Abstract
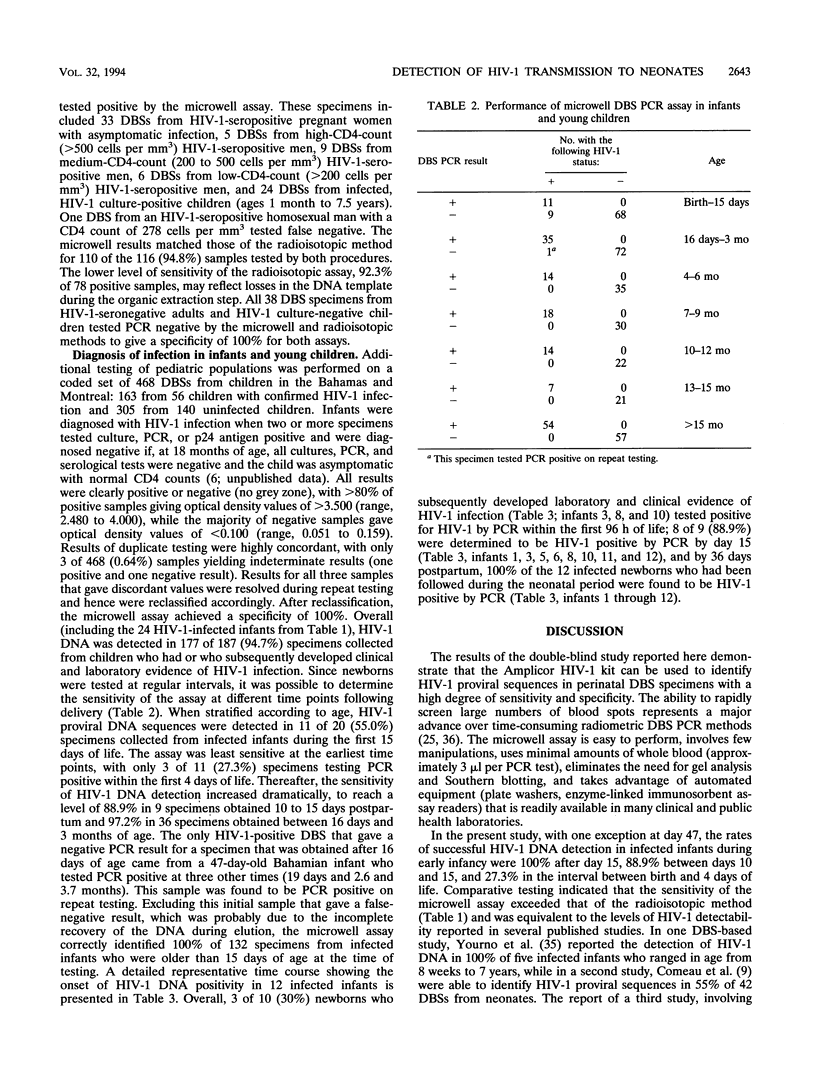
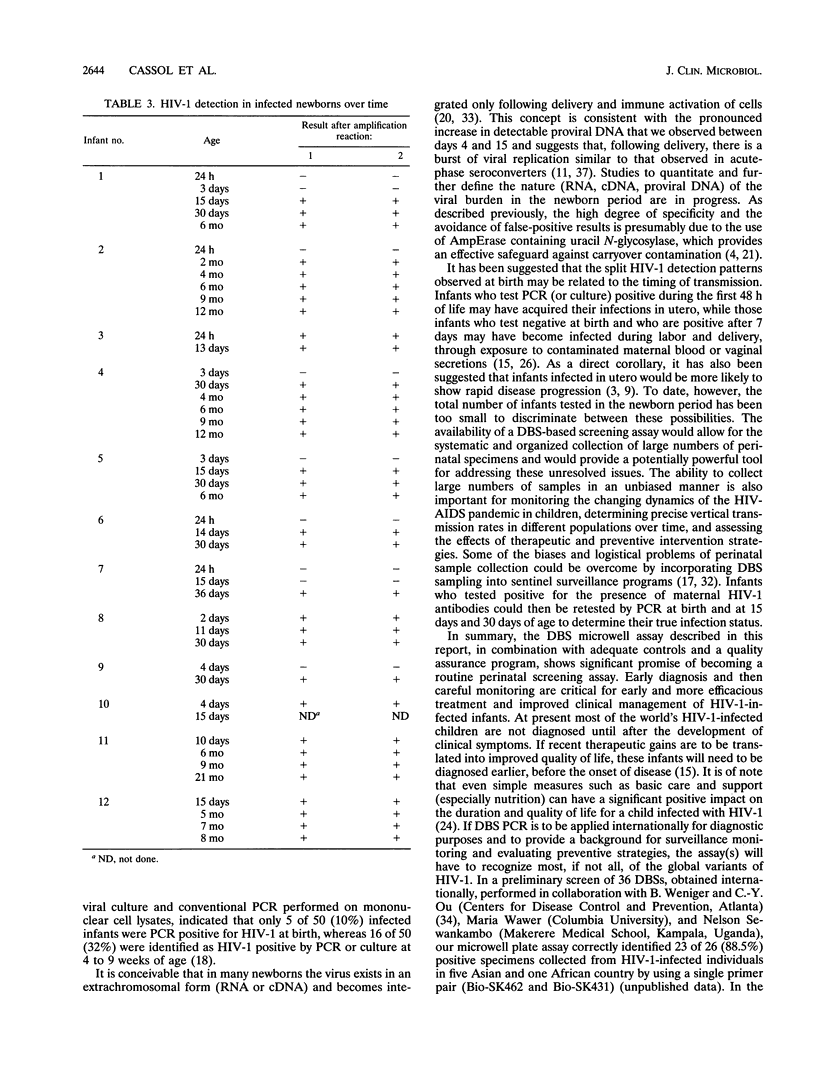
The testing of dried blood spots (DBSs) for the presence of human immunodeficiency type 1 (HIV-1) proviral DNA by PCR was first described in 1991. The technology has proven to be particularly valuable for resolving the infection status in HIV-1-indeterminate infants born to HIV-1-seropositive mothers. To broaden the applicability of DBS PCR, we adapted it to a standardized, commercially available microwell plate amplification and detection kit, Amplicor HIV-1, produced by Roche Diagnostic Systems. The microwell assay is rapid and easy to perform and uses equipment that is readily available in routine diagnostic laboratories. The high level of performance of the assay was demonstrated in 1,168 duplicate tests performed on 584 DBSs from 178 uninfected and 100 HIV-1-infected individuals, including 56 children with perinatally acquired HIV-1. Of 12 infants who were followed prospectively from birth, 3 (25%) were infected in utero (PCR positive at birth) and 9 (75%) were infected intrapartum (PCR negative, culture negative at birth). Overall, HIV-1 DNA was identified in 3 of 11 (27.3%) DBSs collected from infected infants during the first 4 days of life, 8 of 9 (88.9%) DBSs collected between 10 and 15 days postpartum, and 166 of 167 (99.4%) DBSs collected after 15 days of age. All 320 DBSs from uninfected children were PCR DNA negative. These findings indicate that use of the Roche microwell DBS PCR assay provides a powerful new approach for large-scale perinatal screening programs and population-based studies of vertical transmission.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annunziato P. W., Frenkel L. M. The epidemiology of pediatric HIV-1 infection. Pediatr Ann. 1993 Jul;22(7):401–405. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-19930701-05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowsky W., Krasinski K., Pollack H., Hoover W., Kaul A., Ilmet-Moore T. Early diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 6 months of age: comparison of polymerase chain reaction, culture, and plasma antigen capture techniques. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):616–619. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassol S. A., Lapointe N., Salas T., Hankins C., Arella M., Fauvel M., Delage G., Boucher M., Samson J., Charest J. Diagnosis of vertical HIV-1 transmission using the polymerase chain reaction and dried blood spot specimens. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassol S., Salas T., Arella M., Neumann P., Schechter M. T., O'Shaughnessy M. Use of dried blood spot specimens in the detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):667–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.667-671.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassol S., Salas T., Gill M. J., Montpetit M., Rudnik J., Sy C. T., O'Shaughnessy M. V. Stability of dried blood spot specimens for detection of human immunodeficiency virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3039–3042. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3039-3042.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comeau A. M., Hsu H. W., Schwerzler M., Mushinsky G., Grady G. F. Detection of HIV in specimens from newborn screening programs. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 18;326(25):1703–1703. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206183262515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cvetkovich T. A., Frenkel L. M. Current management of HIV infection in children. Pediatr Ann. 1993 Jul;22(7):428–435. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-19930701-09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evengård B., Linder E., Lundbergh P. Standardization of a filter-paper technique for blood sampling. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1988 Jun;82(3):295–303. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1988.11812246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Powell D., Lightfoote M., Koenig S., Fauci A. S., Benn S., Rabson A., Daugherty D., Gendelman H. E., Hoggan M. D. Biological and biochemical characterization of a cloned Leu-3- cell surviving infection with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):280–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE R., SUSI A. A SIMPLE PHENYLALANINE METHOD FOR DETECTING PHENYLKETONURIA IN LARGE POPULATIONS OF NEWBORN INFANTS. Pediatrics. 1963 Sep;32:338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman S., Oleske J. The maturation of an epidemic: update on pediatric HIV infection. AIDS. 1993;7 (Suppl 1):S225–S234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff R., Berardi V. P., Weiblen B. J., Mahoney-Trout L., Mitchell M. L., Grady G. F. Seroprevalence of human immunodeficiency virus among childbearing women. Estimation by testing samples of blood from newborns. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):525–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivine A., Yakudima A., Le May M., Pena-Cruz V., Huang A. S., McIntosh K. A comparative study of virus isolation, polymerase chain reaction, and antigen detection in children of mothers infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Pediatr. 1990 Mar;116(3):372–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82823-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. HIV DNA integration: observations and interferences. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(9):839–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. S. Maternal-fetal transmission of HIV-1 infection. Pediatr Ann. 1993 Jul;22(7):413–416. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-19930701-07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maish W. A. Drug therapy for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children. J Pediatr Health Care. 1993 Jul-Aug;7(4):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0891-5245(93)90043-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe E. R. Utility of PCR for DNA analysis from dried blood spots on filter paper blotters. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Nov;1(2):99–106. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. L., Peckham C. Risk factors for vertical transmission of HIV-1 and early markers of HIV-1 infection in children. AIDS. 1993;7 (Suppl 1):S91–S97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primary HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 5;325(10):733–735. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109053251012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. F., Ou C. Y., Rayfield M., Thomas P. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Abrams E., Krasinski K., Selwyn P. A., Moore J., Kaul A. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for early detection of the proviral sequences of human immunodeficiency virus in infants born to seropositive mothers. New York City Collaborative Study of Maternal HIV Transmission and Montefiore Medical Center HIV Perinatal Transmission Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 22;320(25):1649–1654. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906223202503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Andrews K. A., Kan Y. W. Newborn screening by DNA analysis of dried blood spots. Hum Genet. 1989 May;82(2):134–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00284045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Lamonica C. A. HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T cell activation and proviral integration. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourno J., Conroy J. A novel polymerase chain reaction method for detection of human immunodeficiency virus in dried blood spots on filter paper. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2887–2892. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2887-2892.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourno J. Direct polymerase chain reaction for detection of human immunodeficiency virus in blood spot residues on filter paper after elution of antibodies: an adjunct to serological surveys for estimating vertical transmission rates among human immunodeficiency virus antibody-positive newborns. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1364–1367. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1364-1367.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu T., Mo H., Wang N., Nam D. S., Cao Y., Koup R. A., Ho D. D. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of HIV-1 patients with primary infection. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.8356453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


