Abstract
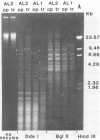
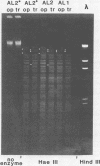
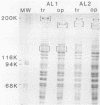
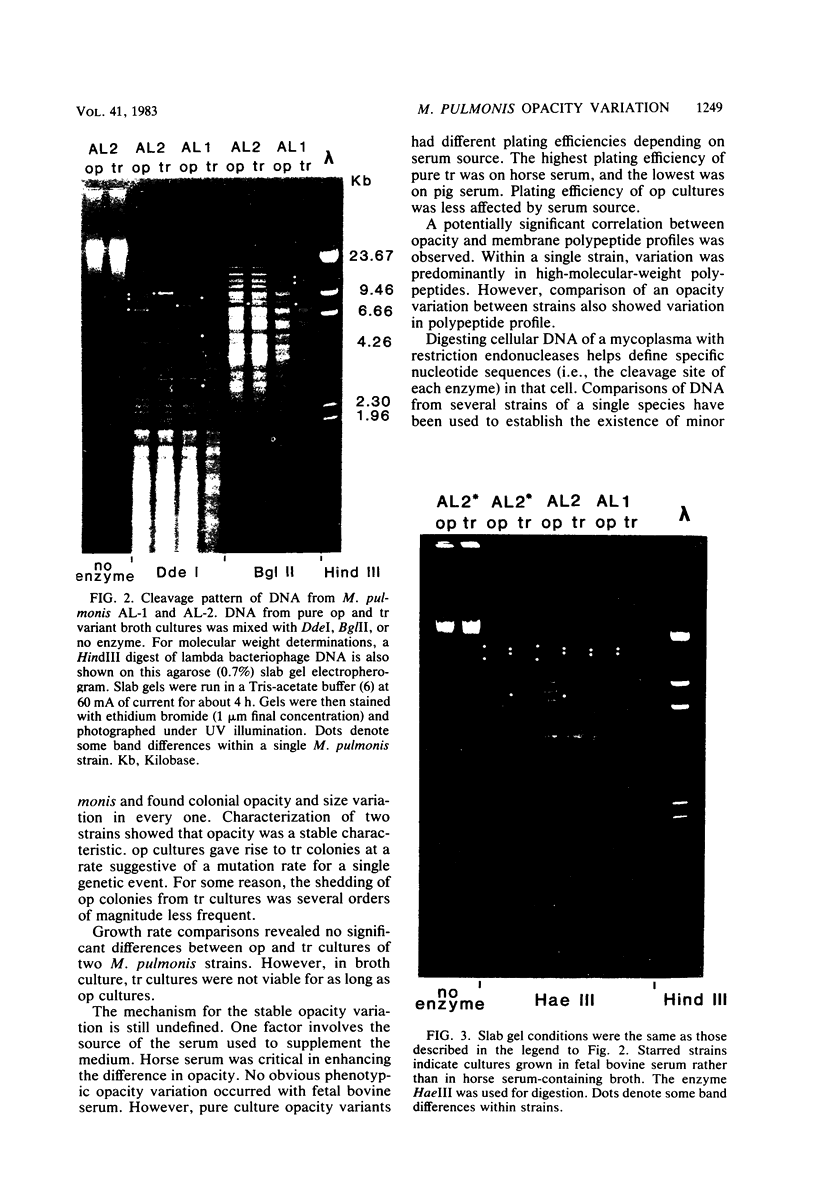
Colonial size and opacity variation were observed in four independently isolated strains of the murine pathogen Mycoplasma pulmonis. Selecting colonial opacity variants of similar size, we identified opaque and transparent stable variants. Opaque colony-derived broth cultures shed transparent colonies at a rate of about 1.2 X 10(-8) per CFU per generation. The reverse conversion was about two orders of magnitude less frequent. Appearance of opacity and plating efficiency of each pure culture were altered by changing the serum source used to supplement the growth medium. Horse or sheep serum was most efficient at accentuating visualization of opacity differences. Fetal bovine serum was least efficient. In two M. pulmonis strains, each opacity variant showed a distinctive polypeptide profile, as displayed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In the same strains, distinctive intrastrain differences were found by agarose gel electrophoresis to display the DNA fragments produced after digestion by several endonucleases. Each pure culture variant retained these differences in DNA even when grown in a medium supplemented with a serum which did not accentuate visualization of the opacity phenotype. Characterization of variants in 30 other M. pulmonis strains is in progress.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anilionis A., Riley M. Conservation and variation of nucleotide sequences within related bacterial genomes: Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):355–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.355-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Razin S., Stephens E. B., Harasawa R., Barile M. F. Genomic and phenotypic analyses of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.604-609.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darai G., Zöller L., Matz B., Delius H., Speck P. T., Flügel R. M. Analysis of Mycoplasma hyorhinis genome by use of restriction endonucleases and by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):788–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.788-794.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterization of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. I. Identification and properties of isolates. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1416–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1416-1424.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw K. A. Electrophoretic patterns of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):493–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw K. A., Fallon R. J. Serological heterogeneity of Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):501–510. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G. Variation in the virulence of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis related to susceptibility to killing by macrophages in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):289–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankiewicz E., Liivak M., Dernuet S. Lysogenic mycobacteria: phage variations and changes in host cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):409–416. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W. Rates in vitro changes of gonococcal colony opacity phenotypes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):481–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.481-485.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Whitcomb R. F., Clark H. F., Williamson D. L. Pathogenic mycoplasmas: cultivation and vertebrate pathogenicity of a new spiroplasma. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.841314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivieso-Garcia A., Rosendal S. Variation in colony size of Mycoplasma mycoides subspecies mycoides isolated form goats. Vet Rec. 1982 May 15;110(20):470–471. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.20.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]