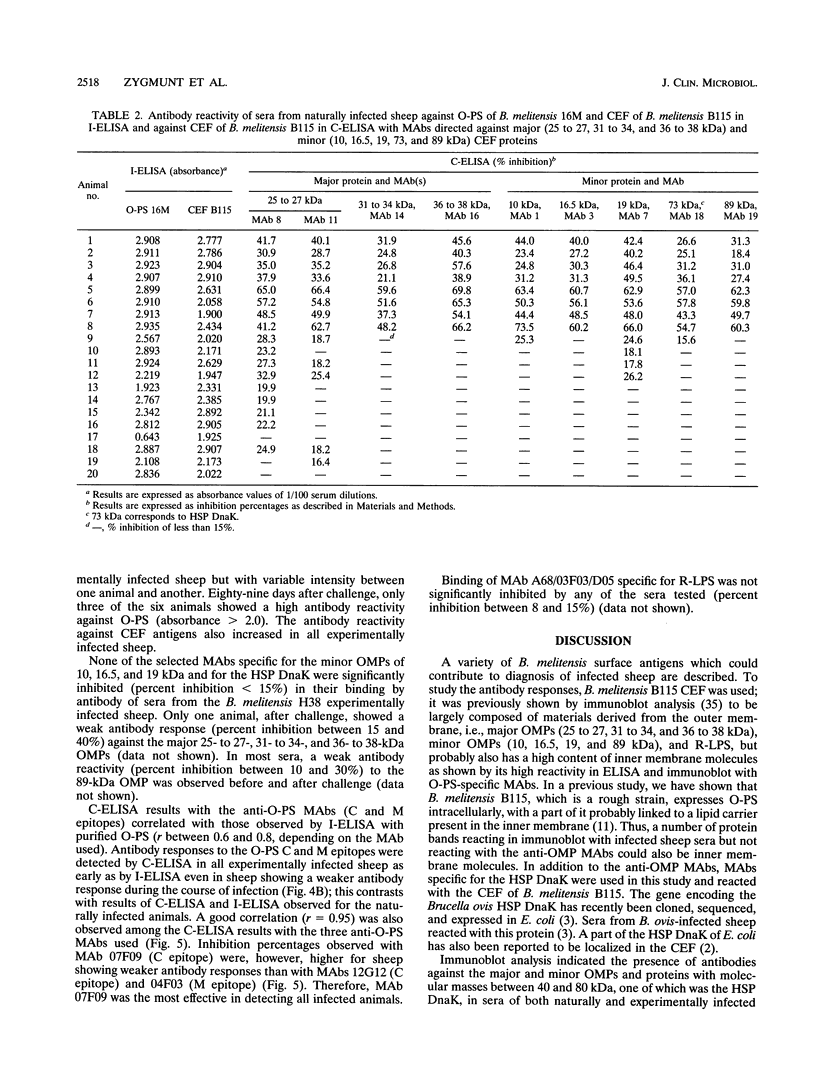
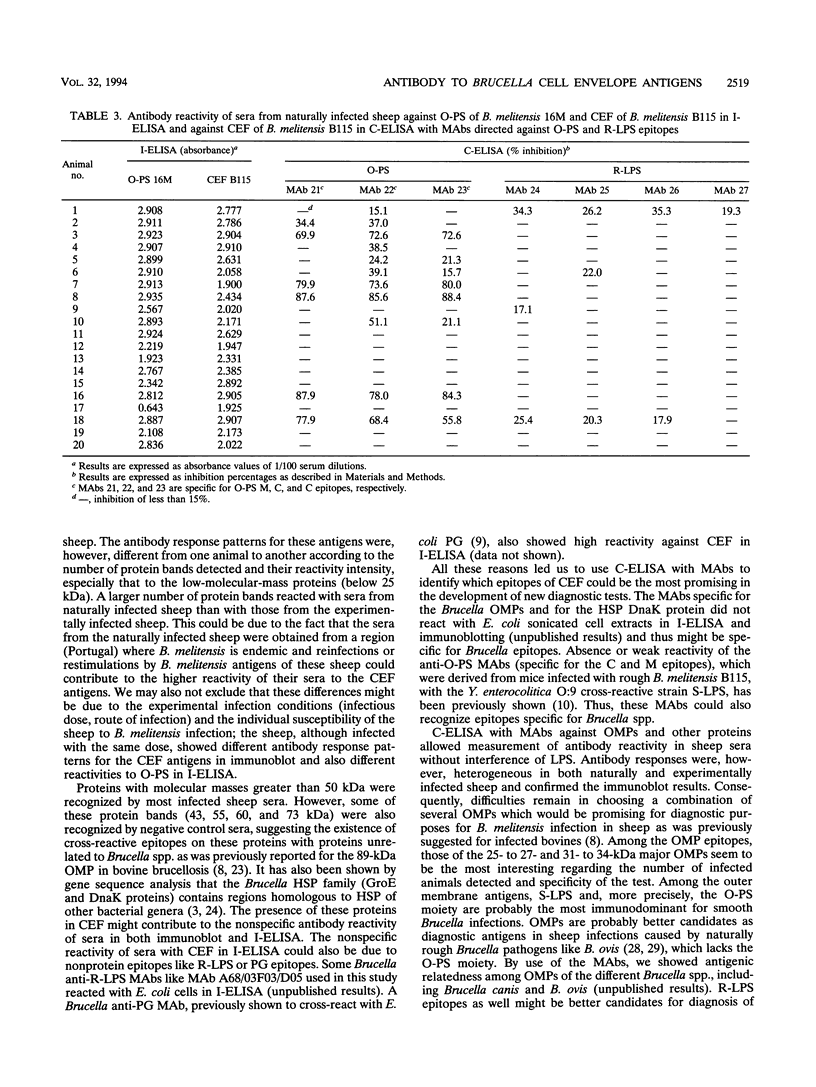
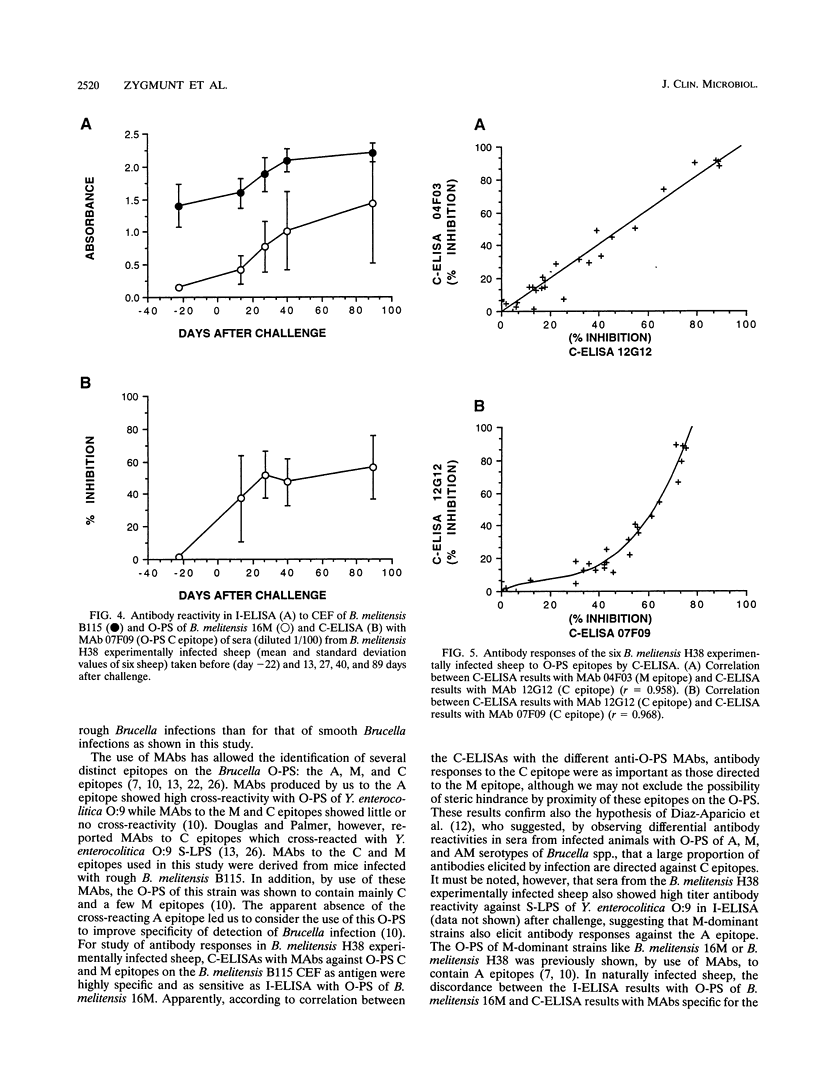
Cell envelope fraction (CEF) of Brucella melitensis B115 was used to investigate antibody responses of B. melitensis naturally and strain H38 experimentally infected sheep by immunoblotting, indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (I-ELISA), and competitive ELISA (C-ELISA) with monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). MAbs used were directed to outer membrane proteins with molecular masses of 10, 16.5, 19, 25 to 27, 31 to 34, 36 to 38, and 89 kDa; to the heat shock protein DnaK, to O-polysaccharide (O-PS) common (C) and M epitopes; and to rough lipopolysaccharide (R-LPS) epitopes. In immunoblotting, all infected sheep sera tested recognized a large number of protein bands, including the above-cited proteins and other proteins for which MAbs have not been defined. The antibody response pattern was different from one animal to another, even within the experimentally infected sheep which were infected under the same experimental conditions. A number of protein bands were recognized by the sheep sera prior to experimental infection and by other uninfected sheep sera. The antibody reactivity to these antigens and others might explain the nonspecific antibody reactivity of sera in I-ELISA with CEF. C-ELISA confirmed also the individual variability of the antibody responses of infected sheep to protein antigens. Antibody responses to O-PS C and M epitopes were detected in all experimentally infected sheep and in half of the naturally infected sheep, but these responses were also heterogeneous in relation to their intensities. Antibody responses to R-LPS epitopes detected by use of C-ELISA with the anti-R-LPS MAbs were low or negative in most of the infected animals. Despite antibody response heterogeneity for CEF antigens, immunoblot and C-ELISA results indicated that, among the CEF antigens, the O-PS epitopes (C and M epitopes) and epitopes of the major 25- to 27- and 31- to 34-kDa outer membrane proteins seem to be the most promising for detecting B. melitensis infection in sheep.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bukau B., Reilly P., McCarty J., Walker G. C. Immunogold localization of the DnaK heat shock protein in Escherichia coli cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jan;139(1):95–99. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cellier M. F., Teyssier J., Nicolas M., Liautard J. P., Marti J., Sri Widada J. Cloning and characterization of the Brucella ovis heat shock protein DnaK functionally expressed in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8036–8042. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8036-8042.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Jacques I., Bosseray N., Limet J. N., Bowden R., Dubray G., Plommet M. Protection conferred on mice by monoclonal antibodies directed against outer-membrane-protein antigens of Brucella. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Mar;34(3):175–180. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-3-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Jacques I., Bowden R. A., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Monoclonal antibodies to Brucella rough lipopolysaccharide: characterization and evaluation of their protective effect against B. abortus. Res Microbiol. 1993 Jul-Aug;144(6):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(93)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Jacques I., de Wergifosse P., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Protection against Brucella melitensis or Brucella abortus in mice with immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM monoclonal antibodies specific for a common epitope shared by the Brucella A and M smooth lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):312–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.312-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Kerkhofs P., Limet J. N. Antibody response to Brucella outer membrane proteins in bovine brucellosis: immunoblot analysis and competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3168–3174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3168-3174.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Zygmunt M. S., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Characterization of O-polysaccharide specific monoclonal antibodies derived from mice infected with the rough Brucella melitensis strain B115. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jul;139(7):1551–1556. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-7-1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Zygmunt M. S., Nicolle J. C., Dubray G., Limet J. N. O-chain expression in the rough Brucella melitensis strain B115: induction of O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies and intracellular localization demonstrated by immunoelectron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1211–1219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Zygmunt M. S., de Wergifosse P., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Demonstration of peptidoglycan-associated Brucella outer-membrane proteins by use of monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jul;138(7):1543–1550. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-7-1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., de Wergifosse P., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Identification of seven surface-exposed Brucella outer membrane proteins by use of monoclonal antibodies: immunogold labeling for electron microscopy and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3980–3987. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3980-3987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Palmer D. A. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify the distribution of A and M epitopes on smooth Brucella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1353-1356.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Porins of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.16-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Charriaut C. Evidence of three major polypeptide species and two major polysaccharide species in the Brucella outer membrane. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Aparicio E., Aragón V., Marín C., Alonso B., Font M., Moreno E., Pérez-Ortiz S., Blasco J. M., Díaz R., Moriyón I. Comparative analysis of Brucella serotype A and M and Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 polysaccharides for serological diagnosis of brucellosis in cattle, sheep, and goats. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Dec;31(12):3136–3141. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.12.3136-3141.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Miguel M. J., Moriyón I. Demonstration of a peptidoglycan-linked lipoprotein and characterization of its trypsin fragment in the outer membrane of Brucella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):678–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.678-684.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Miguel M. J., Moriyón I., López J. Brucella outer membrane lipoprotein shares antigenic determinants with Escherichia coli Braun lipoprotein and is exposed on the cell surface. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):258–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.258-262.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques I., Olivier-Bernardin V., Dubray G. Induction of antibody and protective responses in mice by Brucella O-polysaccharide-BSA conjugate. Vaccine. 1991 Dec;9(12):896–900. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limet J. N., Bosseray N., Garin-Bastuji B., Dubray G., Plommet M. Humoral immunity in mice mediated by monoclonal antibodies against the A and M antigens of Brucella. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Sep;30(1):37–43. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limet J. N., Cloeckaert A., Bezard G., Van Broeck J., Dubray G. Antibody response to the 89-kDa outer membrane protein of Brucella in bovine brucellosis. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Dec;39(6):403–407. doi: 10.1099/00222615-39-6-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Adams L. G., Ficht T. A. Characterization of the heat shock response in Brucella abortus and isolation of the genes encoding the GroE heat shock proteins. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2425–2431. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2425-2431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J., Hunter D. M., Sowa B. A., Wu A. M., Adams L. G. Protection against Brucella abortus in mice with O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):961–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.961-963.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. A., Douglas J. T. Analysis of Brucella lipopolysaccharide with specific and cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2331–2337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2331-2337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Deyoe B. L., Canning P. C. Protection of mice against Brucella abortus infection by inoculation with monoclonal antibodies recognizing Brucella O-antigen. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Dec;50(12):2158–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezu-Boj J. I., Moriyón I., Blasco J. M., Gamazo C., Díaz R. Antibody response to Brucella ovis outer membrane proteins in ovine brucellosis. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):489–494. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.489-494.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezu-Boj J. I., Moriyón I., Blasco J. M., Marín C. M., Diaz R. Comparison of lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane protein-lipopolysaccharide extracts in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of Brucella ovis infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.938-942.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. M., Verstreate D. R., Perera V. Y., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins from rough strains of four Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):188–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.188-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowa B. A., Kelly K. A., Ficht T. A., Frey M., Adams L. G. SDS-soluble and peptidoglycan-bound proteins in the outer membrane-peptidoglycan complex of Brucella abortus. Vet Microbiol. 1991 May;27(3-4):351–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90160-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Rowe G. E., Duncan J. R., Eis M. J., Widom J., Ganem B., Morein B. Effectiveness of natural and synthetic complexes of porin and O polysaccharide as vaccines against Brucella abortus in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2808–2817. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2808-2817.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt M. S., Debbarh H. S., Cloeckaert A., Dubray G. Antibody response to Brucella melitensis outer membrane antigens in naturally infected and Rev1 vaccinated sheep. Vet Microbiol. 1994 Mar;39(1-2):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt M. S., Dubray G., Bundle D. R., Perry M. P. Purified native haptens of Brucella abortus B19 and B. melitensis 16M reveal the lipopolysaccharide origin of the antigens. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;139(4):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]