Abstract
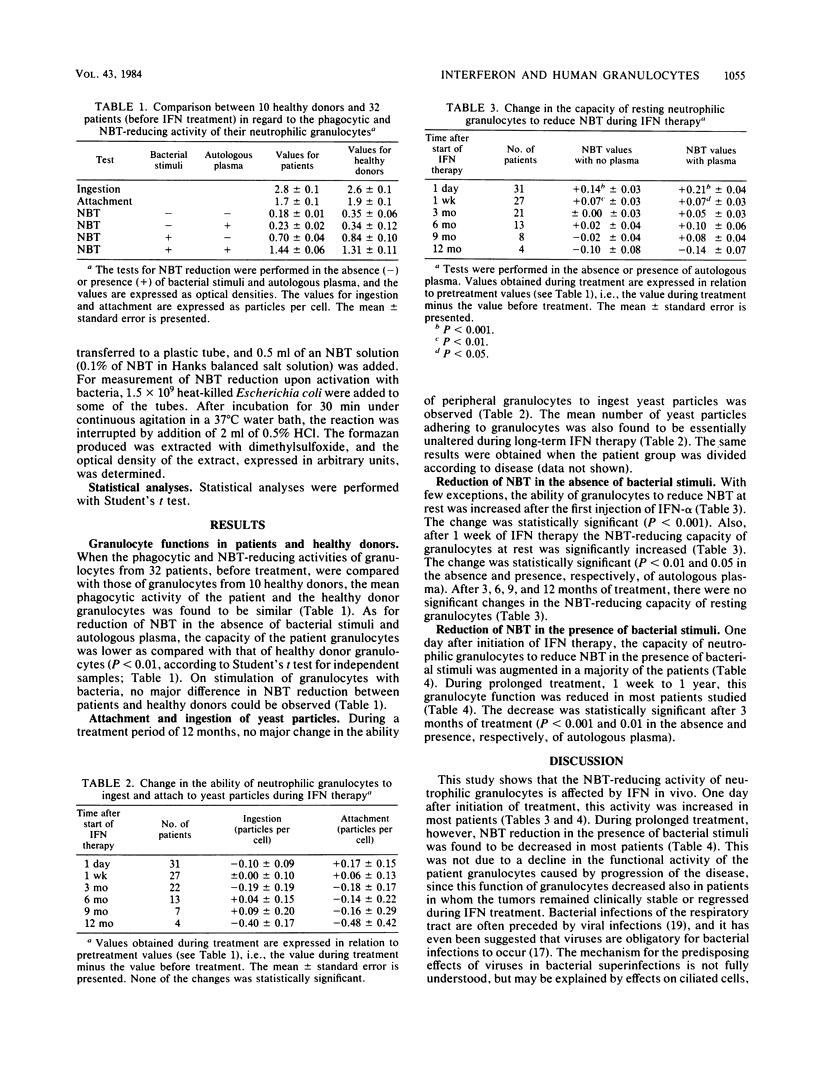
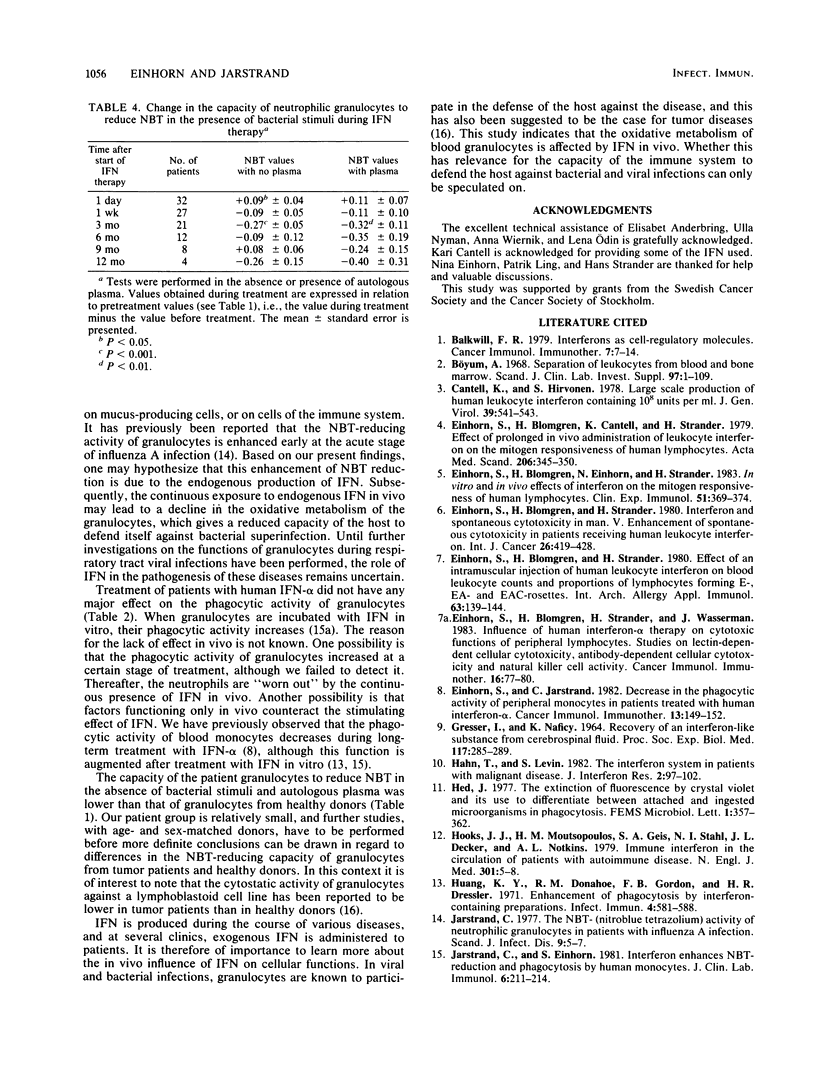
The ability of neutrophilic granulocytes to phagocytize yeast particles and to reduce Nitro Blue Tetrazolium at rest and on activation with bacterial stimuli was monitored in 32 patients receiving treatment with human interferon alpha. The ability of these cells to attach to and ingest yeast particles was not altered to any major extent during 1 year of interferon treatment. In most patients, the Nitro Blue Tetrazolium-reducing activity increased after the first injection of interferon. During prolonged treatment with interferon alpha, 1 week to 1 year, granulocytes activated with bacteria exhibited a reduced Nitro Blue Tetrazolium activity in most patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantell K., Hirvonen S. Large-scale production of human leukocyte interferon containing 10(8) units per ml. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):541–543. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Cantell K., Strander H. Effect of prolonged in vivo administration of leukocyte interferon on the mitogen responsiveness of human lymphocytes. Acta Med Scand. 1979;206(5):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb13525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Einhorn N., Strander H. In vitro and in vivo effects of interferon on the response of human lymphocytes to mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Effect of an intramuscular injection of human leukocyte interferon on blood leukocyte counts and proportions of lymphocytes forming E, EA and EAC rosettes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;63(2):139–144. doi: 10.1159/000232619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Interferon and spontaneous cytotoxicity in man. V. Enhancement of spontaneous cytotoxicity in patients receiving human leukocyte interferon. Int J Cancer. 1980 Oct 15;26(4):419–428. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H., Wasserman J. Influence of human interferon-alpha therapy on cytotoxic functions of blood lymphocytes. Studies on lectin-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and natural killer cell activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;16(2):77–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00199235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Jarstrand C. Decrease in the phagocytic activity of peripheral monocytes in patients treated with human interferon-alpha. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1982;13(3):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00205379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRESSER I., NAFICY K. RECOVERY OF AN INTERFERON-LIKE SUBSTANCE FROM CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:285–289. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T., Levin S. The interferon system in patients with malignant disease. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(1):97–102. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Donahoe R. M., Gordon F. B., Dressler H. R. Enhancement of phagocytosis by interferon-containing preparations. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):581–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.581-588.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarstrand C., Einhorn S. Effect of interferon on human neutrophilic granulocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;16(2):123–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00199244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarstrand C., Einhorn S. Interferon enhances NBT-reduction and phagocytosis by human monocytes. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981 Nov;6(3):211–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarstrand C. The NBT (Nitroblue Tetrazolium) activity of neutrophil granulocytes in patients with influenza A infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(1):5–7. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-1.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepow M. L., Balassanian N., Emmerich J., Roberts R. B., Rosenthal M. S., Wolinsky E. Interrelationships of viral, mycoplasmal, and bacterial agents in uncomplicated pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Apr;97(4):533–545. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S., Hahn T. Evaluation of the human interferon system in viral disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):475–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosli C. G. Synergism between respiratory viruses and bacteria. Yale J Biol Med. 1968 Apr-Jun;40(5-6):522–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAELS R. H., WEINBERGER M. M., HO M. CIRCULATING INTERFERON-LIKE VIRAL INHIBITOR IN PATIENTS WITH MENINGITIS DUE TO HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jun 3;272:1148–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196506032722203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Fikrig S. M., Smithwick E. M. Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils. A diagnostic acid. Lancet. 1968 Sep 7;2(7567):532–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H., Cantell K. Production of interferon by human leukocytes in vitro. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1966;44(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell D. J., Wilbur J. R., Merigan T. C. Interferon production in human mumps infections. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):320–324. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


