Abstract
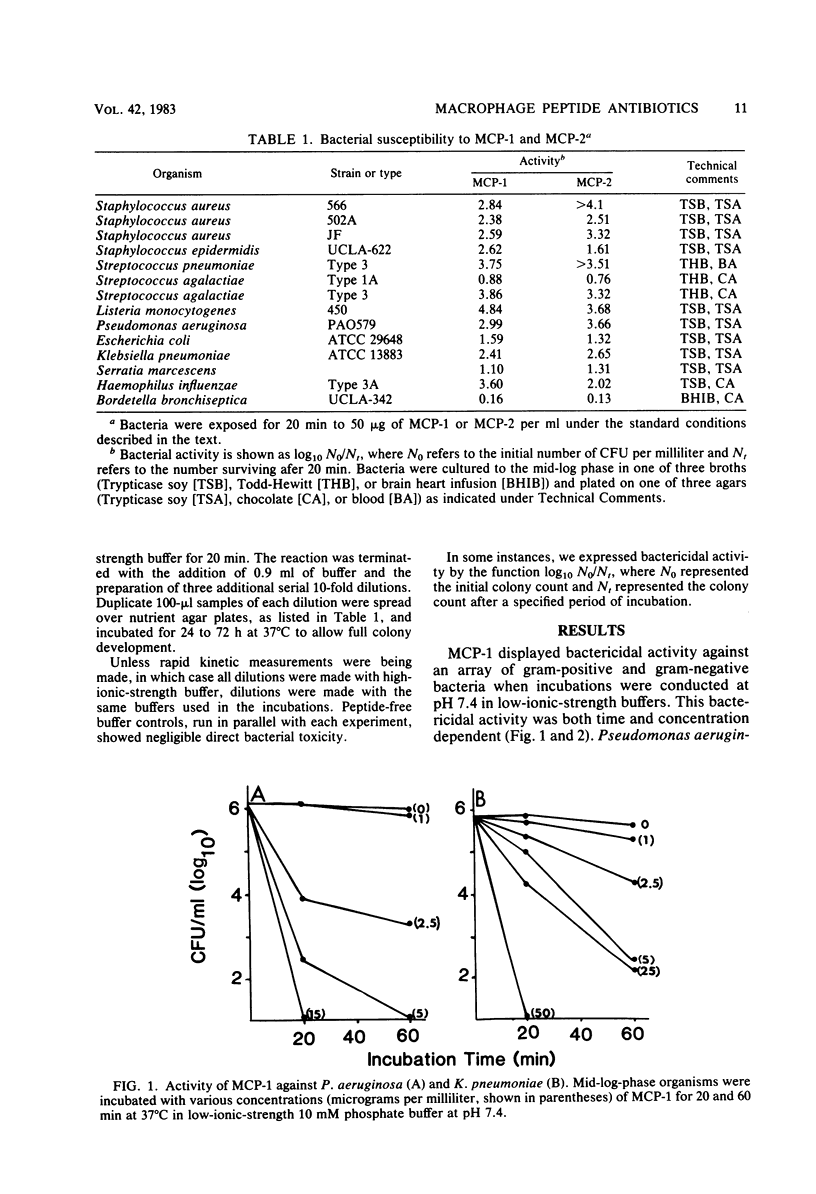
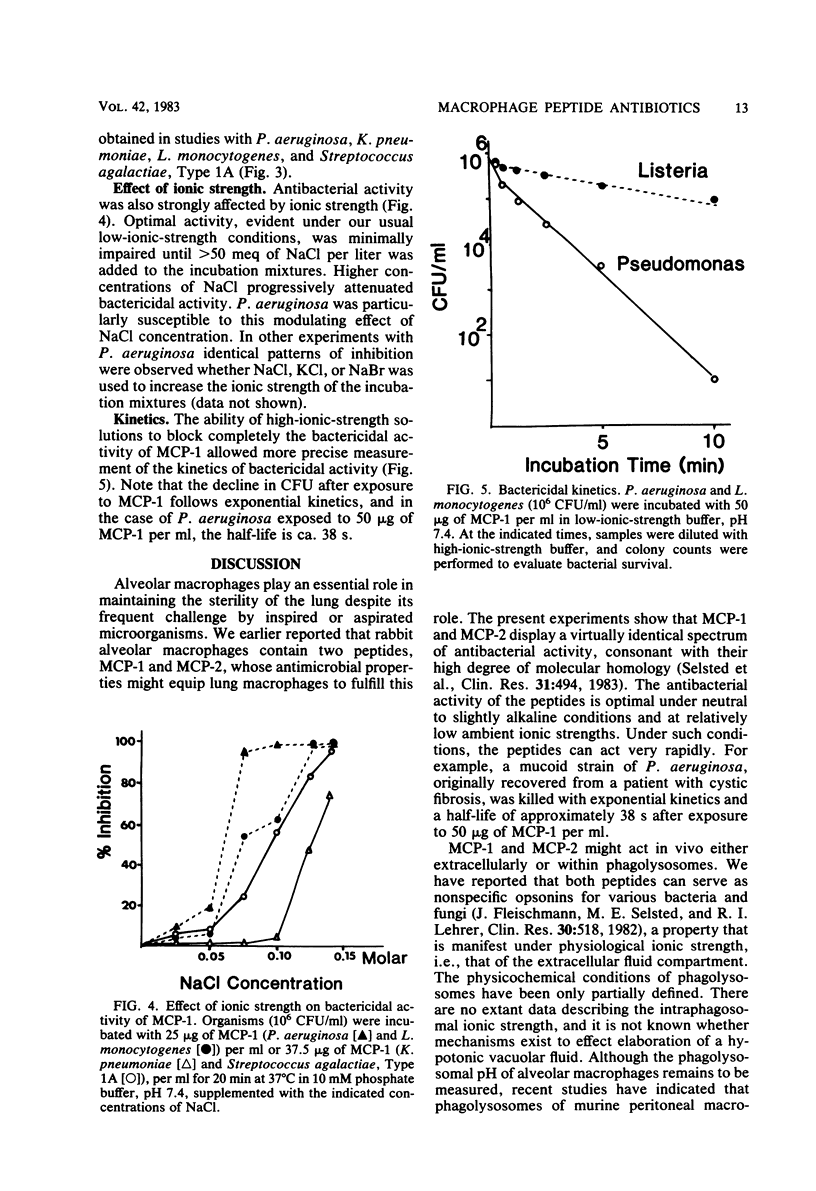
Microbicidal cationic proteins 1 and 2, peptides derived from rabbit lung macrophages, were tested for bactericidal activity against various bacterial species. Both were highly active against diverse gram-positive and gram-negative organisms under conditions of near-neutral pH (between 7 and 8) and relatively low ionic strength. Susceptible species included Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, and Serratia marcescens. Streptococcus agalactiae, type 1A, was less susceptible than the aforementioned organisms or S. agalactiae, type 3. Bordetella bronchiseptica, a common commensal and pathogen of the rabbit respiratory tract, was completely resistant to both peptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geisow M. J., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R. Temporal changes of lysosome and phagosome pH during phagolysosome formation in macrophages: studies by fluorescence spectroscopy. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):645–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E., Fleischmann J. Increased content of microbicidal cationic peptides in rabbit alveolar macrophages elicited by complete Freund adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):775–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.775-778.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T. Resistance of Bordetella pertussis phase I to mucociliary clearance by rabbit tracheal mucous membrane. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Takino T. Scanning electronmicroscopic studies of Bordetella bronchiseptica on the rabbit tracheal mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):159–161. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins in rabbit alveolar macrophages: a potential host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.180-192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Szklarek D., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins of rabbit alveolar macrophages: amino acid composition and functional attributes. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):723–731. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.723-731.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Geisow M., Garcia R., Harper A., Miller R. The respiratory burst of phagocytic cells is associated with a rise in vacuolar pH. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):406–409. doi: 10.1038/290406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


