Abstract
The N terminus of the scrapie isoform of prion protein (PrPSc) can be truncated without loss of scrapie infectivity and, correspondingly, the truncation of the N terminus of the cellular isoform, PrPC, still permits conversion into PrPSc. To assess whether additional segments of the PrP molecule can be deleted, we previously removed regions of putative secondary structure in PrPC; in the present study we found that deletion of each of the four predicted helices prevented PrPSc formation, as did deletion of the stop transfer effector region and the C178A mutation. Removal of a 36-residue loop between helices 2 and 3 did not prevent formation of protease-resistant PrP; the resulting scrapie-like protein, designated PrPSc106, contained 106 residues after cleavage of an N-terminal signal peptide and a C-terminal sequence for glycolipid anchor addition. Addition of the detergent Sarkosyl to cell lysates solubilized PrPSc106, which retained resistance to digestion by proteinase K. These results suggest that all the regions of proposed secondary structure in PrP are required for PrPSc formation, as is the disulfide bond stabilizing helices 3 and 4. The discovery of PrPSc106 should facilitate structural studies of PrPSc, investigations of the mechanism of PrPSc formation, and the production of PrPSc-specific antibodies.
Keywords: prion diseases, protein solubility, prion protein structure, protein aggregation, prion replication
The importance of understanding the conversion of cellular prion protein (PrPC) into the scrapie isoform (PrPSc) has been heightened by the possibility that bovine prions have been transmitted to teenagers and young adults who developed variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD) (1, 2). The unusual neuropathology of vCJD is characterized by numerous PrP plaques surrounded by spongiform change, and this histopathology has been reproduced in macaques inoculated with bovine prions (3). More than 160,000 cattle have died of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) since the disease was first reported (4, 5). It is thought that BSE began with the increased survival of prions in meat and bone meal (MBM) fed to cattle, the preparation of which was changed in the late 1970s (6). Because it became unprofitable, organic solvents were abandoned in the preparation of MBM. The result of these alterations in the practice of industrial cannibalism is the appearance of a new prion disease. The number of cattle with BSE reported annually is declining after the ban on feeding MBM (5), a scenario that is strikingly similar to the ritualistic cannibalism responsible for kuru in the highlands of New Guinea (7).
During PrPSc formation, PrPC undergoes a profound conformational change (8). This structural transition is generally accompanied by the acquisition of insolubility in nondenaturing detergents and resistance to digestion by proteinase K (9–11). Structural studies of PrPSc have been limited by the insolubility of the molecule (12–15), while synthetic and recombinant fragments of PrP analogous to PrPC have been more amenable to structural investigations (16–18).
Faced with these difficulties and those attendant with achieving high-level expression of undegraded recombinant PrP (17, 19), we took advantage of the inadvertent molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding chicken PrP (20) to study the structural features of mammalian PrP by molecular modeling. Four regions of putative secondary structure were identified, using several structure prediction algorithms (21, 22). Although there was disagreement as to whether certain regions adopt α-helical or β-sheet structures, all the analyses predicted these regions would adopt secondary structure. Accordingly, we produced synthetic peptides corresponding to each of the four regions designated H1, H2, H3, and H4; unexpectedly, in aqueous buffers H1, H3, and H4 adopted β-sheet structures (22). Mixing H1 in a β-sheet conformation with H2 in a coil converted H2 into β-sheet (23). A longer peptide [PrP-(90–145)] of 56 residues containing H1 and H2 adopted an α-helical conformation in aqueous buffers and exhibited chemical shifts indicating an α-helix in the H1 region (16). The secondary structure as determined by NMR in the H2 region was less clear. The H3 and H4 regions were identified in NMR studies of a C-terminal fragment of 111 residues, PrP-(121–231) (18). Those studies also identified a short α-helix in the loop between H2 and H3 as well as a short β-strand consisting of residues 161–164.
METHODS
Construction of Modified PrPs.
MHM2 and MHM2 with residues 23–88 deleted [MHM2 (del 23–88)] as well as their open reading frame (ORF) cassettes with BglII/XhoI termini were described previously (24–26). All further modifications were made using the MHM2 (del 23–88) insert in pSP72 vector or the partial KpnI/XhoI insert subcloned into pBC vector. The location of the KpnI site is described below. For cloning of MHM2 (del 23–88, 177–200) and MHM2 (del 23–88)C178A, an SfuI site was created in MHM2 (del 23–88) by digesting it with AvaII and AspI to cleave off a part of the insert and ligating double-stranded synthetic oligonucleotides to fill in; the sequences of oligonucleotides were GACCGCTACTATCGGGAGAATATGTATCGGTATCCGAACCAGGTGTACTACCGGCCGGTGGATCAGTATTCGAACCAGAATAACTTCGTGCATGACT (sense) and CAGTCATGCACGAAGTTATTCTGGTTCGAATACTGATCCACCGGCCGGTAGTACACCTGGTTCGGATACCGATACATATTCTCCCGATAGTAGCG (antisense). The MHM2 (del 23–88) insert in the plasmids was digested with two restriction endonucleases to cleave off a part of the insert and ligated with double-stranded synthetic oligonucleotides to fill in. Constructs, restriction endonucleases used, and sequences of oligonucleotides (sense/antisense) are as follows: MHM2 (del 23–88, 95–107)I138M, KpnI/NaeI, CATGAAACACATGGCC/GGCCATGTGTTTCATGGTAC; MHM2 (del 23–88, 108–121)I138M, KpnI/EcoO109I, CCATAATCAGTGGAATAAGCCTAGTAAGCCTAAGACTAATGGG/GCCCCCATTAGTCTTAGGCTTACTAGGCTTATTCCACTGATTATGGGTAC; MHM2 (del 23–88, 122–140), KpnI/AvaII, CCACAATCAATGGAACAAACCTAGTAAGCCTAAGACTAACATGAAACACATGGCCGGCGCTGCAGCTGCTGGTGCCGTCGTCGGTAATGATTGGGAG/ GTCCTCCCAATCATTACCGACGACGGCACCAGCAGCTGCAGCGCCGGCCATGTGTTTCATGTTAGTCTTAGGCTTACTAGGTTTGTTCCATTGATTGTGGGTAC; MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176), EcoO109I/AspI, GGCCTAGGAGGATACATGCTGGGAAGCGCTATGAGCAGGCCTATGATACATTTCGACT/CAGTCGAAATGTATCATAGGCCTGCTCATAGCGCTTCCCAGCATGTATCCTCCTAG; MHM2 (del 23–88, 177–200), SfuI/StuI, CGAACCAGAATAACTTCGTTCATGATGTTAAGATGATGGAGCGCGTTGTTGAGCAGATGTGCGTCACCCAGTACCAGAAGGAGTCCCAGG/CCTGGGACTCCTTCTGGTACTGGGTGACGCACATCTGCTCAACAACGCGCTCCATCATCTTAACATCATGAACGAAGTTATTCTGGTT; MHM2 (del 23–88, 201–217), BstEII/StuI, GTCACCACTACTACCAAGGGCGAGAATTTCACTGAGACTCAGAAGGAGTCACAGG/CCTGTGACTCCTTCTGAGTCTCAGTGAAATTCTCGCCCTTGGTAGTAGTG; and MHM2 (del 23–88)C178A, SfuI/BstEII, CGAATCAGAATAACTTCGTTCATGACGCTGTCAATATCACGATCAAGCAGCATACG/GTGACCGTATGCTGCTTGATCGTGATATTGACAGCGTCATGAACGAAGTTATTCTGATT. The location of the cleavage sites on nucleotide sequence relative to the start of the MHM2 ORF is 282 (KpnI), 337 (NaeI), 367 (EcoO109I), 436 (AvaII), 506 (SfuI), 533 (AspI), 562 (BstEII), and 668 (StuI). Met-138 was created in MHM2 (del 23–88), MHM2 (del 23–88, 95–107), and MHM2 (del 23–88, 108–121) by replacing the EcoO109I/XhoI segment of these constructs with the corresponding segment of the mouse PrP construct with Met-138 (M.S., unpublished work).
Immunoblotting of PrPSc.
The PrP constructs were inserted into the pSPOX.IIneo expression vector (26). ScN2a (scrapie-infected mouse neuroblastoma) cells on 60-mm Petri dishes were transiently transfected with 15 μg of expression construct DNA. Cells were harvested 72 h after transfection with 0.5 ml of lysis buffer containing 10 mM Tris·HCl at pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 0.5% sodium deoxycholate. After low-speed centrifugation, 430 μl of supernatant was digested by proteinase K (20 μg/ml, 30 min, 37°C) and then subjected to ultracentrifugation (100,000 × g, 1 h, 20°C). Proteolytic digestions were terminated with 4 mM 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride (Boehringer Mannheim). Ten microliters of supernatant after low-speed centrifugation was analyzed on a Western immunoblot for total recombinant PrPs, and whole pellets after ultracentrifugation were analyzed for PrPSc isoform of recombinant PrPs. Anti-PrP 13A5 mAb (27) and anti-PrP 3F4 mAb (28) against tagged epitopes were used as primary antibodies. Immunoblots were developed with the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) system (Amersham).
Measuring Solubility of PrPSc.
ScN2a cells on 100-mm Petri dishes were transiently transfected with 40 μg of the MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176) pSPOX expression construct (26). Cells were harvested 72 h after transfection with 1.5 ml of lysis buffer. After a low-speed centrifugation to clarify the cell lysate, 1 vol of lysis buffer containing Sarkosyl (N-lauroylsarcosine) at a concentration of 0, 2.5, 5, or 10% was added to 4 vol of lysate, typically 570 or 700 μl, to give a final concentration of 0, 0.5, 1.0, or 2.0% (vol/vol) Sarkosyl. Some aliquots were digested with proteinase K (20 μg/ml, 30 min, 37°C) and then subjected to ultracentrifugation (100,000 × g, 1 h, 20°C), while others were centrifuged prior to digestion. Proteins in 550 or 800 μl of supernatant were precipitated with 10 vol of methanol. Proteins in the pellets and those precipitated from supernatant fractions were analyzed on Western immunoblots. Anti-PrP 3F4 mAb was used to probe for MHM2 PrPSc106, and anti-Syrian hamster (SHa) PrP polyclonal R073 antiserum probed mainly mouse (Mo) PrPSc. Immunostaining of MHM2 PrPSc106 with R073 antiserum occurred only after longer exposure of films and thus is not seen in the Western blots shown here.
RESULTS
Analysis of Regions Required for PrPSc Formation.
On the basis of the molecular model of PrPC as well as data from circular dichroism (CD) and Fourier-transform infared (FTIR) studies (8, 21), we undertook a systematic study to test the model in terms of the ability of mutagenized PrPC to be converted into PrPSc. These studies were carried out in both cultured mouse neuroblastoma (N2a) cells and transgenic (Tg) mice. In this paper, we describe a map of the regions of putative secondary structure in terms of the requirement for each region to support the formation of PrPSc (Fig. 1) in scrapie-infected N2a cells (ScN2a), using an epitope-tagged molecule, MHM2PrPC, which has previously been shown to be converted into MHM2 PrPSc in ScN2a cells (24, 26, 29). All the PrP constructs expressed in ScN2a cells were cloned in the pSPOX.IIneo vector, and the cells were transiently transfected (26).
Figure 1.
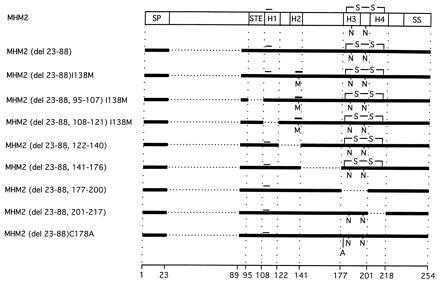
Scheme of MHM2 PrP and modified constructs with deletion(s) and substitution. SP, signal peptide (residues 1–22); STE, stop transfer effector region (residues 95–107); H1 (residues 108–121); H2 (residues 128–140); H3 (residues 177–190); H4 (residues 201–217); SS, signal sequence for anchoring to glycolipid (residues 231–254); –S–S–, a disulfide bond between Cys-178 and Cys-213; N, locations of Asn-linked glycosylation; M, Met-138; and A, Ala-178. Thin bar above H1, location of epitope for the anti-PrP 3F4 mAb; thick bar above H2, location of epitope for the anti-PrP 13A5 mAb; and horizontal dotted lines, location of deletions. The amino acid positions bordering deletions are shown at the bottom. All numbers of residues are based on the MHM2 molecule.
Epitope-Tagged PrP.
The epitope-tagged MHM2PrP has two Met residues, at positions 108 and 111, that are found in SHa- and human PrP; this epitope is recognized by the anti-PrP 3F4 mAb (24, 28). Since PrPC encoded by MHM2 was readily converted into PrPSc in ScN2a cells, it was used to assess the effect of selective deletions of specific domains within the PrP molecule (Fig. 1). As previously described, MHM2 in which residues 23–88 had been deleted supported PrPSc formation in ScN2a cells as evidenced by the production of an anti-PrP 3F4 mAb-reactive protein that was resistant to digestion by proteinase K (25). Recently, residues 33–80 of MoPrP were deleted, and the resulting construct was shown to render Prnp0/0 mice (in which the PrP gene has been ablated) susceptible to scrapie prions (30).
Deletion of the Putative Helices Prevented PrPSc Formation.
Using the MHM2 PrP construct in which residues 23–88 had been deleted, we proceeded to delete the H2 (residues 122–140), H3 (residues 177–200), or H4 (residues 201–217) region in separate constructs. Each of these PrPs with a deleted segment was expressed in ScN2a cells as detected by anti-PrP 3F4 mAb immunostaining (Fig. 2A). The H3 deletion, which no longer contains both consensus sites for Asn-linked glycosylation (31), migrated as a band of Mr ≈ 19 kDa. Two other constructs were also expressed: one with a deletion of the loop between H2 and H3, composed of 36 residues (141), and the other with a point mutation at residue 178, where Ala was substituted for Cys to prevent the formation of a disulfide bond between this residue and Cys-213 (Fig. 2A).
Figure 2.
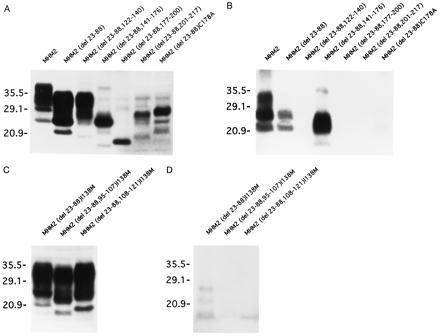
Expression and protease-resistant molecules of recombinant PrPs in ScN2a cells. Numbers on left are kDa. (A) Expression of MHM2, MHM2 (del 23–88), MHM2 (del 23–88, 122–140), MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176), MHM2 (del 23–88, 177–200), MHM2 (del 23–88, 201–217), and MHM2 (del 23–88)C178A in ScN2a cells. (B) Protease-resistant molecules of the recombinant PrPs shown in A. MHM2, MHM2 (del 23–88), and MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176) were converted to the scrapie isoform, whereas MHM2 (del 23–88, 122–140), MHM2 (del 23–88, 177–200), and MHM2 (del 23–88, 201–217) were not. A trace amount of protease-resistant MHM2 (del 23–88)C178A was detected. (C) Expression of MHM2 (del 23–88)I138M, MHM2 (del 23–88, 95–107)I138M, and MHM2 (del 23–88, 108–121)I138M in ScN2a cells. (D) Protease-resistant molecules of the recombinant PrPs shown in C. MHM2 (del 23–88)I138M was converted to the scrapie isoform, while MHM2 (del 23–88, 95–107)I138M and MHM2 (del 23–88, 108–121)I138M were not. Western blots were developed with anti-PrP 3F4 mAb in A and B and with anti-PrP 13A5 mAb in C and D.
PrPSc Formed with Deletion of Segment Between H2 and H3.
Deletion of the H2, H3, or H4 regions as well as mutagenesis of Cys-178 prevented PrPSc formation as determined by resistance to digestion with proteinase K (20 μg/ml, 30 min, 37°C) (Fig. 2B). Interestingly, deletion of the loop between H2 and H3 containing 36 residues (141) did not prevent conversion of the molecule into a protease-resistant isoform. Since the acquisition of protease resistance during PrPSc formation seems to occur within caveolae-like membranous domains (CLDs) and PrPC is targeted to CLDs by its glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor (32, 33), we exposed cells expressing the construct with the loop deletion to PIPLC and found that virtually all of the protease-digestible MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176), designated PrPC106, was released by the enzyme (data not shown) (34). This indicates that PrPC106 transits from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface, where it is bound by a GPI anchor, as is full-length PrPC.
To analyze the deletion of H1 containing residues 108–121, we created an I138M mutation to produce a SHaPrP epitope detectable by the anti-PrP 13A5 mAb (Fig. 2C) (24, 27). Like the deletion of H2–H4, removal of H1 prevented PrPSc formation (Fig. 2D). We also used anti-PrP 13A5 mAb to study deletion of the stop transfer effector (STE) region, composed of residues 95–107 adjacent to H1, which has been implicated in controlling the translocation of PrP synthesized in cell-free systems with dog pancreas microsomal membranes (35). Like the deletions of H1–H4, removal of the STE region also prevented PrPSc formation (Fig. 2 C and D). The weaker immunoblot signals for PrPSc with chimeric constructs carrying the 13A5 mAb epitope compared with those with the 3F4 epitope (Fig. 2) are presumably due to both the lower affinity of 13A5 for PrP compared with 3F4 (24) and the inhibition of PrPSc in ScN2a cells by the substitution of Met for Ile at residue 138 in MoPrP, which creates the 13A5 binding site (36). That conversion of chimeric PrP molecules carrying the 13A5 epitope into PrPSc occurs in cultured murine cells and Tg mice is well documented (26, 37).
PrPSc106 Molecules.
On the basis of the foregoing results, we examined the shift in Mr values after limited digestion with proteinase K for PrPSc106. In the absence of proteinase K, both the MHM2 PrPC and PrPSc isoforms encoded by the transfected constructs were immunostained with anti-PrP 3F4 mAb. The broad range of Mr values is presumably due to Asn-linked glycosylation (Fig. 3). After limited proteolysis, the Mr values were decreased and the range diminished. On the basis of the shift in Mr values, it seems likely that a few amino acid residues may have been removed from the N terminus of PrPSc106 during limited proteolysis; however, resolution of this issue will require microsequencing. Furthermore, some of the aberrantly glycosylated PrP106 molecules, especially those with higher Mr values, may not have been converted into PrPSc106.
Figure 3.
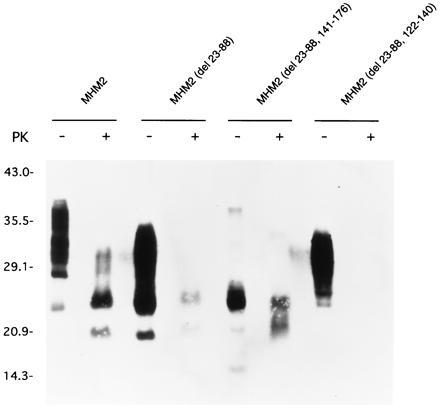
Electrophoretic mobility of recombinant PrPC106 and PrPSc106. Undigested MHM2 (del 23–88, 141–176), also called PrPC106, is mainly seen as a major band at 24–25 kDa and a minor band at 20 kDa. PrPSc106 is seen as two major bands at 20–21 or 24 kDa, showing that the shift of the molecular mass after protease digestion is minimal. Samples were incubated with (+) or without (−) proteinase K (PK). Western blots were developed with anti-PrP 3F4 mAb.
PrPSc106 Is Soluble in Sarkosyl.
Since insolubility in nondenaturing detergents has been an invariant feature of protease-resistant PrPSc (10, 12), we lysed the ScN2a cells expressing PrPSc106 in buffers containing 0.5% Triton X-100 and 0.5% sodium deoxycholate. Under these conditions, PrPC106 was found in the supernatant after centrifugation of the suspension at 100,000 × g for 1 h at 20°C, while PrPSc106 was found in the pellet fraction (data not shown). When N-lauroylsarcosine (Sarkosyl) was added to the lysis buffer, we unexpectedly found that at a concentration of 0.5% Sarkosyl or greater, all of the PrPSc106 was in the supernatant fraction (Fig. 4A). When the Western immunoblot was reprobed to detect MoPrPSc with anti-PrP rabbit polyclonal R073 antiserum, all the immunostaining was found in the pellet fraction and none in the supernatant (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
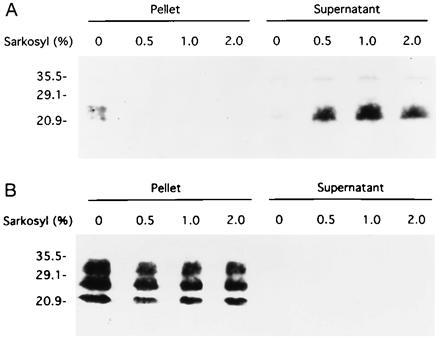
Sedimentation properties of PrPSc106. (A) After lysis of ScN2a cells with or without addition of 0.5, 1.0, or 2.0% Sarkosyl, samples were digested with proteinase K and then centifuged at 100,000 × g for 1 h. Without Sarkosyl, PrPSc106 was found in the pellet fractions after centrifugation at 100,000 × g, but with Sarkosyl added to the lysis buffer prior to ultracentrifugation, it was found in the supernatant fractions. Western blot was developed with anti-PrP 3F4 mAb. (B) MoPrPSc in the same samples was found exclusively in pellet fractions after centrifugation at 100,000 × g whether Sarkosyl was present or not. Western blot was developed with anti-PrP R073 polyclonal antiserum.
To examine the possibility that PrPC106 might exhibit protease resistance due to its altered structure, transfected N2a cells expressing this recombinant protein were analyzed. No protease-resistant PrPC106 was found in either the pellet or supernatant fractions in the presence or absence of 0.5% Sarkosyl (Fig. 5). The same results were obtained whether limited proteolysis was performed before or after centrifugation.
Figure 5.
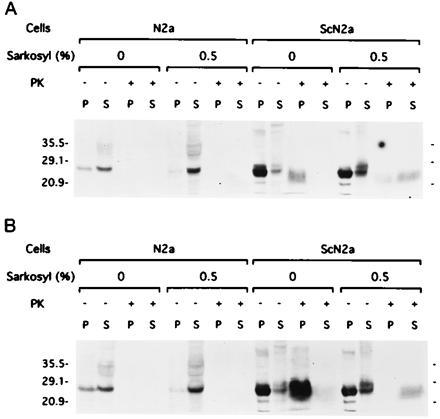
After solubilization in Sarkosyl and ultracentrifugation, PrPSc106 remains resistant to digestion by proteinase K. (A) After lysis of N2a and ScN2a cells with or without addition of 0.5% Sarkosyl, samples were incubated with (+) or without (−) proteinase K (PK) and then centifuged at 100,000 × g for 1 h. In N2a cells, no protease-resistant PrP was found in either the pellet (P) or the supernatant (S) fractions. In ScN2a cells, PrPSc106 was found in the pellet fraction in the absence of Sarkosyl and in the supernatant when Sarkosyl was added. (B) After lysis of N2a and ScN2a cells with or without addition of 0.5% Sarkosyl, samples were centifuged at 100,000 × g for 1 h. The aliquots of the pellet and supernatant fractions were then incubated with (+) or without (−) proteinase K (PK). Western blots were developed with anti-PrP 3F4 mAb.
To determine if PrPSc106 in the supernatant fraction prepared in the presence of 0.5% Sarkosyl exhibits protease resistance, transfected ScN2a cells expressing this recombinant PrP106 were examined (Fig. 5). PrPSc106 was found whether limited proteolysis was performed before (Fig. 5A) or after (Fig. 5B) ultracentrifugation. Thus, PrPSc106 retained its resistance to limited digestion by proteinase K even after solubilization in Sarkosyl and centrifugation to separate it from insoluble proteins such as MoPrPSc (Fig. 4B).
DISCUSSION
The foregoing data argue that all four putative helical regions identified by molecular modeling and the STE region discovered in cell-free translation studies are required for PrPSc formation. Our findings also support the contention that the disulfide bond between Cys residues 178 and 213 found in both PrPC and PrPSc (38) is essential to PrPSc formation. Although disruption of this disulfide by the C178A mutation diminished conversion of this mutated PrPC into PrPSc (Fig. 2 A and B), treatment of fractions enriched for scrapie infectivity with either 2% 2-mercaptoethanol or 100 mM dithiothreitol did not diminish prion titers as measured by bioassays in Syrian hamsters (39). Interestingly, when recombinant PrP-(90–231) corresponding to the residues found in PrP 27–30, the protease-resistant core of PrPSc, was refolded after purification under denaturing conditions, it adopted a structure with high α-helical content similar to mammalian PrPC upon formation of the disulfide bond (17). The disulfide was postulated to stabilize the C-terminal α-helices—i.e., H3 and H4 (21, 40)—a prediction that is supported by NMR structural studies of recombinant PrP-(121–231) expressed in Escherichia coli (18). How accurately data from PrP-(121–231), which lacks the N-terminal 99 amino acids as well as the Asn-linked carbohydrates and the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor, reflect the structure of the C-terminal region of PrPC remains to be established. Structural studies of PrP-(121–231) demonstrated the α-helices that were predicted for the H3 and H4 regions of both PrPC and PrPSc.
Implications for PrPC Structure.
That PrPC106, which lacks residues 23–88 and 141–176, is converted into a PrPSc-like molecule supports the argument that one of the two antiparallel β-strands that forms a small β-sheet, residues 161–164 in Prp-(121–231), is unlikely to be the nidus at which PrPSc formation is initiated (18). Furthermore, the first α-helix (144) found in PrP-(121–231), which was predicted to lie outside the hydrophobic core of the molecule, is also not required for the acquisition of resistance to limited proteolysis. It will be important to determine the tertiary structure of full-length PrPC including not only the structures of the H1 and H2 regions but also the octarepeats. Interestingly, inherited prion diseases are caused not only by point mutations within or adjacent to the H1, H2, H3, and H4 regions (41–43) but also by addition of 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9 octarepeats besides the five that are normally found (44–46). When the human PrP mutation at codon 102 adjacent to H1 was modeled in Tg mice, the animals developed central nervous system dysfunction and produced prions de novo (11, 47). In contrast, Tg mice expressing the codon 178 or 200 human mutations that are within or adjacent to H3 or H4 have not developed disease (G. Telling, Z. Meiner, and S.B.P., unpublished data).
Constraints on the Mechanism of PrPSc Formation.
Our results uncouple the protease resistance and insolubility of PrPSc for the first time. They can be used to argue that aggregation, which must contribute to the insolubility of purified PrPSc, is not required for protease resistance. Results of cell-free studies on the binding of partially denatured PrPC to PrPSc have been interpreted as evidence for conversion of radiolabeled PrPC into PrPSc, which exhibits protease resistance (48, 49). Since the radiolabeled PrPC is inseparable from aggregates of PrPSc, it has not been possible to assess whether or not the PrPC molecule has undergone a conformational change (50). The results reported here may allow development of cell-free systems in which such ambiguities can be resolved. Our findings clearly demonstrate that insolubility and protease resistance are separable in accord with earlier studies in which PrP 27–30 in rod-shaped aggregates was dispersed into liposomes and remained resistant to proteolytic digestion (51). While the rods exhibit the properties of amyloid fibrils and this finding predicted that amyloid plaques found in some but not all prion diseases are composed of PrP (12), subsequent studies showed that the rods are an artifact generated during purification by limited proteolysis in the presence of detergent (52).
Our data show that the solubility of MHM2 PrPSc106 is intermediate between that of full-length PrPC and PrPSc. While PrPC is soluble in a combination of 0.5% Triton X-100 and 0.5% deoxycholate, PrPSc106 is not, but it becomes soluble when Sarkosyl is added under conditions where full-length PrPSc remains insoluble. These findings should facilitate purification of MHM2 PrPSc106 away from PrPC and full-length PrPSc. The data also suggest that the interaction between PrPSc106 molecules or protease-resistant units composed of PrPSc106 molecules is disrupted by detergents more easily than that between full-length PrPSc molecules. It will be important to study the formation of PrPSc106 in Tg mice carrying the null background and to determine if PrPSc106 supports prion infectivity. It will also be of interest to learn whether PrPSc106 polymerizes into amyloid fibrils in vivo as well as in vitro. In recent studies of SHaPrP 27–30, it was possible to uncouple infectivity and amyloidogenicity by using mixtures of detergent and organic solvents (53).
Our finding that PrPSc106 is soluble in Sarkosyl under nondenaturing conditions is consistent with the view that PrPSc formation occurs through a template-assisted conformational change (54). Other findings suggest that PrPSc interacts with PrPC (55) and that this complex binds through PrPC to an auxiliary macromolecule which has been provisionally labeled protein X (56). Alternatively, PrPC may bind protein X prior to binding PrPSc, but in either case, available data argue that PrPSc does not bind to protein X. Recent studies argue that PrPSc formation occurs in CLDs near the surface of the cell (32, 33) and that PrPSc acts as a template in specifying the conformation of nascent PrPSc (57, 58). Presumably, protein X functions as a molecular chaperone within this subcellular compartment to effect the transformation of PrPC into PrPSc.
New Approaches to Studies of Prions.
The ability of ScN2a cells to produce a protease-resistant but soluble PrPSc106 molecule should open many new avenues of investigation. For example, the isolation of PrPSc-specific antibodies by phage display should be greatly facilitated by panning and screening against this soluble PrPSc106 molecule (59). Determining the tertiary structure of PrPSc should be substantially advanced by availability of PrPSc106, as should deciphering the mechanism by which PrPC is converted into PrPSc. The formation of a soluble form of PrPSc in ScN2a cells may also facilitate development of an effective pharmacotherapeutic agent for prion diseases (54). Since the prion diseases are unprecedented in biology and medicine, it is likely that the design of a drug to treat these disorders will require a detailed understanding of the structural transition that PrP undergoes as PrPSc is formed. With the possibility that bovine prions have been transmitted to people in Britain and France, causing variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease (1, 2), the development of an effective therapy for prion diseases has acquired paramount importance.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NS14069, AG08967, AG02132, NS22786, and AG10770), the International Human Frontier Science Program, and the American Health Assistance Foundation, as well as by gifts from the Sherman Fairchild Foundation, the Leila and Harold G. Mathers Foundation, the Bernard Osher Foundation, and Centeon, Inc. T.M. was supported by fellowships from the International Human Frontier Science Program and The French Foundation for Alzheimer Research.
Footnotes
Abbreviations: CLDs, caveolae-like membranous domains; Mo-, mouse; PrP, prion protein; PrPC, cellular PrP; PrPSc, scrapie PrP isoform; SHa-, Syrian hamster; STE, stop transfer effector; Tg, transgenic.
References
- 1.Chazot G, Broussolle E, Lapras C I, Blättler T, Aguzzi A, Kopp N. Lancet. 1996;347:1181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Will R G, Ironside J W, Zeidler M, Cousens S N, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, Poser S, Pocchiari M, Hofman A, Smith P G. Lancet. 1996;347:921–925. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91412-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lasmézas C I, Deslys J-P, Demaimay R, Adjou K T, Lamoury F, Dormont D, Robain O, Ironside J, Hauw J-J. Nature (London) 1996;381:743–744. doi: 10.1038/381743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wells G A H, Scott A C, Johnson C T, Gunning R F, Hancock R D, Jeffrey M, Dawson M, Bradley R. Vet Rec. 1987;121:419–420. doi: 10.1136/vr.121.18.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anderson R M, Donnelly C A, Ferguson N M, Woolhouse M E J, Watt C J, Udy H J, MaWhinney S, Dunstan S P, Southwood T R E, Wilesmith J W, Ryan J B M, Hoinville L J, Hillerton J E, Austin A R, Wells G A H. Nature (London) 1996;382:779–788. doi: 10.1038/382779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wilesmith J W. Semin Virol. 1994;5:179–187. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gajdusek D C. Science. 1977;197:943–960. doi: 10.1126/science.142303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pan K-M, Baldwin M, Nguyen J, Gasset M, Serban A, Groth D, Mehlhorn I, Huang Z, Fletterick R J, Cohen F E, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:10962–10966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Prusiner S B, Bolton D C, Groth D F, Bowman K A, Cochran S P, McKinley M P. Biochemistry. 1982;21:6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Meyer R K, McKinley M P, Bowman K A, Braunfeld M B, Barry R A, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Telling G C, Haga T, Torchia M, Tremblay P, DeArmond S J, Prusiner S B. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1736–1750. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.14.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Prusiner S B, McKinley M P, Bowman K A, Bolton D C, Bendheim P E, Groth D F, Glenner G G. Cell. 1983;35:349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Caughey B W, Dong A, Bhat K S, Ernst D, Hayes S F, Caughey W S. Biochemistry. 1991;30:7672–7680. doi: 10.1021/bi00245a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gasset M, Baldwin M A, Fletterick R J, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Safar J, Roller P P, Gajdusek D C, Gibbs C J., Jr J Biol Chem. 1993;268:20276–20284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang H, Kaneko K, Nguyen J T, Livshits T L, Baldwin M A, Cohen F E, James T L, Prusiner S B. J Mol Biol. 1995;250:514–526. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mehlhorn I, Groth D, Stöckel J, Moffat B, Reilly D, Yansura D, Willett W S, Baldwin M, Fletterick R, Cohen F E, Vandlen R, Henner D, Prusiner S B. Biochemistry. 1996;35:5528–5537. doi: 10.1021/bi952965e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riek R, Hornemann S, Wider G, Billeter M, Glockshuber R, Wüthrich K. Nature (London) 1996;382:180–182. doi: 10.1038/382180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Scott M, Butler D, Bredesen D, Wälchli M, Hsiao K, Prusiner S B. Protein Eng. 1988;2:69–76. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harris D A, Falls D L, Johnson F A, Fischbach G D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang Z, Gabriel J-M, Baldwin M A, Fletterick R J, Prusiner S B, Cohen F E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:7139–7143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gasset M, Baldwin M A, Lloyd D, Gabriel J-M, Holtzman D M, Cohen F, Fletterick R, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:10940–10944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nguyen J, Baldwin M A, Cohen F E, Prusiner S B. Biochemistry. 1995;34:4186–4192. doi: 10.1021/bi00013a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rogers M, Serban D, Gyuris T, Scott M, Torchia T, Prusiner S B. J Immunol. 1991;147:3568–3574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rogers M, Yehiely F, Scott M, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:3182–3186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Scott M R, Köhler R, Foster D, Prusiner S B. Protein Sci. 1992;1:986–997. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barry R A, Prusiner S B. J Infect Dis. 1986;154:518–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kascsak R J, Rubenstein R, Merz P A, Tonna-DeMasi M, Fersko R, Carp R I, Wisniewski H M, Diringer H. J Virol. 1987;61:3688–3693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3688-3693.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Taraboulos A, Rogers M, Borchelt D R, McKinley M P, Scott M, Serban D, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:8262–8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fischer M, Rülicke T, Raeber A, Sailer A, Moser M, Oesch B, Brandner S, Aguzzi A, Weissmann C. EMBO J. 1996;15:1255–1264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Locht C, Chesebro B, Race R, Keith J M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:6372–6376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Taraboulos A, Scott M, Semenov A, Avrahami D, Laszlo L, Prusiner S B. J Cell Biol. 1995;129:121–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vey M, Pilkuhn S, Wille H, Nixon R, DeArmond S J, Smart E J, Anderson R G W, Taraboulos A, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:14945–14949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stahl N, Borchelt D R, Hsiao K, Prusiner S B. Cell. 1987;51:229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yost C S, Lopez C D, Prusiner S B, Myers R M, Lingappa V R. Nature (London) 1990;343:669–672. doi: 10.1038/343669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Priola S A, Caughey B, Race R E, Chesebro B. J Virol. 1994;68:4873–4878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.4873-4878.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Scott M, Groth D, Foster D, Torchia M, Yang S-L, DeArmond S J, Prusiner S B. Cell. 1993;73:979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90275-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Turk E, Teplow D B, Hood L E, Prusiner S B. Eur J Biochem. 1988;176:21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Prusiner S B, Groth D F, Cochran S P, Masiarz F R, McKinley M P, Martinez H M. Biochemistry. 1980;19:4883–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang Z, Prusiner S B, Cohen F E. Folding Design. 1996;1:13–19. doi: 10.1016/S1359-0278(96)00007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Doh-ura K, Tateishi J, Sasaki H, Kitamoto T, Sakaki Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;163:974–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hsiao K, Baker H F, Crow T J, Poulter M, Owen F, Terwilliger J D, Westaway D, Ott J, Prusiner S B. Nature (London) 1989;338:342–345. doi: 10.1038/338342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kitamoto T, Amano N, Terao Y, Nakazato Y, Isshiki T, Mizutani T, Tateishi J. Ann Neurol. 1993;34:808–813. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Goldfarb L G, Brown P, McCombie W R, Goldgaber D, Swergold G D, Wills P R, Cervenáková L, Baron H, Gibbs C J J, Gajdusek D C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:10926–10930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Poulter M, Baker H F, Frith C D, Leach M, Lofthouse R, Ridley R M, Shah T, Owen F, Collinge J, Brown G, Hardy J, Mullan M J, Harding A E, Bennett C, Doshi R, Crow T J. Brain. 1992;115:675–685. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.3.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Goldfarb L G, Brown P, Little B W, Cervenáková L, Kenney K, Gibbs C J, Jr, Gajdusek D C. Neurology. 1993;43:2392–2394. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.11.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hsiao K K, Scott M, Foster D, Groth D F, DeArmond S J, Prusiner S B. Science. 1990;250:1587–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.1980379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kocisko D A, Come J H, Priola S A, Chesebro B, Raymond G J, Lansbury P T, Jr, Caughey B. Nature (London) 1994;370:471–474. doi: 10.1038/370471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Caughey B, Kocisko D A, Raymond G J, Lansbury P T., Jr Chem Biol. 1995;2:807–817. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kaneko K, Peretz D, Pan K-M, Blochberger T, Wille H, Gabizon R, Griffith O H, Cohen F E, Baldwin M A, Prusiner S B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:11160–11164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.11160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gabizon R, McKinley M P, Groth D F, Kenaga L, Prusiner S B. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:4950–4955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.McKinley M P, Meyer R, Kenaga L, Rahbar F, Cotter R, Serban A, Prusiner S B. J Virol. 1991;65:1440–1449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1340-1351.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wille H, Zhang G-F, Baldwin M A, Cohen F E, Prusiner S B. J Mol Biol. 1996;259:608–621. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cohen F E, Pan K-M, Huang Z, Baldwin M, Fletterick R J, Prusiner S B. Science. 1994;264:530–531. doi: 10.1126/science.7909169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Prusiner S B, Scott M, Foster D, Pan K-M, Groth D, Mirenda C, Torchia M, Yang S-L, Serban D, Carlson G A, Hoppe P C, Westaway D, DeArmond S J. Cell. 1990;63:673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90134-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Telling G C, Scott M, Mastrianni J, Gabizon R, Torchia M, Cohen F E, DeArmond S J, Prusiner S B. Cell. 1995;83:79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bessen R A, Marsh R F. J Virol. 1994;68:7859–7868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.7859-7868.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Telling, G. C., Parchi, P., DeArmond, S. J., Cortelli, P., Montagna, P., Gabizon, R., Lugaresi, E., Gambetti, P. & Prusiner, S. B. (1996) Science, in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 59.Williamson R A, Peretz D, Smorodinsky N, Bastidas R, Serban H, Mehlhorn I, DeArmond S J, Prusiner S B, Burton D R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:7279–7282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


