Abstract
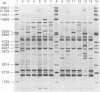
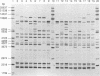
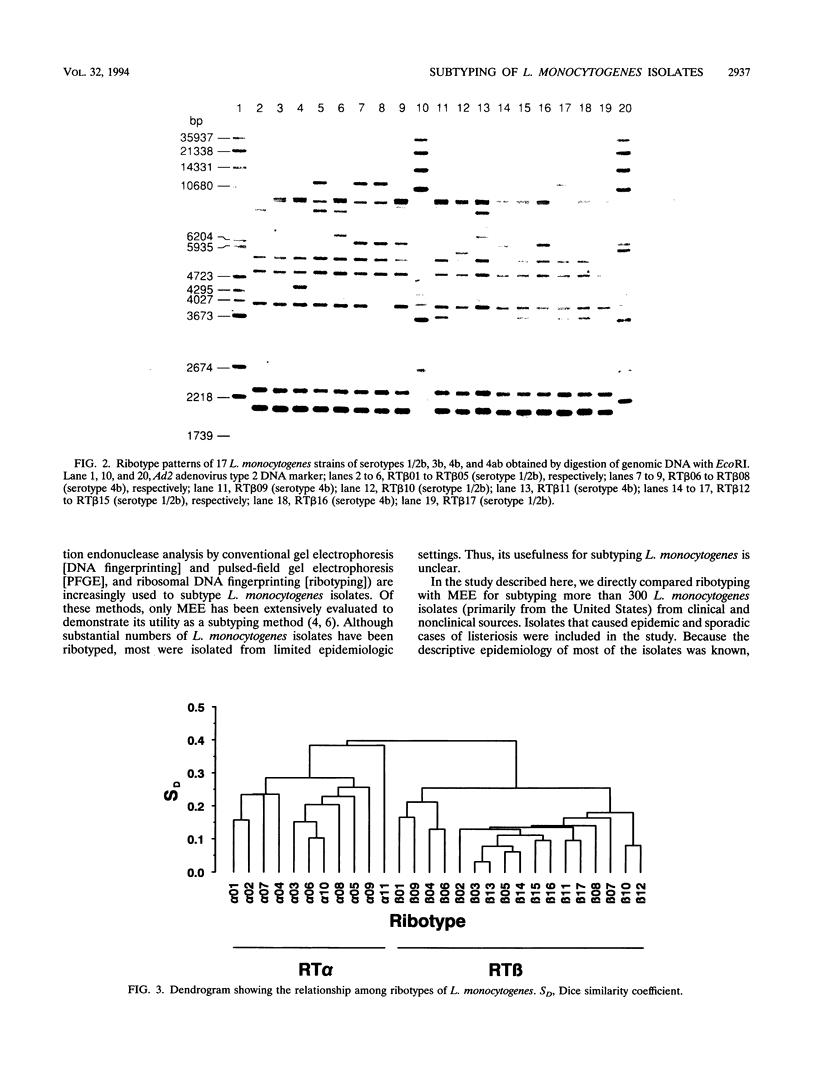
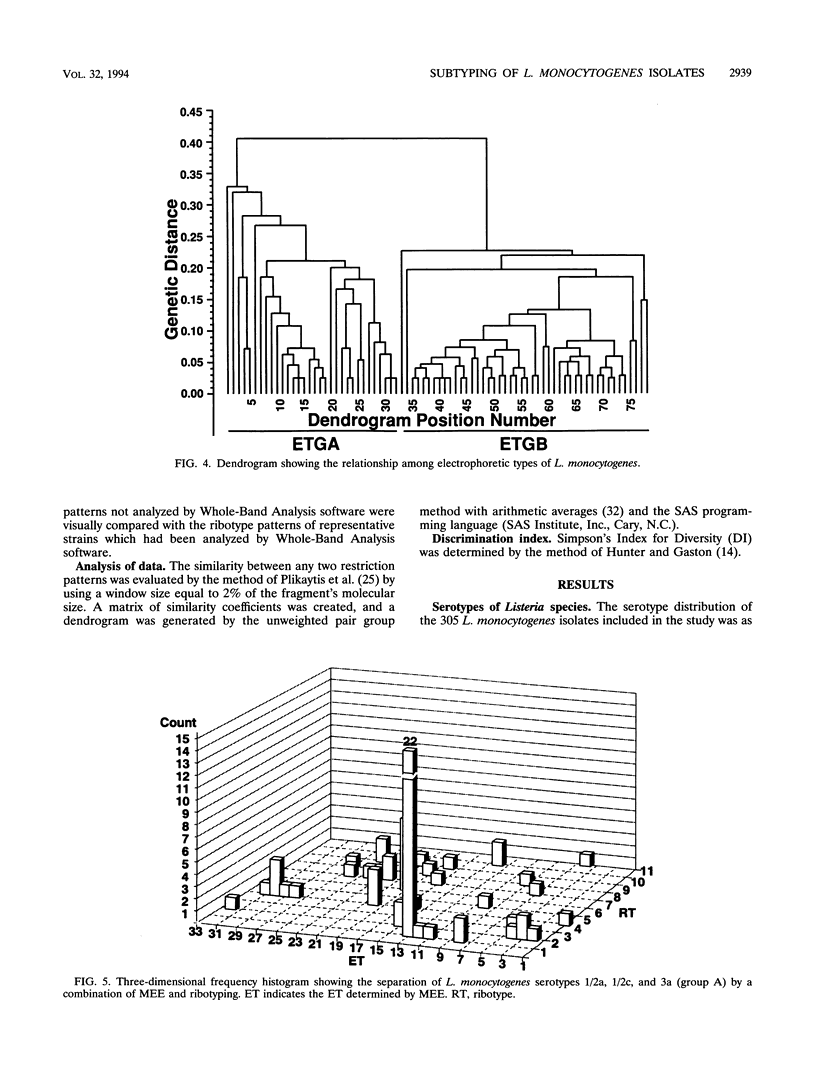
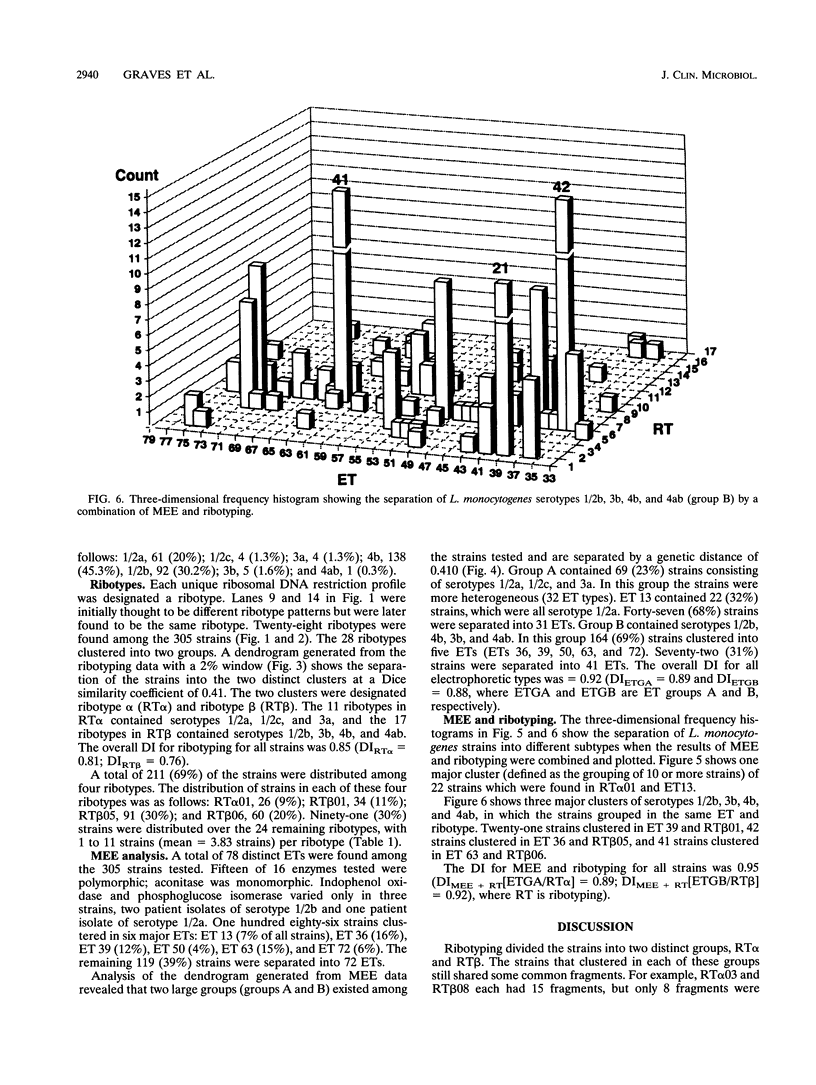
Ribotyping was compared with multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE) for subtyping 305 Listeria monocytogenes isolates from clinical and nonclinical sources. For ribotyping, EcoRI-restricted genomic DNA fragments of L. monocytogenes strains were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and Southern blots were probed with a cloned Escherichia coli rrnB operon (plasmid pKK3535) labeled with digoxigenin. The L. monocytogenes isolates were divided into 28 distinct ribotypes, while MEE analysis divided the same isolates into 78 electrophoretic types (ETs). On the basis of their ribotype profiles, the strains were divided into two subgroups. The ribotype alpha (RT alpha) subgroup contained serotypes 1/2a, 1/2c, and 3a, and the ribotype beta (RT beta) subgroup contained serotypes 1/2b, 3b, 4b, and 4ab. This division is in complete agreement with MEE analysis, which divides the species into two subgroups (ET groups A and B), with the same serotype distribution in each subgroup. Overall, MEE was more discriminating than ribotyping. However, in several instances ribotyping discriminated between isolates within the same ET. Ribotyping was more discriminating for serotypes 1/2a, 1/2c, and 3a (Simpson's Index for Diversity [DI] = 0.81) than for serotypes 1/2b and 4b (DI = 0.76). A substantial proportion (69%) of serotype 1/2b and 4b strains clustered in five ETs and five ribotypes. These data suggest that ribotyping and MEE do not provide adequate discrimination between strains of serotypes 1/2b and 4b. Methods such as pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis should be explored for further discrimination of strains of these serotypes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baloga A. O., Harlander S. K. Comparison of methods for discrimination between strains of Listeria monocytogenes from epidemiological surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2324–2331. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2324-2331.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Gellin B. G., Weaver R., Schwartz B., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M. W., Pinner R. W., Broome C. V. Analysis of clinical and food-borne isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in the United States by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2133-2141.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Schwartz B., Gellin B. G., Plikaytis B. D., Weaver R. E. Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jun;8(3):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C. Typing of human, animal, food, and environmental isolates of Listeria monocytogenes by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1624-1629.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosch R., Buchrieser C., Rocourt J. Subtyping of Listeria monocytogenes serovar 4b by use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90080-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordillo M. E., Singh K. V., Murray B. E. Comparison of ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for subspecies differentiation of strains of Enterococcus faecalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1570–1574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1570-1574.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R., Gaston M. A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson's index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2465–2466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2465-2466.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet C., Bille J., Rocourt J. Typing of Listeria monocytogenes by restriction polymorphism of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene region. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Feb;276(3):356–365. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGowan A. P., O'Donaghue K., Nicholls S., McLauchlin J., Bennett P. M., Reeves D. S. Typing of Listeria spp. by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1993 May;38(5):322–327. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-5-322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S. I., Audurier A., Marquet-Van der Mee N., Notermans S., Wernars K. A comparative study of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and conventional phage typing for epidemiological studies of Listeria monocytogenes isolates. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jun;143(5):507–512. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlin J., Hall S. M., Velani S. K., Gilbert R. J. Human listeriosis and paté: a possible association. BMJ. 1991 Sep 28;303(6805):773–775. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6805.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocera D., Altwegg M., Martinetti Lucchini G., Bannerman E., Ischer F., Rocourt J., Bille J. Characterization of Listeria strains from a foodborne listeriosis outbreak by rDNA gene restriction patterns compared to four other typing methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;12(3):162–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01967106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørrung B., Gerner-Smidt P. Comparison of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE), ribotyping, restriction enzyme analysis (REA) and phage typing for typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Aug;111(1):71–79. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinner R. W., Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Hayes P. S., Deaver K. A., Weaver R. E., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M., Broome C. V., Wenger J. D. Role of foods in sporadic listeriosis. II. Microbiologic and epidemiologic investigation. The Listeria Study Group. JAMA. 1992 Apr 15;267(15):2046–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Plikaytis B. B. Numerical analysis of normalized whole-cell protein profiles after sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Deaver K. A., Wenger J. D., Plikaytis B. D., Mascola L., Pinner R. W., Reingold A. L., Broome C. V. Role of foods in sporadic listeriosis. I. Case-control study of dietary risk factors. The Listeria Study Group. JAMA. 1992 Apr 15;267(15):2041–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Broome C. V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B., Hexter D., Broome C. V., Hightower A. W., Hirschhorn R. B., Porter J. D., Hayes P. S., Bibb W. F., Lorber B., Faris D. G. Investigation of an outbreak of listeriosis: new hypotheses for the etiology of epidemic Listeria monocytogenes infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):680–685. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]