Abstract
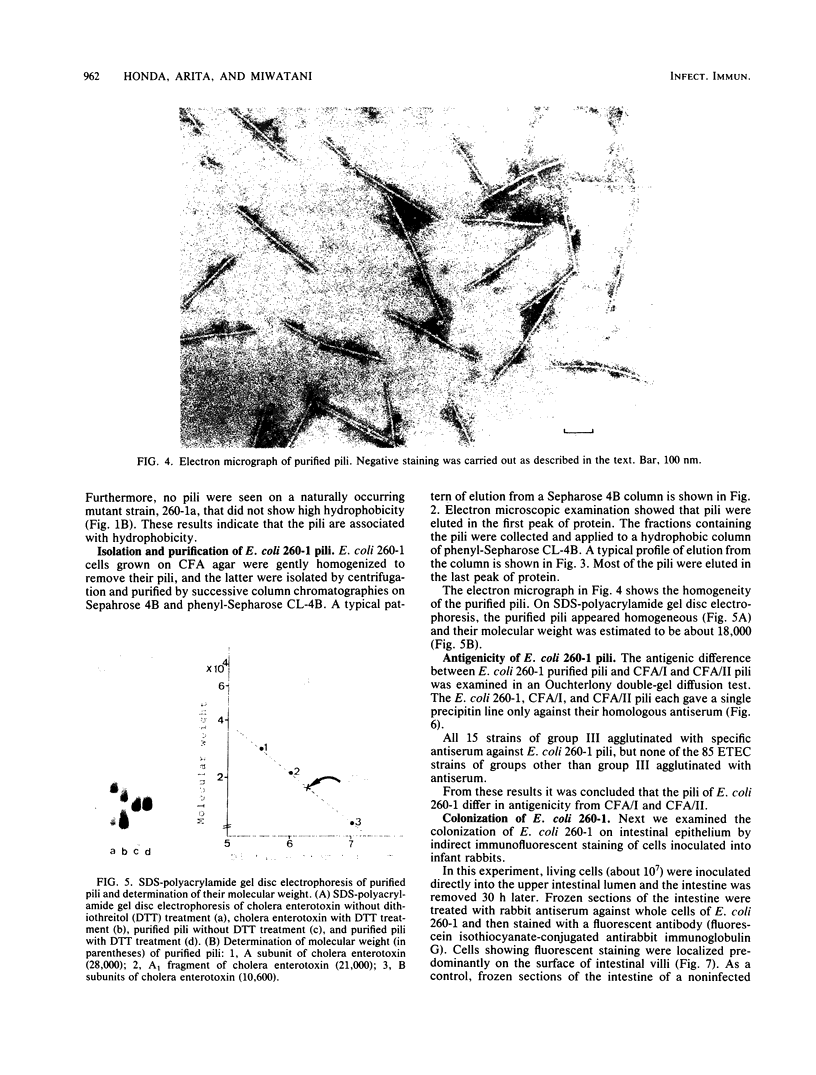
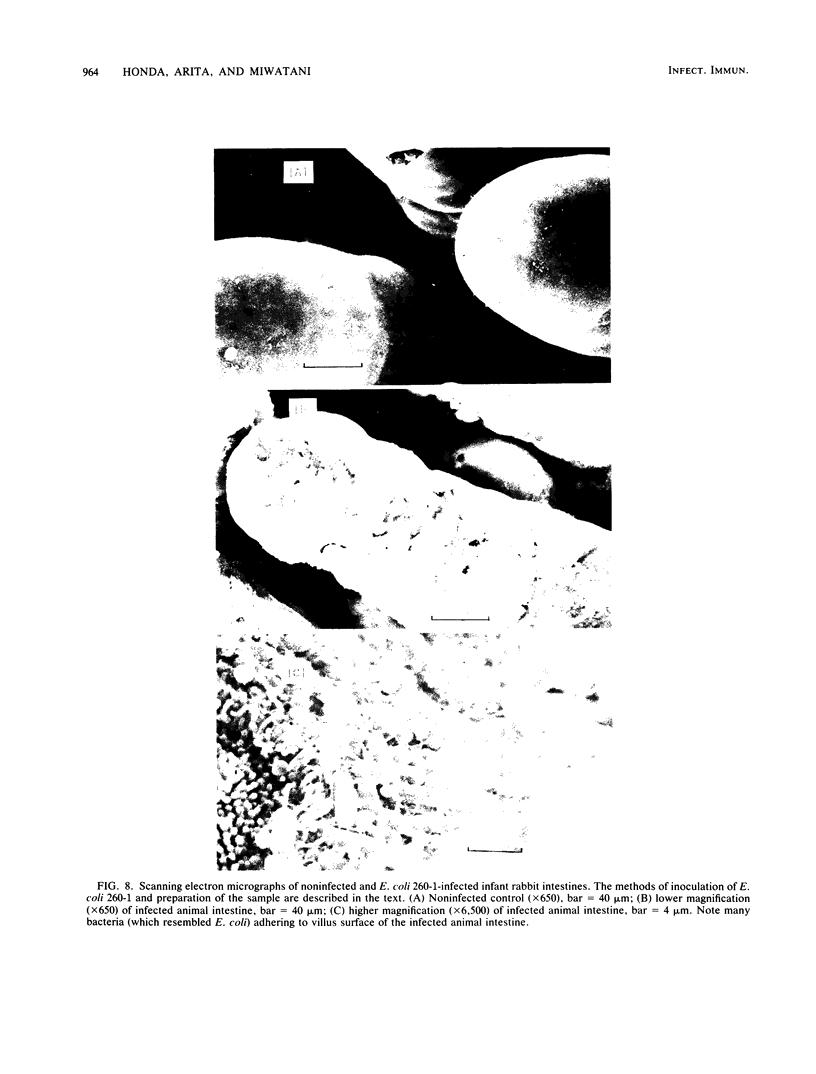
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains were divided into five groups on the basis of their bacterial surface hydrophobicity (Honda et al., FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 17:273-276, 1983). Strains in group III showed heat-stable high hydrophobicity, although they did not show mannose-resistant hemagglutination with either human or bovine erythrocytes. E. coli strain 260-1 in group III was characterized. Electron microscopic examination revealed the presence of pili on the surface of this strain, but not on that of strain 260-1a, which is a mutant of 260-1 showing low hydrophobicity. When strain 260-1 was grown at 18 degrees C, it did not produce pili or show high hydrophobicity. On homogenization of strain 260-1 grown at 37 degrees C the high hydrophobicity and the pili on its surface were lost. These results indicate that the pili of strain 260-1 are associated with the hydrophobicity. Strain 260-1 pili were purified to homogeneity by successive column chromatographies on Sepharose 4B and phenyl-Sepharose CL-4B. Their molecular weight was estimated to be about 18,000. An antigenic difference between purified pili of strain 260-1 and colonization factor antigens I and II was demonstrated. The colonization ability of E. coli 260-1 was shown by animal experiments on suckling mice and infant rabbits. From these results it is concluded that the pili of strains in group III of human enterotoxigenic E. coli, which may play a role in colonization, are of a new type.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Whitehead J. S., Kim Y. S. Interaction of Escherichia coli K88 antigen with porcine intestinal brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):897–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.897-901.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Gorbach S. L. Attachment pili from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):362–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.362-368.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Gorbach S. L. Serotypes of attachment pili of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1254–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1254-1260.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S., Pauley J. A. Purification and characterization of the CFA/I antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.738-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Akhtar Q., Glass R. I., Kibriya A. K. A simple assay to detect Escherichia coli producing heat labile enterotoxin: results of a field study of the Biken tests in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):609–610. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Further evaluation of the Biken test (modified Elek test) for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing heat-labile enterotoxin and application of the test to sampling of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):60–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.60-62.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Selection and characteristics of a Vibrio cholerae mutant lacking the A (ADP-ribosylating) portion of the cholera enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial colonization factor CFA/1 protein from human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Purification, characterization and N-terminal sequence. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Primary structure of the CFA1 fimbrial protein from human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):339–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hjertén S. A new test based on 'salting out' to measure relative surface hydrophobicity of bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R. The interaction of the K88 antigen with porcine intestinal epithelial cell brush borders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 1;632(2):326–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. V., Cravioto A., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. New fimbrial antigenic type (E8775) that may represent a colonization factor in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1119–1124. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1119-1124.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Faris A., Freer J., Habte D., Hallberg D., Ljungh A. Hydrophobic surface properties of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) with different colonization factors (CFA/i, CFA/ii, K88 and K99) and attachment to intestinal epithelial cells. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevers P., Picken R., Schmidt G., Jann B., Jann K., Golecki J. R., Kist M. Characterization of pili associated with Escherichia coli O18ac. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.685-691.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]