Abstract
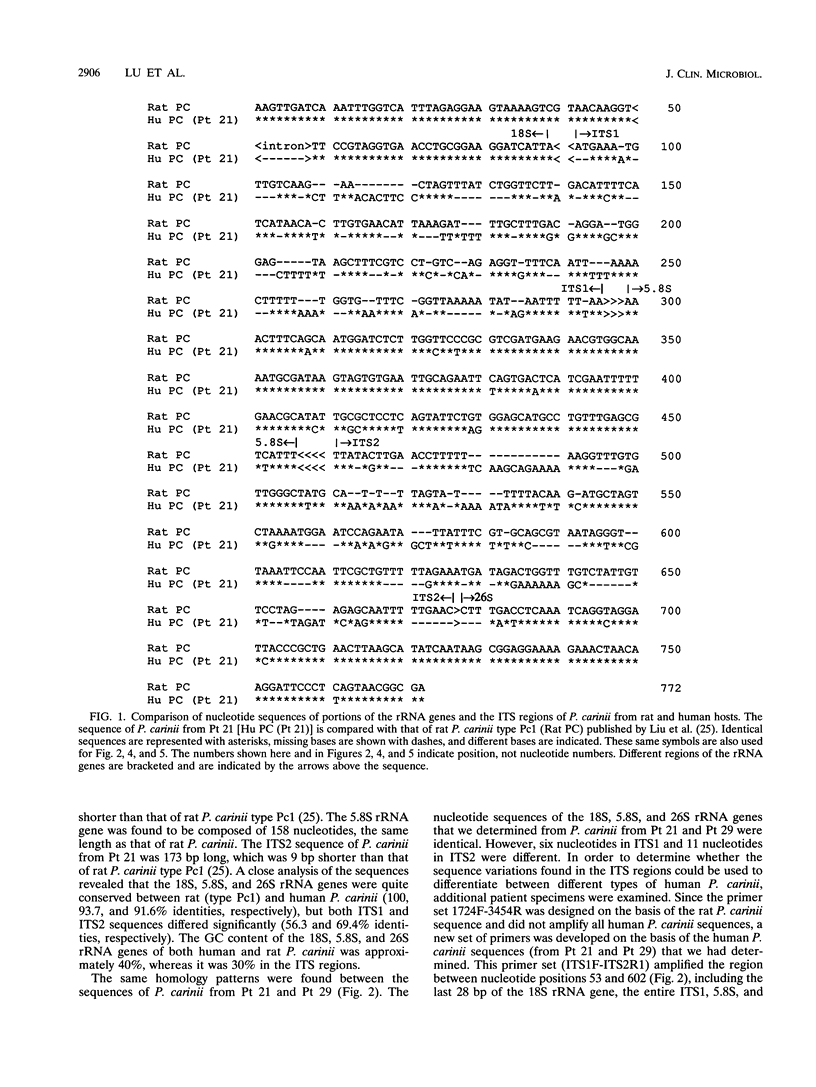
Small portions of the 18S and the 26S rRNA genes, the entire 5.8S rRNA gene, and internal transcribed spacers ITS1 and ITS2 (located between the 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes and between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes, respectively) of Pneumocystis carinii that infect humans were cloned and sequenced. The nucleotide sequences of the 18S, 5.8S, and 26S rRNA genes determined in the study were approximately 90% homologous to those of P. carinii that infect rats, while the sequences of ITS1 and ITS2 of P. carinii from the two different hosts were only 60% homologous. The 18S, 5.8S, and 26S rRNA gene sequences of P. carinii from 15 patient specimens were determined and were found to be identical to each other, whereas the ITS sequences were found to be variable. With the observed sequence variation, it was possible to classify the ITS1 sequences into two types and the ITS2 sequences into three types. P. carinii strains that had the same type of ITS1 sequence could have a different type of ITS2 sequence. On the basis of the sequence types of the two ITS regions, P. carinii from the 15 patients were classified into four groups. P. carinii from three patient specimens were found to contain two different ITS sequence patterns. More surprisingly, one additional specimen was found to have one ITS sequence typical of P. carinii isolates that infect humans and another typical of P. carinii isolates that infect rats. The studies indicate that it is possible to type P. carinii strains on the basis from one patient, suggesting that coinfection with more than one strain of P. carinii may occur in the same patient.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry T., Colleran G., Glennon M., Dunican L. K., Gannon F. The 16s/23s ribosomal spacer region as a target for DNA probes to identify eubacteria. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Aug;1(1):51–56. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Ebbets D. Growth and metabolism of Pneumocystis carinii in axenic culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1385–1394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1385-1394.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Kaselis M., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Genetic stability and diversity of Pneumocystis carinii infecting rat colonies. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4801–4813. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4801-4813.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Growth and serial passage of Pneumocystis carinii in the A549 cell line. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.245-251.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Zhang J., Kaselis M., Giuntoli D., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Evidence for two genetic variants of Pneumocystis carinii coinfecting laboratory rats. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1217–1223. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1217-1223.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin M. M., Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Shaw M. M., Smith J. W. A culture method allowing production of relatively pure Pneumocystis carinii trophozoites. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):31S–32S. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Pneumocystis jiroveci n. sp. from man: morphology, physiology, and immunology in relation to pathology. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:13–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Harmsen A. G., Haidaris C. G., Haidaris P. J. Pneumocystis carinii is not universally transmissible between mammalian species. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2886–2890. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2886-2890.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillis D. M., Dixon M. T. Ribosomal DNA: molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q Rev Biol. 1991 Dec;66(4):411–453. doi: 10.1086/417338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillis D. M., Moritz C., Porter C. A., Baker R. J. Evidence for biased gene conversion in concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.1987647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. T., Steele P. E., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Pneumocystis carinii karyotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1785–1795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1785-1795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Gigliotti F. Nomenclature for Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):432–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostman J. R., Edlind T. D., LiPuma J. J., Stull T. L. Molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas cepacia determined by polymerase chain reaction ribotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2084–2087. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2084-2087.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Bauer N. L., Shaw M. M., Durkin M. M., Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Proliferation of rat Pneumocystis carinii on cells sheeted on microcarrier beads in spinner flasks. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1659–1662. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1659-1662.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Lu J. J., Bartlett M. S., Durkin M. M., Liu T. H., Wang J., Jiang B., Smith J. W. Nucleotide sequence variation in Pneumocystis carinii strains that infect humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):754–757. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.754-757.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Niu M. T., Yoganathan T., Buck G. A. Characterization of the rRNA-encoding genes and transcripts, and a group-I self-splicing intron in Pneumocystis carinii. Gene. 1992 Oct 1;119(2):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90268-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Leibowitz M. J. Variation and in vitro splicing of group I introns in rRNA genes of Pneumocystis carinii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2415–2421. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
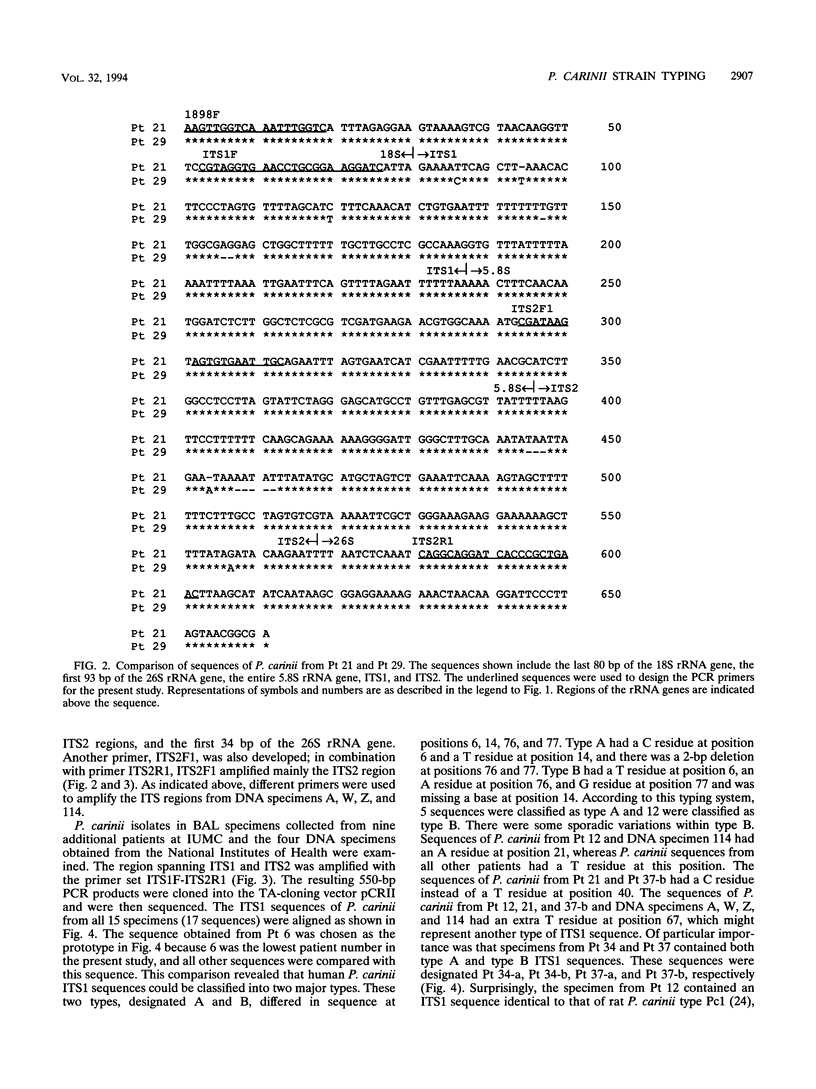
- Sloand E., Laughon B., Armstrong M., Bartlett M. S., Blumenfeld W., Cushion M., Kalica A., Kovacs J. A., Martin W., Pitt E. The challenge of Pneumocystis carinii culture. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 Mar-Apr;40(2):188–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulian A. G., Sullivan D. W., Linke M. J., Halsey N. A., Quinn T. C., MacPhail A. P., Hernandez-Avila M. A., Hong S. T., Walzer P. D. Geographic variation in the humoral response to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):1243–1247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Stringer S. L., Zhang J., Baughman R., Smulian A. G., Cushion M. T. Molecular genetic distinction of Pneumocystis carinii from rats and humans. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 Nov-Dec;40(6):733–741. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R., Blase M. A., Walzer P. D., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: sequence from ribosomal RNA implies a close relationship with fungi. Exp Parasitol. 1989 May;68(4):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Fuchimoto M., Egawa K., Nakamura Y. Use of Pneumocystis carinii genomic DNA clones for DNA hybridization analysis of infected human lungs. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):593–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Howe D. K., Visvesvara G. S., McLaughlin G. L. Identification of Acanthamoeba at the generic and specific levels using the polymerase chain reaction. J Protozool. 1992 May-Jun;39(3):378–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Pixley F. J., Banerji S., Sinclair K., Miller R. F., Moxon E. R., Hopkin J. M. Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii DNA of rat and human origin. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Nov;43(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Debault L. E., Graves D. C. Ultrastructural localization of epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies produced to rat Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):18S–20S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


