Abstract
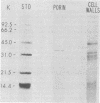
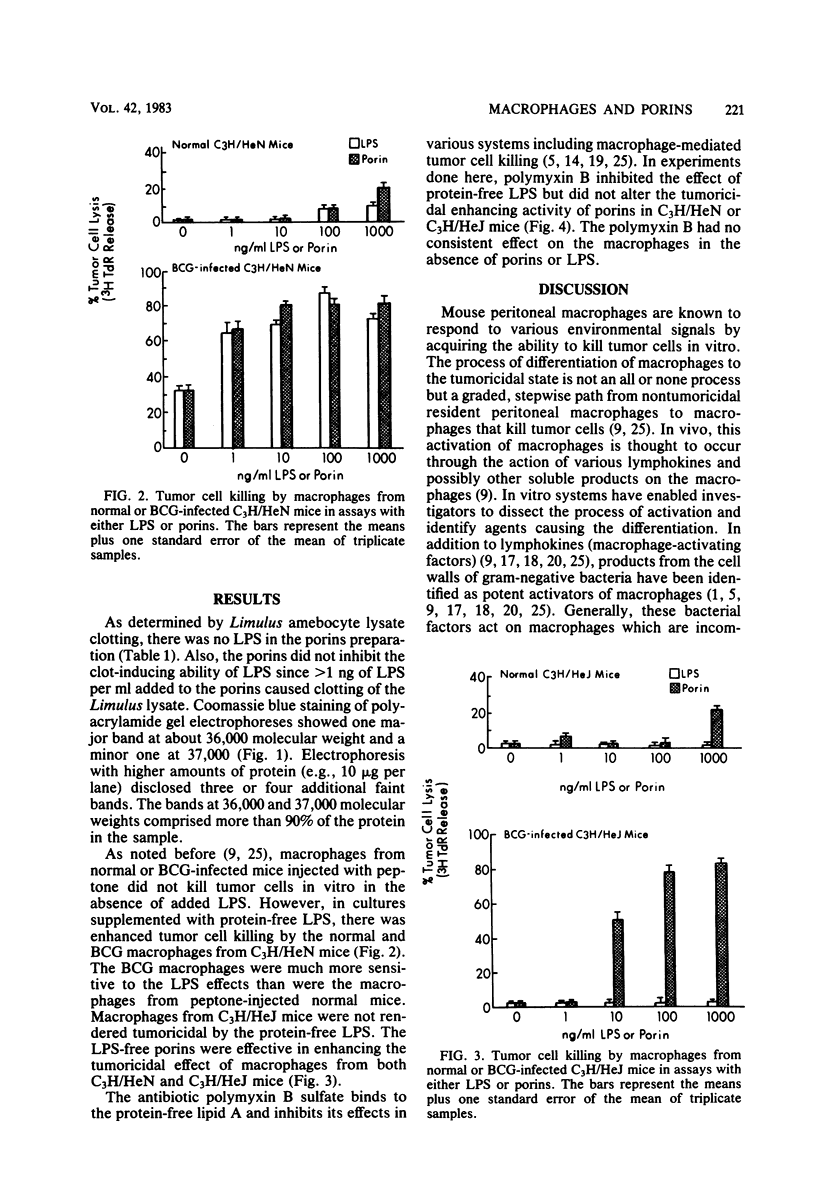
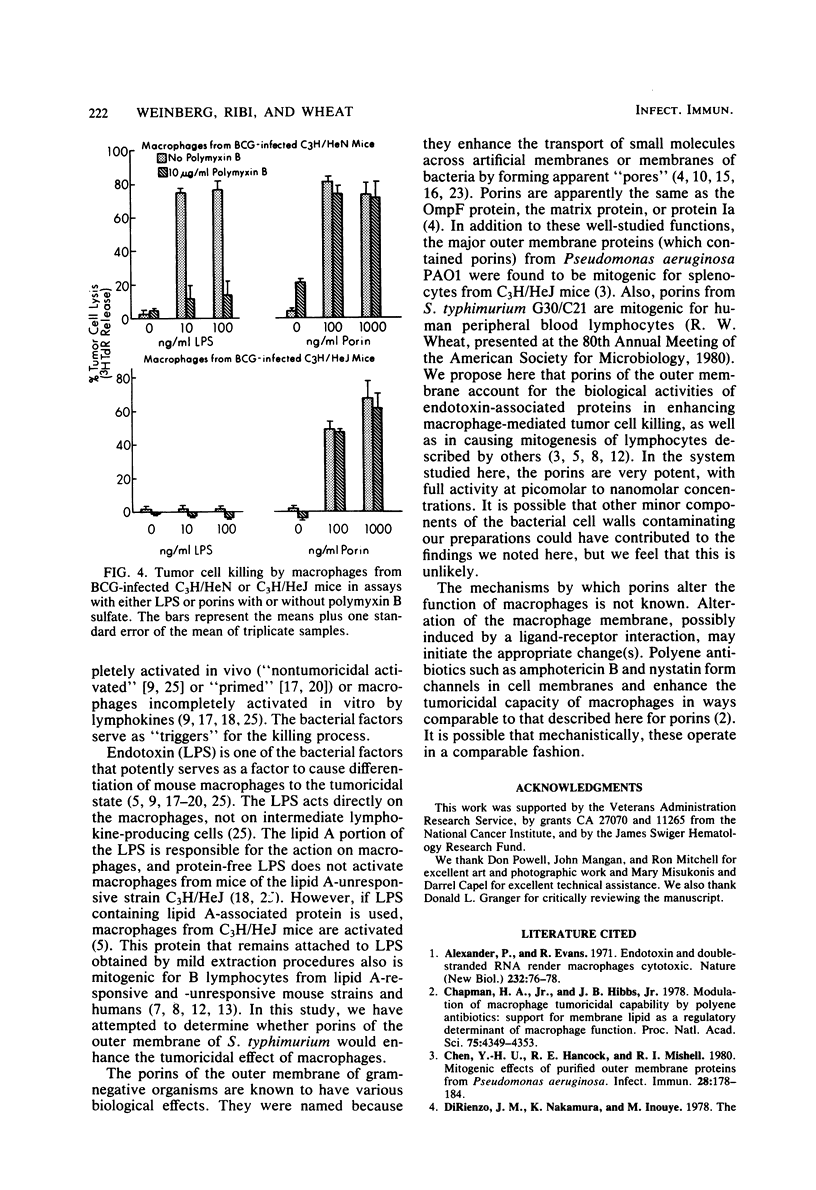
Various microbial products are known to influence the function of mouse peritoneal macrophages. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and certain lipid A-associated proteins are known to enhance the tumoricidal effects of macrophages. The purpose of this study was to determine whether porins (outer membrane proteins) of Salmonella typhimurium G30/C21 would influence the activity of macrophages from lipid A-responsive and -unresponsive mice. Porins, extracted by a combined sodium dodecyl sulfate-EDTA method from cell walls, were free of LPS as determined by Limulus amebocyte lysate assay and appeared as a band at approximately 36,000 molecular weight on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In tumor cell killing assays done under LPS-free conditions, the porins in doses of 1 to 10 ng/ml enhanced the tumoricidal effect of macrophages from bacillus Calmette-Guérin-infected C3H/HeN or C3H/HeJ mice. Protein-free LPS enhanced the tumoricidal activity of macrophages from bacillus Calmette-Guérin-infected C3H/HeN but not C3H/HeJ mice. The tumoricidal-enhancing activity of protein-free LPS was blocked by the lipid A-binding antibiotic polymyxin B sulfate, but the effects of porins were not altered by the polymyxin B sulfate. These results suggest that porins, proteins known to alter membrane function, may alter macrophage function by interaction with macrophage membranes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander P., Evans R. Endotoxin and double stranded RNA render macrophages cytotoxic. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):76–78. doi: 10.1038/newbio232076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Modulation of macrophage tumoricidal capability by polyene antibiotics: support for membrane lipid as a regulatory determinant of macrophage function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Hancock R. E., Mishell R. I. Mitogenic effects of purified outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.178-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Yang S. T., Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. Macrophage stimulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. II. Evidence for differentiation signals delivered by lipid A and by a protein rich fraction of lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., White D., Leive L. Identification of outer membrane proteins, including known lymphocyte mitogens, as the endotoxin protein of Escherichia coli 0111. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1290–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Characterization of the chemical and physical properties of a novel B-lymphocyte activator, endotoxin protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):685–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.685-696.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Endotoxin protein is a mitogen and polyclonal activator of human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):713–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. The macrophage as an antineoplastic surveillance cell: biological perspectives. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):549–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Curry B. J. The use of polymyxin B and C3H/HeJ mouse spleen cells as criteria for endotoxin contamination. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Identification of the outer membrane protein of E. coli that produces transmembrane channels in reconstituted vesicle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Outer membrane of Salmonella. Isolation of protein complex that produces transmembrane channels. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2176–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: development of macrophage cytotoxic activity requires completion of a sequence of short-lived intermediary reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: control of macrophage tumoricidal capacity by the LPS gene. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Doe W. F., McIntosh A. T. Functional characterization of a stable, noncytolytic stage of macrophage activation in tumors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1511–1520. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Effect of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90673-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Ribi E., Cantrell J. L. Isolation of a nontoxic lipid A fraction containing tumor regression activity. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2654–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Okajima Y., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 2. Physical properties of the functional oligomeric aggregates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Characterization of the effects of endotoxin on macrophage tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]