Abstract
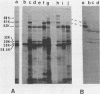
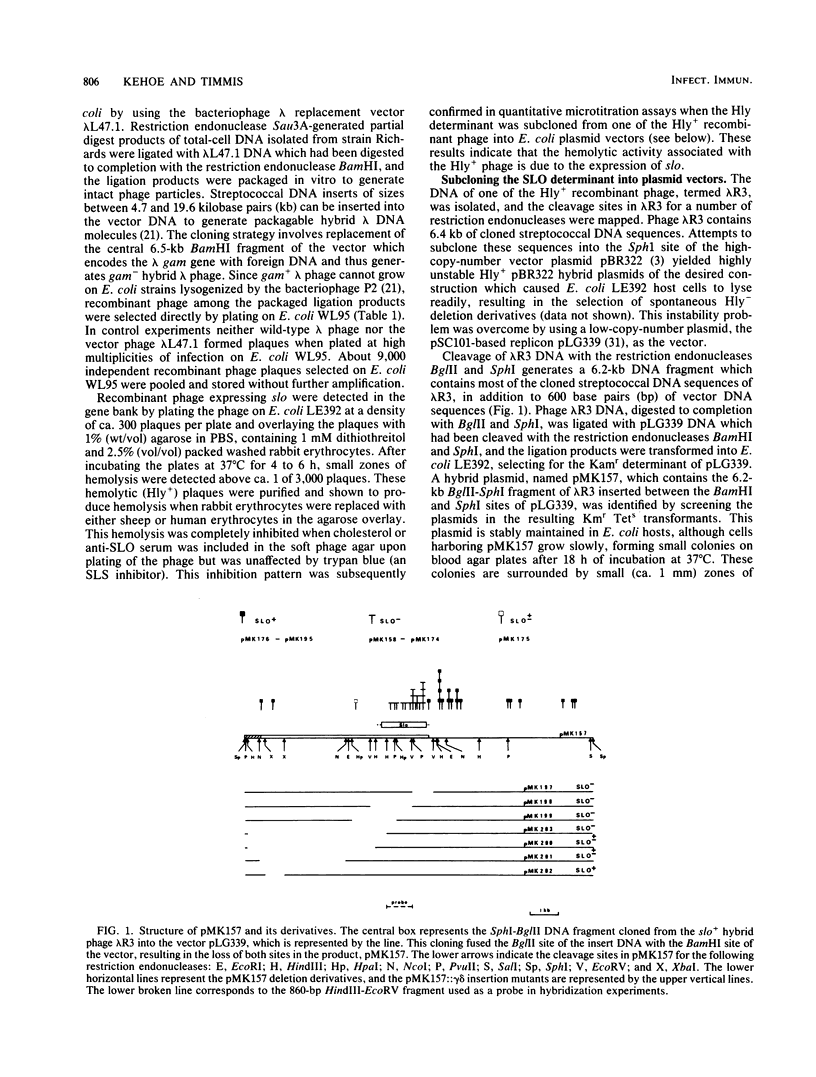
A gene bank of Streptococcus pyogenes Richards was constructed in Escherichia coli by using the bacteriophage replacement vector lambda L47.1, and hybrid phage expressing streptolysin O (SLO) were identified among the recombinants. DNA sequences encoding SLO were subcloned from an slo+ hybrid phage into a low-copy-number vector plasmid to yield an slo+ hybrid plasmid, pMK157. This plasmid contains 5.6 kilobase pairs of cloned streptococcal DNA sequences, is stable, and expresses SLO at easily detectable levels in E. coli. Transposon gamma delta insertion mutants and in vitro-generated deletion mutants of pMK157 were isolated and analyzed. This analysis showed that a single gene is sufficient for production of SLO in E. coli and allowed this slo gene to be mapped to within +/- 100 base pairs. Two forms of the slo gene product, with molecular weights of 68,000 and 61,000, were detected in E. coli minicells harboring slo+ plasmids and by immunoblotting of E. coli whole cells harboring slo+ plasmids. Southern blotting hybridization experiments with the cloned SLO DNA sequences as probes failed to demonstrate homology between the cloned SLO determinant and DNA isolated from bacteria expressing thiol-activated cytolysins related to SLO.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. R., Van Epps D. E. Suppression of chemotatic activity of human neutrophils by streptolysin O. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):353–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Wilkins B. M., Lanka E. Overlapping genes at the DNA primase locus of the large plasmid ColI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):855–869. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Buckingham L. Resistance to streptolysin O in mammalian cells treated with oxygenated derivatives of cholesterol. Cholesterol content of resistant cells and recovery of streptolysin O sensitivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 12;603(2):278–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L. Characteristics of streptolysin O hemolysis: kinetics of hemoglobin and 86rubidium release. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1022–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1022-1027.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Schlegel R. Effect of streptolysin O on erythrocyte membranes, liposomes, and lipid dispersions. A protein-cholesterol interaction. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):160–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S. The gamma delta sequence of F is an insertion sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):347–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Duncan J., Foster T., Fairweather N., Dougan G. Cloning, expression, and mapping of the Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin determinant in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1105-1111.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Sellwood R., Shipley P., Dougan G. Genetic analysis of K88-mediated adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):122–126. doi: 10.1038/291122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P. Molecular cloning in the Streptococci. Basic Life Sci. 1982;19:195–210. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4142-0_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Parkinson J. S. Overlapping genes at the cheA locus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5370–5374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Fairweather N. F., Spratt B. G. Versatile low-copy-number plasmid vectors for cloning in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Andersen B. R. Streptolysin O inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis and mobility: nonimmune phenomenon with species specificity. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):27–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.27-33.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W. The chain that links the heart to the throat. Circulation. 1973 Jul;48(1):9–18. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Crowther C. Mobilization of the non-conjugative IncQ plasmid RSF1010. Genet Res. 1981 Jun;37(3):311–316. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]