Abstract
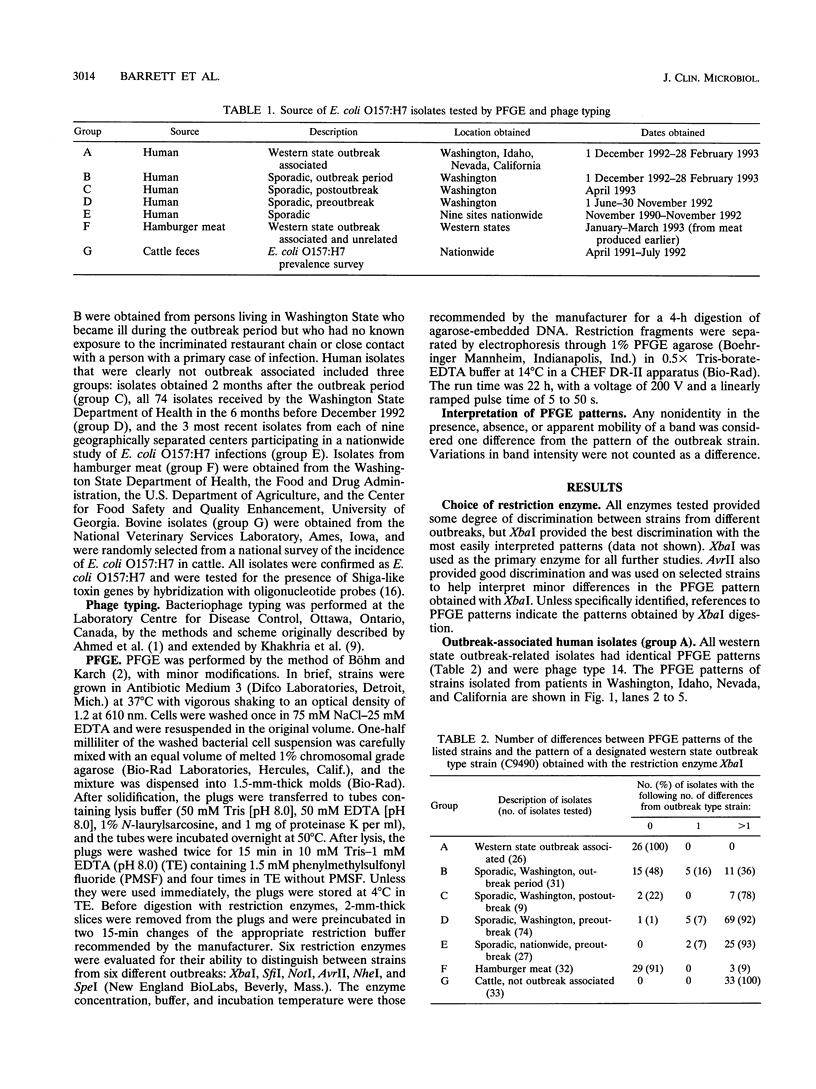
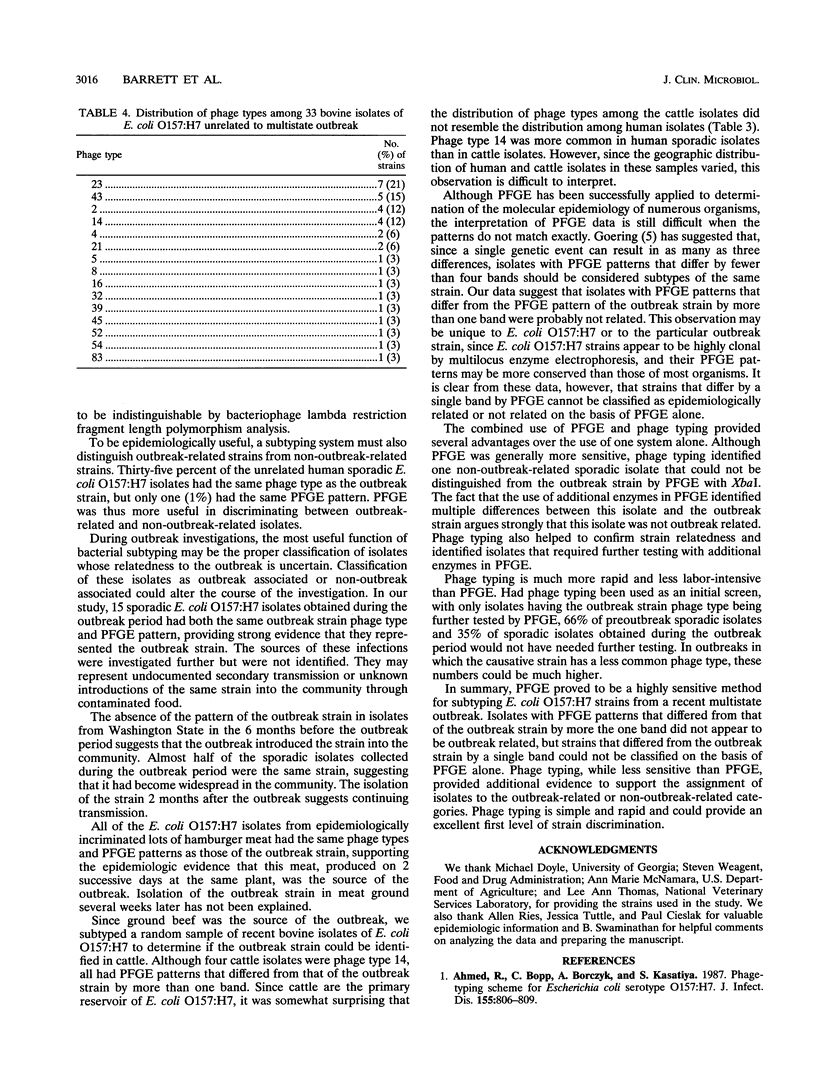
Two hundred thirty-three isolates of Escherichia coli O157:H7 were analyzed by both pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and bacteriophage typing. All 26 isolates from persons whose illness was associated with a recent multistate outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 infections linked to the consumption of undercooked hamburgers and all 27 isolates from incriminated lots of hamburger meat had the same phage type and the same PFGE pattern. Twenty-five of 74 E. coli O157:H7 isolates from Washington State and 10 of 27 isolates from other states obtained during the 6 months before the outbreak had the same phage type as the outbreak strain, but only 1 isolate had the same PFGE pattern. PFGE thus appeared to be a more sensitive method than bacteriophage typing for distinguishing outbreak and non-outbreak-related strains. The PFGE patterns of seven preoutbreak sporadic isolates and five sporadic isolates from the outbreak period differed from that of the outbreak strain by a single band, making it difficult to identify these isolates as outbreak or non-outbreak related. Phage typing and PFGE with additional enzymes were helpful in resolving this problem. While not as sensitive as PFGE, phage typing was helpful in interpreting PFGE data and could have been used as a simple, rapid screen to eliminate the need for performing PFGE on unrelated isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Bopp C., Borczyk A., Kasatiya S. Phage-typing scheme for Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):806–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm H., Karch H. DNA fingerprinting of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2169–2172. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2169-2172.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. N., Khambaty F. M., Wachsmuth I. K., Tauxe R. V., Barrett T. J. Molecular characterization of Vibrio cholerae O1 strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jul;32(7):1685–1690. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.7.1685-1690.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V. Molecular epidemiology of nosocomial infection: analysis of chromosomal restriction fragment patterns by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1993 Oct;14(10):595–600. doi: 10.1086/646645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin P. M., Tauxe R. V. The epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7, other enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and the associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:60–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Tümmler B. New approaches in genome analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: application to the analysis of Pseudomonas species. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2763–2776. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakhria R., Duck D., Lior H. Extended phage-typing scheme for Escherichia coli O157:H7. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Dec;105(3):511–520. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. L., O'Leary M. J., Cohen M. L., Norris P., Wells J. G., Noll E., Kobayashi J. M., Blake P. A. Escherichia coli O157:H7, an emerging gastrointestinal pathogen. Results of a one-year, prospective, population-based study. JAMA. 1988 Jun 24;259(24):3567–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Neill R. J. DNA probes for Shiga-like toxins I and II and for toxin-converting bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1292-1297.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff S. M., Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Lewis J. H., Hargrett-Bean N., Kobayashi J. M. Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Strong D., Taylor D. E., Salama S. M., Davidson C., Tabor H. Campylobacter fetus diarrhea in a Hutterite colony: epidemiological observations and typing of the causative organism. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):721–724. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.721-724.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadpour M., Grimm L. M., Desai B., Alfi D., Ongerth J. E., Tarr P. I. Molecular epidemiology of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains by bacteriophage lambda restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis: application to a multistate foodborne outbreak and a day-care center cluster. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Dec;31(12):3179–3183. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.12.3179-3183.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Faruque S. M., Kay B. A., Haider K., Alam K., Alam A. N., Tzipori S., Wachsmuth I. K. DNA probe analysis of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli: detection of EAF-positive isolates of traditional enteropathogenic E. coli serotypes among Bangladeshi paediatric diarrhoea patients. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Apr;6(2):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90052-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow D. L., Woodruff B. A., Brady R. C., Griffin P. M., Tippen S., Donnell H. D., Jr, Geldreich E., Payne B. J., Meyer A., Jr, Wells J. G. A waterborne outbreak in Missouri of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with bloody diarrhea and death. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):812–819. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Clausen C. R., Newland J. W., Neill R. J., Moseley S. L. Genotypic variation in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolated from patients in Washington, 1984-1987. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):344–347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Shipman L. D., Greene K. D., Sowers E. G., Green J. H., Cameron D. N., Downes F. P., Martin M. L., Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and other Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli from dairy cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):985–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.985-989.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wachsmuth I. K., Wilson R. A. Genetic evidence of clonal descent of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1124–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Mazurek G. H., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Pang Y., Murphy D. T., Wallace R. J., Jr DNA polymorphisms in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: a tool for epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1551-1556.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




