Abstract
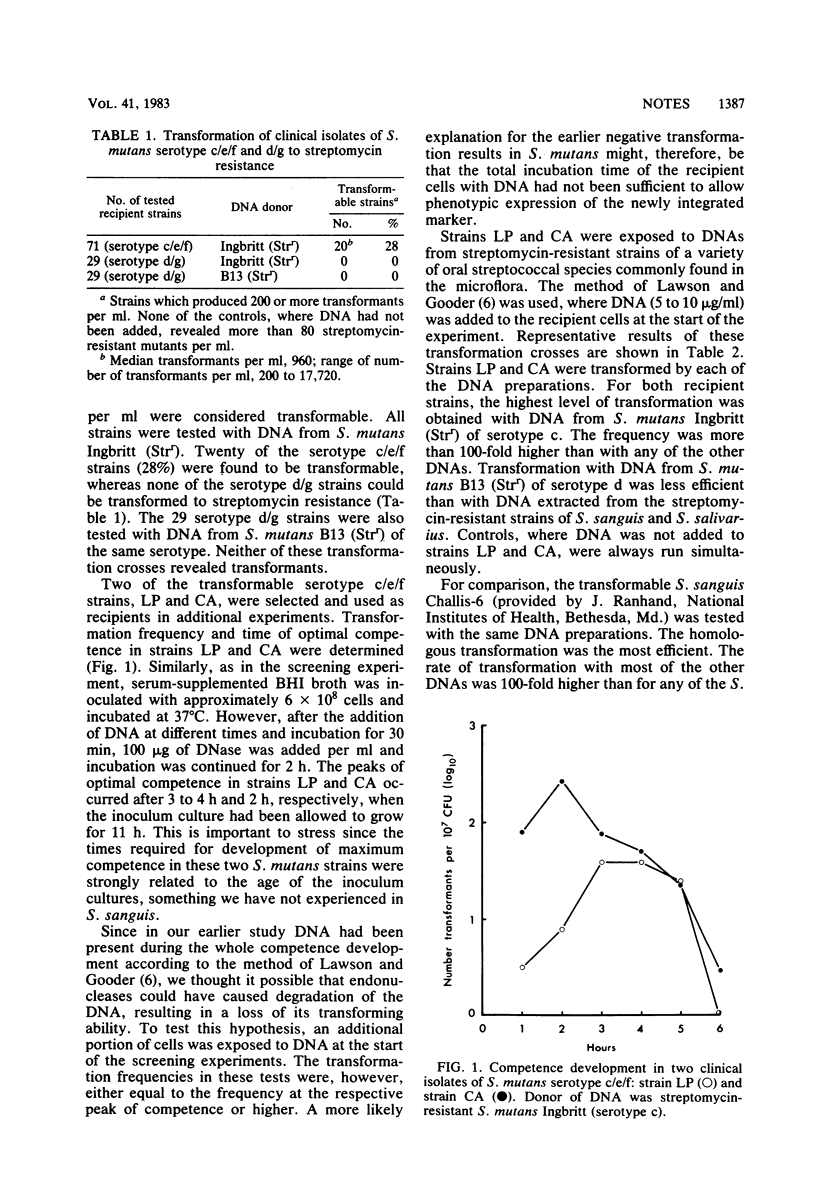
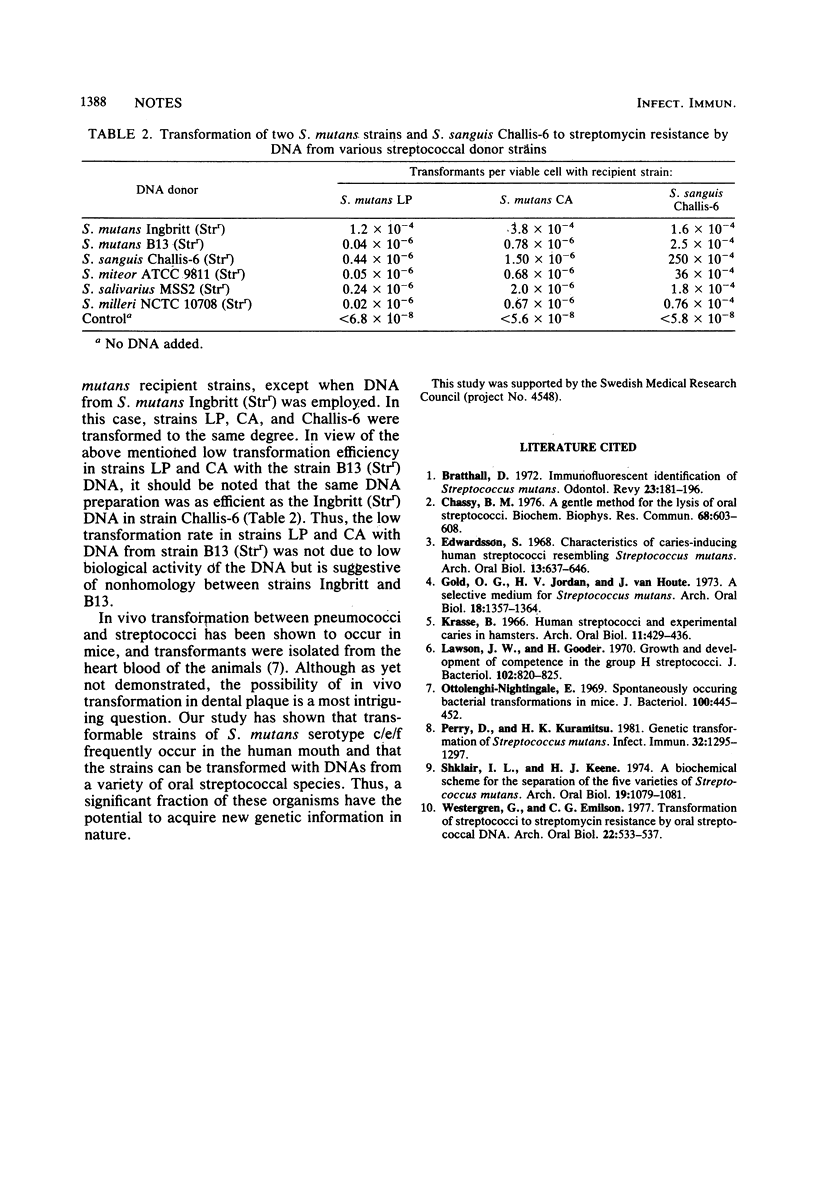
A total of 100 strains of Streptococcus mutans serotypes c/e/f and d/g, freshly isolated from dental plaque, were screened for their ability to undergo genetic transformation to streptomycin resistance. Of the serotype c/e/f strains, 28% were found to be transformable, whereas none of the serotype d/g strains could be transformed by donor DNA from streptomycin-resistant S. mutans strains of either serotype c or d/g. Two of the transformable serotype c/e/f strains were transformed by DNAs from a variety of oral streptococcal species commonly found in the microflora.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Immunofluorescent identification of Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1972;23(2):181–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M. A gentle method for the lysis of oral streptococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardsson S. Characteristics of caries-inducing human streptococci resembling Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):637–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold O. G., Jordan H. V., Van Houte J. A selective medium for Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Nov;18(11):1357–1364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson J. W., Gooder H. Growth and development of competence in the group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):820–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.820-825.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi-Nightingale E. Spontaneously occurring bacterial transformations in mice. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):445–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.445-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Kuramitsu H. K. Genetic transformation of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1295–1297. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1295-1297.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shklair I. L., Keene H. J. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Nov;19(11):1079–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Emilson C. G. Transformation of streptococci to streptomycin resistance by oral streptococcal DNA. Arch Oral Biol. 1977;22(8-9):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(77)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


