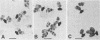Abstract
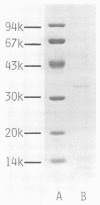
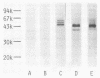
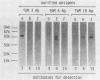
Monoclonal antibodies (TpM 3, TpM 6, and TpM 19) against Toxoplasma gondii insoluble antigens were produced by the hybridization of NS-1, a mouse myeloma cell line, with spleen cells from mice immunized with T. gondii insoluble antigens. TpM 3, TpM 6, and TpM 19 were characterized by the dye test, the latex agglutination test, two types of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, using either T. gondii supernatant antigens or T. gondii insoluble antigens, and immunoperoxidase staining. TpM 3, TpM 6, and TpM 19 antigens were analyzed by the immunoblotting method, using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electrophoretic transfer of the antigens to nitrocellulose sheets. TpM 3, TpM 6, and TpM 19 were all negative by the dye test, the latex agglutination test, and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using T. gondii supernatant antigens but positive by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using T. gondii insoluble antigens. Each antibody gave unique spot patterns in the cytoplasm of tachyzoites, and each detected antigens of ca. 43,000 molecular weight with different electrophoretic patterns. Purified TpM 3 antigen bound only to TpM 3 but not to TpM 6 or TpM 19. Comparable results were obtained with TpM 6 and TpM 19 antigens. Rabbit anti-T. gondii sera reacted with both TpM 3 and TpM 19 antigens. However, human anti-T. gondii sera reacted only with TpM 3 antigen. These results indicate that T. gondii insoluble antigens contained at least three types of 43,000-molecular-weight antigens that have been revealed for the first time in this paper.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Handman E., Remington J. S. Use of monoclonal antibodies to detect antigens of Toxoplasma gondii in serum and other body fluids. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):12–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.12-16.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Kobayashi A. Toxoplasma gondii: electron microscopic study on the dye test reaction. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Oct;40(2):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Kamei K., Fujita T., Shioiri-Nakano K., Tsunematsu Y. Purification of Toxoplasma antigen for hemagglutination tests. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Nov;18(6):892–901. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1969.18.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W., Remington J. S. Detection and characterization of membrane antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2578–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Remington J. S. Serological and immunochemical characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Balfour A. H. An investigation of the antigenic structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Autumn;3(3):235–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Van Knapen F., Atkinson H. J., Balfour A. H., Lee D. L. A new soluble antigen preparation of Toxoplasma gondii and its use in serological diagnosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):239–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., LUNDE M. N. A hemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., McDonald P. J., Neoh S. H. Molecular weight analysis of the major polypeptides and glycopeptides of Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):934–943. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper L. H., Crabb J. H., Pfefferkorn E. R. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody-resistant antigenic mutant of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1694–1699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper L. H., Crabb J. H., Pfefferkorn E. R. Purification of a major membrane protein of Toxoplasma gondii by immunoabsorption with a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubayashi H., Akao S. Immuno-electron microscopic studies on toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jul;15(4):486–491. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for detection of monoclonal antibodies: experience with antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Arakawa M., Kasahara T., Shioiri-Nakano K., Hiraoka K. Detection of toxoplasma membrane antigens transferred from SDS-polyacrylamide gel to nitrocellulose with monoclonal antibody and avidin-biotin, peroxidase anti-peroxidase and immunoperoxidase methods. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino N., Yoneda C. The fine structure and mode of division of Toxoplasma gondii. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Feb;75(2):218–227. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.00970050220015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtyseck E., Mehlhorn H. Ultrastructural study of characteristic organelles (paired organelles, micronemes, micropores) of sporozoa and related organisms. Z Parasitenkd. 1970;34(2):97–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00260383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Feldman H. A. Identification of the activator system for antibody to Toxoplasma as the classical complement pathway. J Infect Dis. 1980 Mar;141(3):366–369. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.3.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Endo T., Brandis H. Hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibody with specificity for Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1980 Apr;66(2):192–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Melton M. L. The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1968 Apr;54(2):209–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryon J. C. Toxoplasma gondii: ultrastructure and antigenicity of purified tachyzoite pellicle. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Oct;48(2):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]