Abstract
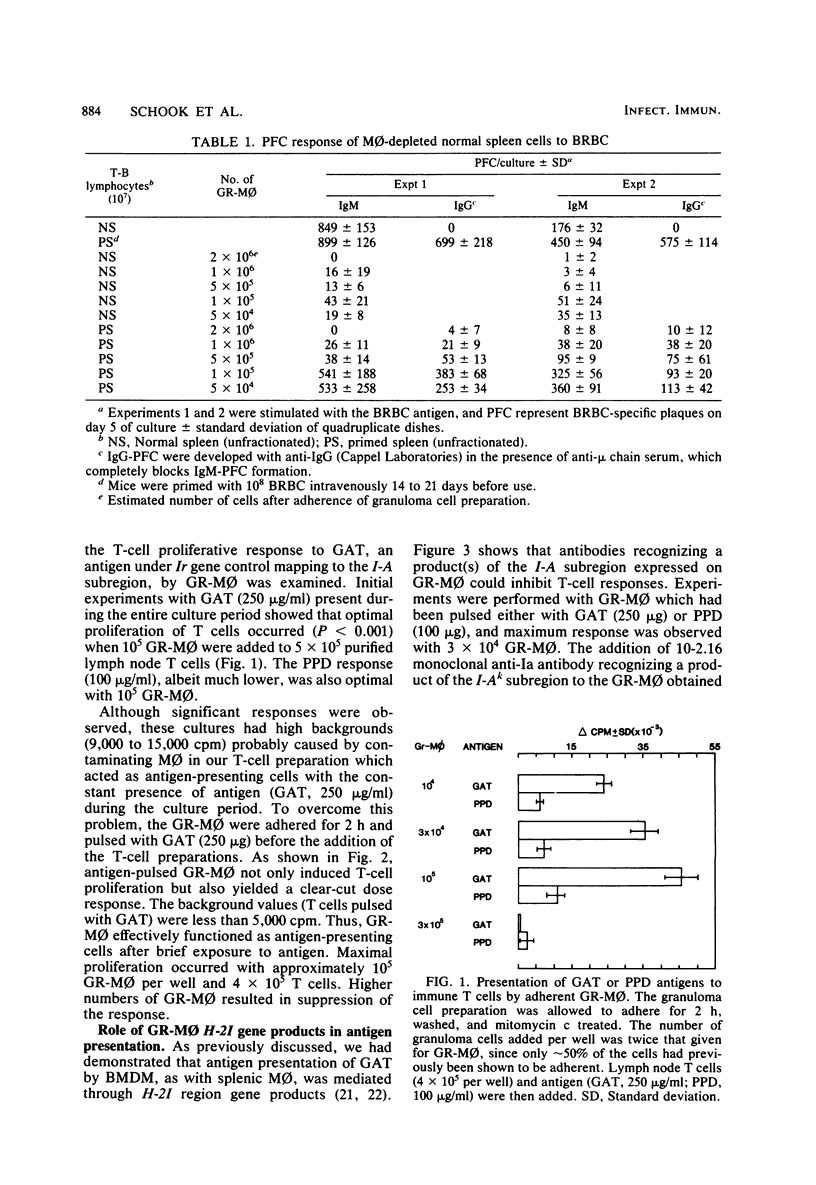
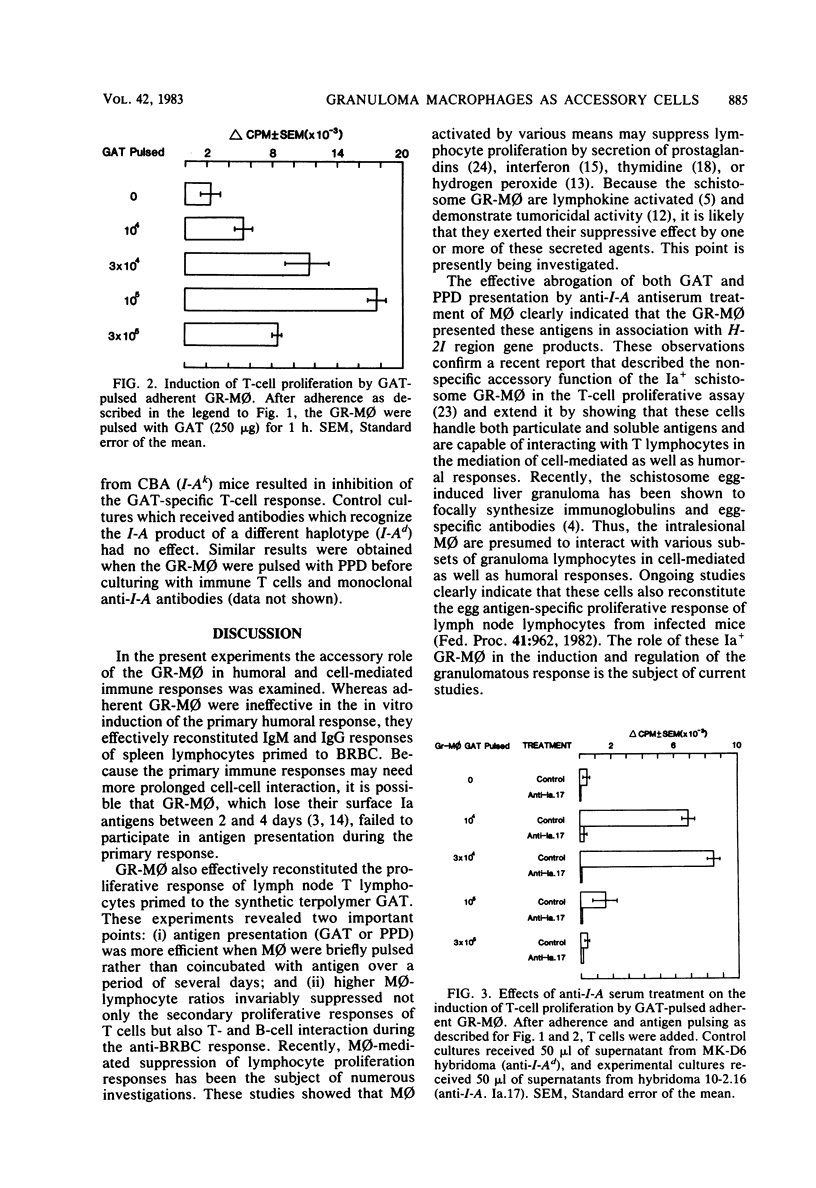
In murine schistosomiasis mansoni, the inflammatory macrophage comprises 30% of the granuloma which forms around parasite eggs in the tissue. These granuloma macrophages (GR-Mphi) displayed dense Fc and C3 receptors, and about 50% expressed H-2I region-encoded determinants (Ia antigens). These GR-Mphi were able to effectively reconstitute the burro erythrocyte-specific immunoglobulin M and G antibody response of primed macrophage-depleted spleen cells. However, in contrast to splenic macrophages, GR-Mphi gave only minimal reconstitution of the primary immunoglobulin M response. The reconstitution of the T-cell proliferative response to L-glutamic60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10, an antigen under Ir gene control, was also observed when GR-Mphi were added to purified lymph node T-cells. The addition of a monoclonal antibody recognizing a determinant on the Ia complex effectively blocked L-glutamic60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 presentation by GR-Mphi. These studies demonstrated that inflammatory GR-Mphi could function as antigen-presenting cells and that this accessory function was mediated by H-2I region gene products.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsden A. F., Boros D. L. Fc-receptor-bearing macrophages isolated from hypersensitivity and foreign-body granulomas. Delineation of macrophage dynamics, fc receptor density/avidity and specificity. Am J Pathol. 1979 Aug;96(2):457–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Amsden A. F., Hood A. T. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. IV. Immunoglobulin and antibody production by vigorous and immunomodulated liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1050–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Granulomatous inflammations. Prog Allergy. 1978;24:183–267. doi: 10.1159/000401230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S., Pelley R. P. The secretion of migration inhibitory factor by intact schistosome egg granulomas maintained in vitro. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):224–226. doi: 10.1038/246224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Etlinger H. M., Chiller J. M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing C., Pincus S. H., Sachs D. H., Dickler H. B. A subpopulation of adherent accessory cells bearing both I-A and I-E or C subregion antigens is required for antigen-specific murine T lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1680–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Macrophage-T cell interactions involving Listeria monocytogenes--role of the H-2 gene complex. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2395–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K., NORDIN A. A. Plaque formation in agar by single antibody-producing cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Toews G. B., Lyons C. R., Uhr J. W. Antigen presentation by guinea pig alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless S. E., Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L., Heppner G. H. Tumoricidal macrophages isolated from liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):284–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann C., Sorg C. Immune interferon. I. Production by lymphokine-activated murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):719–725. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederhuber J. E., Allen P., Mayo L. The expression of Ia antigenic determinants on macrophages required for the in vitro antibody response. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1342–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederhuber J. E. The role of I region gene products in macrophage - T lymphocyte interaction. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:28–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz H. G., Niethammer D., Jackson R. C., Lemke H., Huget R., Flad H. D. Biochemical characterization of a factor released by macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jul;18(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Klingenstein R. J., Richman J. A., Strober W., Berzofsky J. A. The murine Kupffer cell. I. Characterization of the cell serving accessory function in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schook L. B., Allen P. M., Niederhuber J. E. Bone marrow-derived macrophage as accessory cells in antigen-induced T cell proliferation. H-2I region requirements for L-glutamic60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 response. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):661–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schook L. B., Bingham E. L., Gutmann D. H., Niederhuber J. E. Characterization and expression of H-21 region gene products on bone marrow-derived macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):991–997. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Wyler D. J., Wright J. A. Ia antigen expression and antigen-presenting function by macrophages isolated from hypersensitivity granulomas. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2739–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Parker C. W. Prostaglandins, macrophages, and immunity. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine G. H., Katz D. R., Feldmann M. Dendritic cells induce T cell proliferation to synthetic antigens under Ir gene control. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1817–1822. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews G. B., Bergstresser P. R., Streilein J. W. Epidermal Langerhans cell density determines whether contact hypersensitivity or unresponsiveness follows skin painting with DNFB. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Domingo E. O., Cowan R. B. Granuloma formation around schistosome eggs as a manifestation of delayed hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):735–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock J. V., Boros D. L. Alteration of granuloma angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity by regulatory T lymphocytes in murine schistosomiasis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):465–470. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.465-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Atrophy of the thymic cortex in mice with granulomatous schistosomiasis mansoni. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1063-1069.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Comparison of Fc, C3 receptors and Ia antigens on the inflammatory macrophage isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of schistosome-infected mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Sep;30(3):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


