Abstract
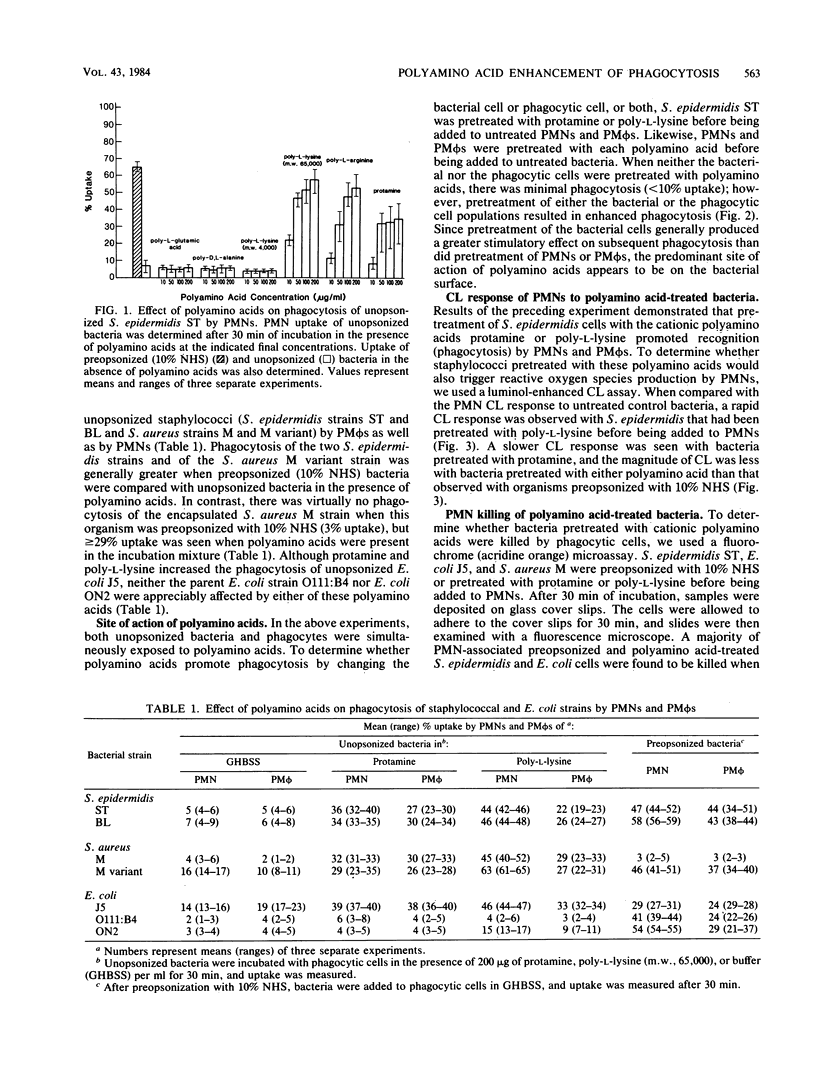
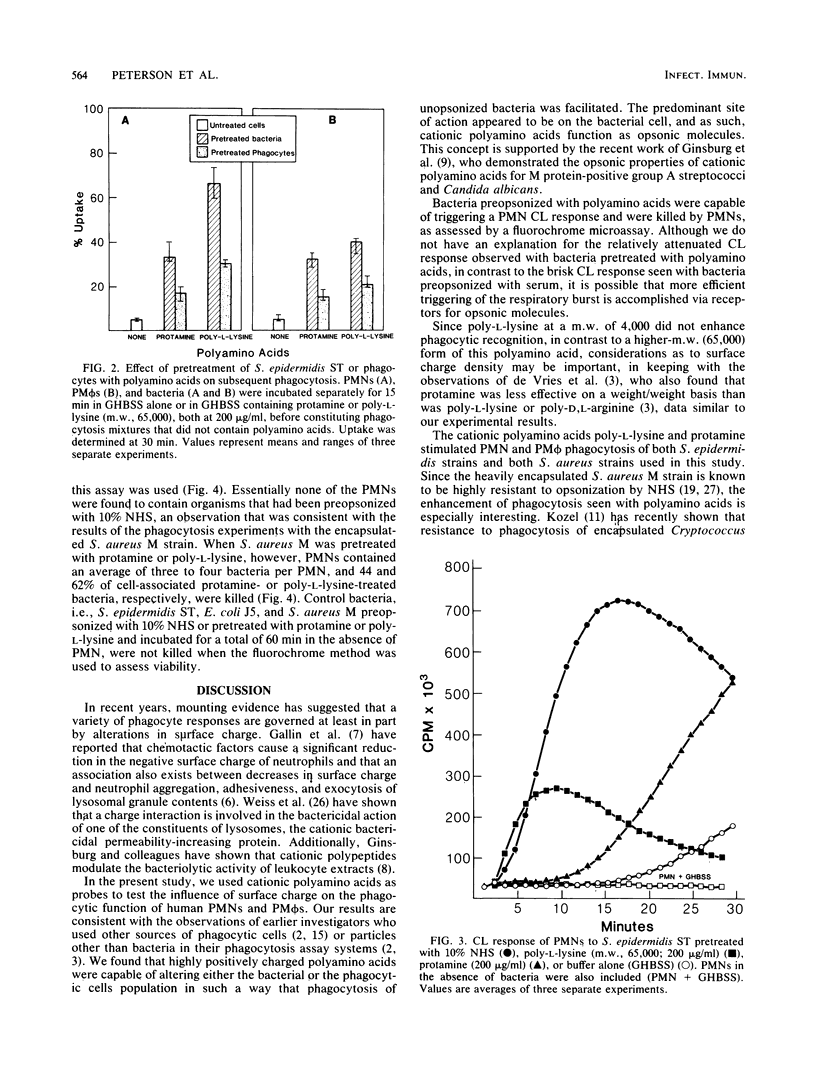
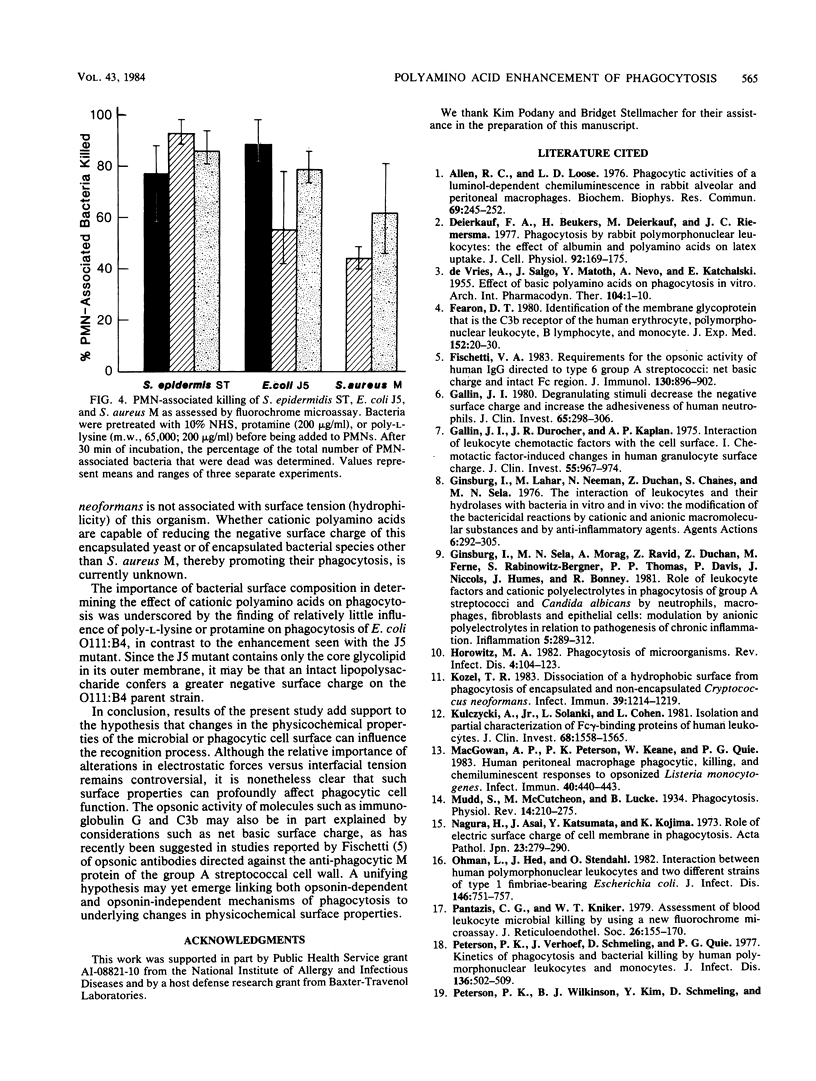
Cationic polyamino acids are known to enhance a variety of cell-cell interactions by virtue of their ability to alter electrostatic forces of cell surfaces. In this study, the effect of polyamino acids on phagocytosis of 3H-labeled bacteria by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and peritoneal macrophages was investigated. Negatively charged and neutral polyamino acids did not influence phagocytosis of unopsonized Staphylococcus epidermidis, whereas protamine, poly-L-arginine, and poly-L-lysine stimulated phagocytosis in a dose-dependent manner. At 50 micrograms/ml, greater than 30% uptake by PMNs was seen with each of these cationic polyamino acids. Although cationic polyamino acids promoted PMN and peritoneal macrophage phagocytosis of unopsonized S. epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus M (encapsulated) and M variant (unencapsulated), and Escherichia coli J5, little effect was seen with the parent E. coli O111:B4 or a serotype O222:H16 strain. Pretreatment of bacteria and phagocytes separately demonstrated that the phagocytosis-promoting property of polyamino acids is manifest predominantly on the bacteria. Bacteria pretreated with cationic polyamino acids also elicited a PMN chemiluminescent response, and PMN-associated bacteria were killed, as determined by a fluorochrome microassay. Thus, cationic polyamino acids promote the phagocytosis and killing of many but not all bacterial strains, and in this respect polyamino acids function as opsonins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE VRIES A., SALGO J., MATOTH Y., NEVO A., KATCHALSKI E. Effect of basic polyamino acids on phagocytosis in vitro. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1955 Nov 1;104(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deierkauf F. A., Beukers H., Deierkauf M., Riemersma J. C. Phygocytosis by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes: the effect of albumin and polyamino acids on latex uptake. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Aug;92(2):169–175. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Requirements for the opsonic activity of human IgG directed to type 6 group A streptococci: net basic charge and intact Fc region. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):896–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli decrease the neagative surface charge and increase the adhesiveness of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI109672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Durocher J. R., Kaplan A. P. Interaction of leukocyte chemotactic factors with the cell surface. I. Chemotactic factor-induced changes in human granulocyte surface charge. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):967–974. doi: 10.1172/JCI108026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Lahav M., Ne'eman N., Duchan Z., Chanes S., Sela M. N. The interaction of leukocytes and their hydrolases with bacteria in vitro and in vivo: the modification of the bactericidal and bacteriolytic reactions by cationic and anionic macromolecular substances and by anti-inflammatory agents. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):292–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01972246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Sela M. N., Morag A., Ravid Z., Duchan Z., Ferne M., Rabinowitz-Bergner S., Thomas P. P., Davies P., Niccols J. Role of leukocyte factors and cationic polyelectrolytes in phagocytosis of group A streptococci and Candida albicans by neutrophils, macrophages, fibroblasts and epithelial cells: modulation by anionic polyelectrolytes in relation to pathogenesis of chronic inflammation. Inflammation. 1981 Dec;5(4):289–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00911094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R. Dissociation of a hydrophobic surface from phagocytosis of encapsulated and non-encapsulated cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1214–1219. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1214-1219.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Solanki L., Cohen L. Isolation and partial characterization of Fc gamma-binding proteins of human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1558–1565. doi: 10.1172/JCI110410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGowan A. P., Peterson P. K., Keane W., Quie P. G. Human peritoneal macrophage phagocytic, killing, and chemiluminescent responses to opsonized Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):440–443. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.440-443.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Asai J., Katsumata Y., Kojima K. Role of electric surface charge of cell membrane in phagocytosis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1973 May;23(2):279–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1973.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman L., Hed J., Stendahl O. Interaction between human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and two different strains of type 1 fimbriae-bearing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis C. G., Kniker W. T. Assessment of blood leukocyte microbial killing by using a new fluorochrome microassay. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Aug;26(2):155–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and bacterial killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):502–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Rommel F. A rapid micro method for the simultaneous determination of phagocytic-microbiocidal activity of human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Hoidal J. R., Nguyen B. Y., Verhoef J., Quie P. G., Peterson P. K. Human alveolar macrophage cytophilic immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis of protein A-positive staphylococci. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):63–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI110442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Keane W. F., Hoidal J. R., Freiberg M. R., Elliott G. R., Peterson P. K. Peritoneal macrophages and opsonins: antibacterial defense in patients undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Human polymorphonuclear leucocyte receptors for staphylococcal opsonins. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):231–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Victor M., Elsbach P. Role of charge and hydrophobic interactions in the action of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of neutrophils on gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):540–549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


