Abstract
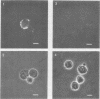
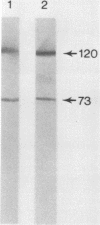
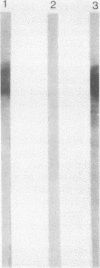
Four antigens of Mycoplasma hyorhinis GDL were defined by murine monoclonal antibodies. Components of broth-grown mycoplasmas were separated under reducing conditions by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and subsequent protein blots were stained with individual antibodies. Each antibody reacted with a distinct component with relative molecular weights of 120,000, 73,000, 51,000, and 38,000, respectively (termed p120, p73, p51, and p38). Trypsin treatment of protein blots specifically abrogated binding of antibodies, suggesting that the epitopes recognized were associated with proteins. By using indirect immunofluorescence and immunoferritin techniques, mycoplasmas colonizing the surface of chronically infected BW5147 murine T-lymphoblastoid cells were selectively stained with antibody to p120, indicating the localization of the corresponding epitope at the mycoplasma surface. Protein blots of mycoplasmas derived from BW5147 cell cultures were stained with antibody to p120, revealing a component identical to that observed with broth-grown organisms. These results establish the identity of a surface protein antigen of M. hyorhinis GDL expressed at the surface of organisms during their colonization of host cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asa P. B., Acton R. T., Cassell G. H., Wise K. S. Identification and characterization of protein antigens of two mycoplasma species. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):997–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER M., LEACH R. H. A MYCOPLASMA WHICH INDUCES ACIDITY AND CYTOPATHIC EFFECT IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:285–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck D. W., Kennett R. H., McGarrity G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for cell culture mycoplasmas. In Vitro. 1982 Apr;18(4):377–381. doi: 10.1007/BF02796338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Cassell G. H., Minion F. C., Wise K. S. Mycoplasma host-cell interactions resulting in chronic inflammation: acquisition of host antigens and other mechanisms. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):633–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Göbel U., Bredt W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin localized to tip structure by monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):765–767. doi: 10.1038/298765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Strominger J. L. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with immunogenic mycoplasma proteins present in human hematopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2734–2738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Weiss R. L. Mycoplasma capping on lymphocytes. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):583–587. doi: 10.1038/276583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., McIntosh M. A., Robbins J., Wise K. S. Cloned genomic DNA sequences from Mycoplasma hyorhinis encoding antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennegoor C., Polak-Vogelzang A. A., Hekman A. Monoclonal antibodies against Mycoplasma hyorhinis. A secondary effect of immunization with cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Cassell G. H., Action R. T. Selective association of murine T lymphoblastoid cell surface alloantigens with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4479–4483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Minion F. C., Cheung H. C. Translocation of Thy-1 antigen and a fluorescent lipid probe during lymphoblastoid cell interaction with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S210–S218. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]