Abstract
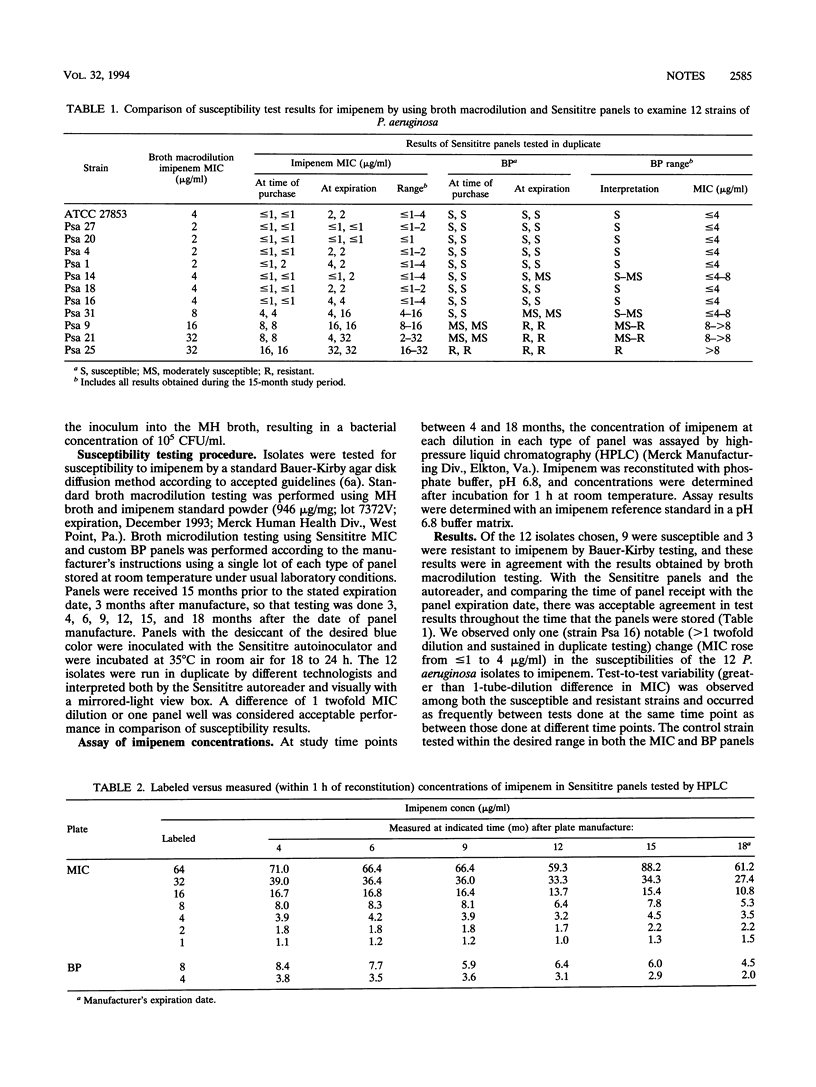
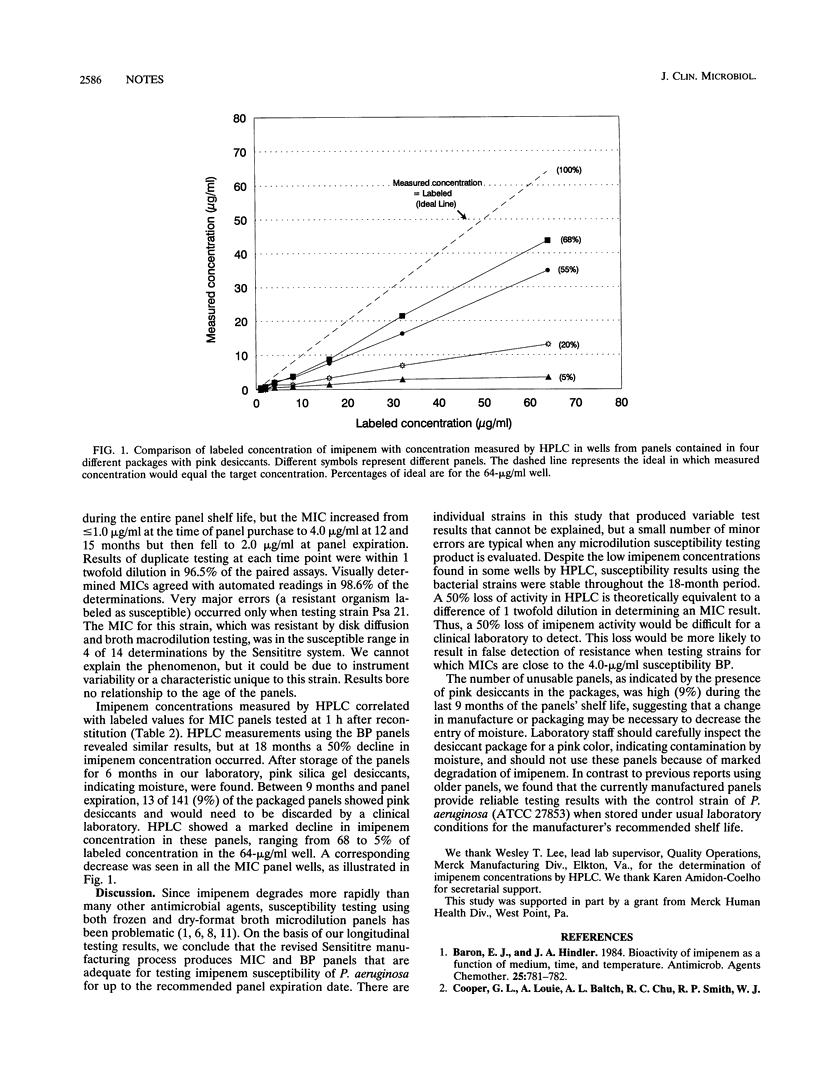
We performed a 15-month study using 11 clinical strains and 1 control strain (ATCC 27853) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to determine whether changes in the manufacturing process of Sensititre predried panels result in a reliable test of susceptibility to imipenem. MIC and breakpoint susceptibility results remained stable during the manufacturer's recommended shelf life of 18 months and compared well with standard agar disk diffusion and broth macrodilution results. Imipenem concentrations measured by high-pressure liquid chromatography were acceptable through 15 months but declined in the breakpoint panels by approximately 50% at 18 months. Between 9 months and panel expiration, 13 of 141 (9%) of the MIC panel packages had moisture entry, as indicated by pink desiccants, with a resultant loss of imipenem activity of 32 to 100%. It appears that the new manufacturing process produces MIC panels that are reliable for imipenem susceptibility testing until the labeled expiration date, provided that packages containing pink desiccants are not used.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron E. J., Hindler J. A. Bioactivity of imipenem as a function of medium, time, and temperature. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):781–782. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Louie A., Baltch A. L., Chu R. C., Smith R. P., Ritz W. J., Michelsen P. Influence of zinc on Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptibilities to imipenem. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2366–2370. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2366-2370.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynes R. P., Culver D. H. Resistance to imipenem among selected gram-negative bacilli in the United States. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1992 Jan;13(1):10–14. doi: 10.1086/646417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grist R. External factors affecting imipenem performance in dried microdilution MIC plates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):535–536. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.535-536.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1992 Jan;13(1):7–9. doi: 10.1086/646416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke E. J., Lambert K. G., Parsonnet K. C., Macone A. B., Goldmann D. A. False resistance to imipenem with a microdilution susceptibility testing system. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):827–829. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.827-829.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Allen S. D., Harris E. E., Tilton R. C. Automated reading of MIC microdilution trays containing fluorogenic enzyme substrates with the Sensititre Autoreader. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.187-191.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Kays M. B., Friedrich L. V., Brown E. W., Koonce J. R. Pseudoresistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resulting from degradation of imipenem in an automated susceptibility testing system with predried panels. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):398–400. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.398-400.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


