Abstract
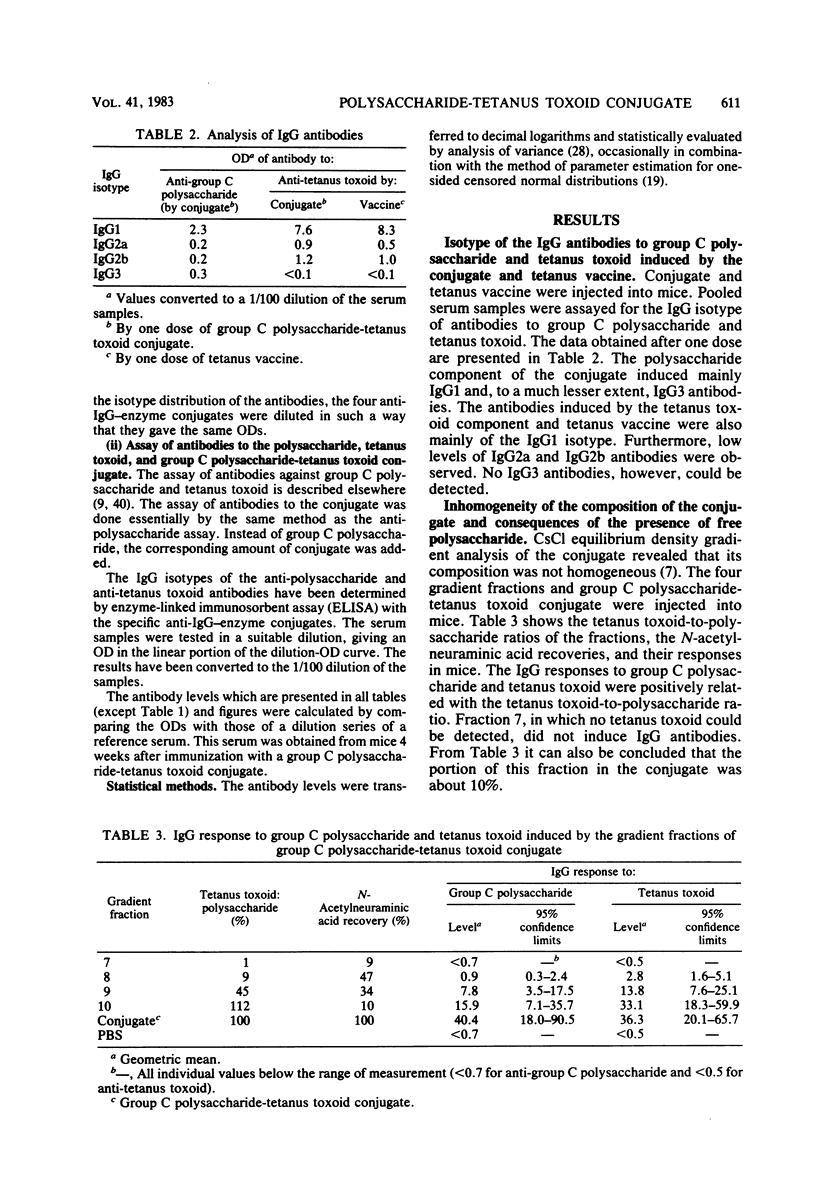
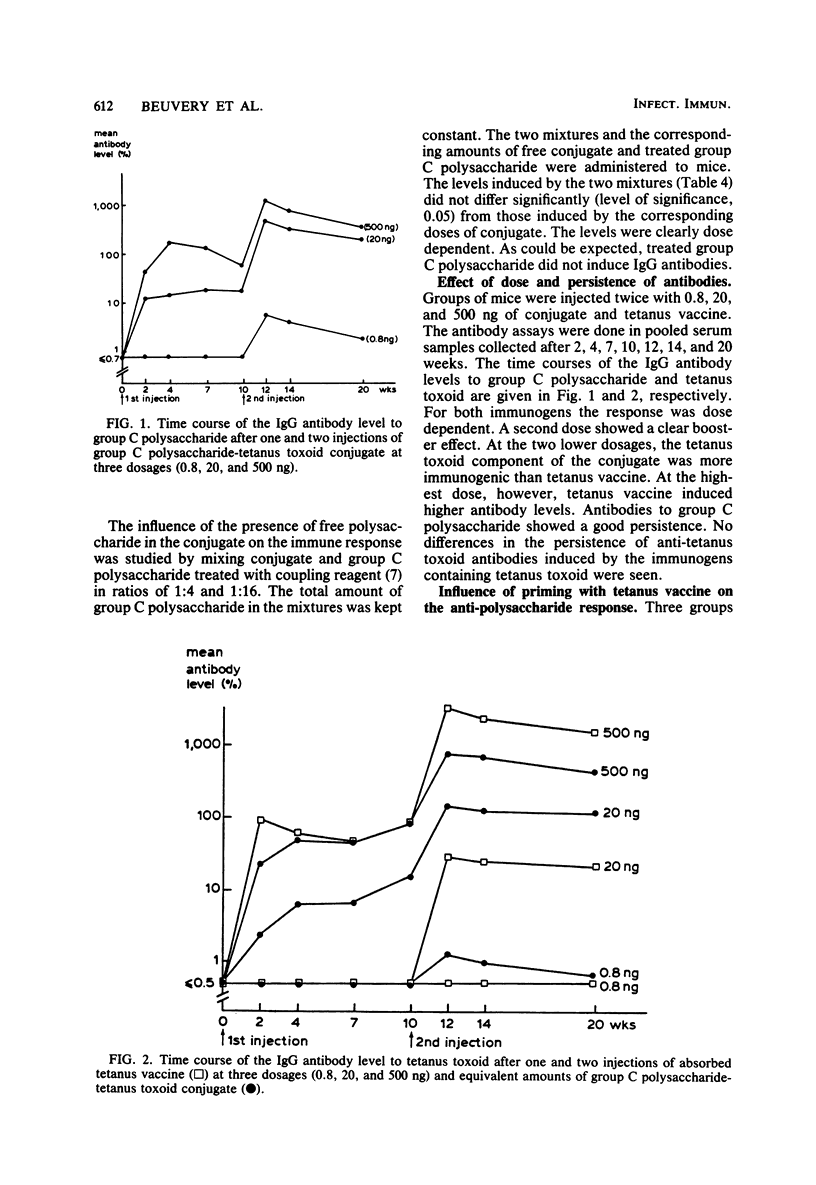
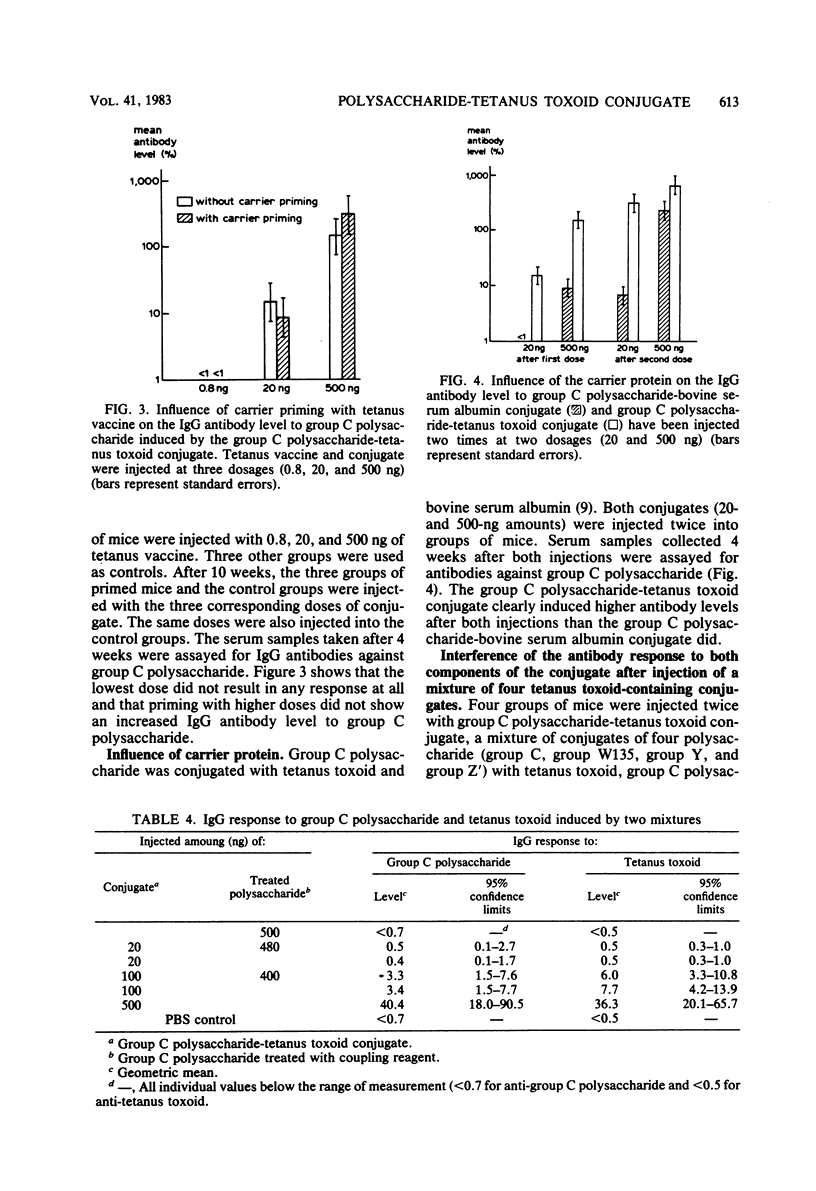
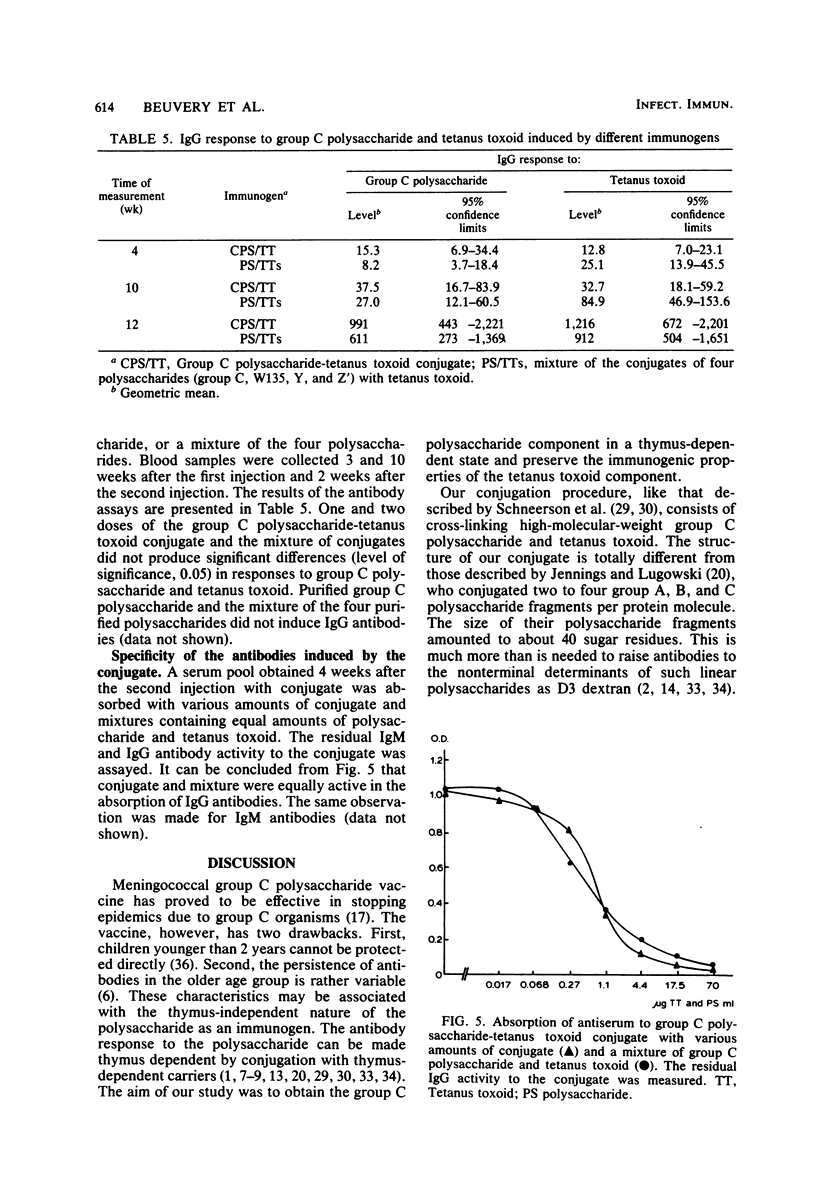
Neisseria meningitidis group C polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate was prepared to obtain the polysaccharide component in a thymus-dependent form and to preserve the immunogenic properties of the tetanus toxoid component. Biochemical and immunochemical analyses of this conjugate revealed that (i) it was composed of equal amounts of polysaccharide and protein; (ii) the antigenic activity of the polysaccharide component was greatly reduced; (iii) it contained about 10% free polysaccharide; (iv) the composition was not homogeneous; and (v) only 5% of the tetanus toxoid component was present at the surface of the conjugate molecules. In this study, the influence of these characteristics on the antibody response to both components in mice was investigated. The dose-response relationship, the persistence of antibodies, a possible antigenic competition, and the specificities of the antibodies induced were also studied. Our data suggest that the conjugate behaves as a pronounced thymus-dependent antigen, that the tetanus toxoid component is more immunogenic at lower dosages (0.8 and 20 ng) than equivalent doses of tetanus vaccine, that the presence of free polysaccharide does not influence the induction of antibodies to polysaccharide by the conjugate, and that no antibodies to new structures in the conjugate are induced. These characteristics favor the application of this conjugate as a vaccine for human use.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakatsu Y., Ashwell G., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on dextrans. V. Specificity and cross-reactivity with dextrans of the antibodies formed in rabbits to isomaltonic and isomaltotrionic acids coupled to bovine serum albumin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):858–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. H., Stashak P. W. Quantitative and qualitative studies on the primary antibody response to pneumococcal polysaccharides at ehe cellular level. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1342–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. I. Dose-response studies and the effect of prior immunization on the magnitude of the antibody response. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):469–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., Leussink A. B., Van Delft R. W., Tiesjema R. H., Nagel J. Immunoglobulin M and G antibody responses and persistence of these antibodies in adults after vaccination with a combined meningococcal group A and group C polysaccharide vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.579-585.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., Miedema F., van Delft R., Haverkamp J. Preparation and immunochemical characterization of meningococcal group C polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates as a new generation of vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):39–45. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.39-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., van Rossum F., Nagel J. Comparison of the induction of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies in mice with purified pneumococcal type 3 and meningococcal group C polysaccharides and their protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):15–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.15-22.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braley-Mullen H. Antigen requirements for priming of IgG producing B memory cells specific for Type III pneumococcal polysaccharide. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):521–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. P., Brown M., Rittenberg M. B. Immunologic memory to phosphorylcholine. II. PC-KLH induces two antibody populations that dominate different isotypes. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):702–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Rastogi S. C. Further studies on the immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcal type 6A polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):245–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.245-256.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J., Kabat E. A., Dorner M. M., Liao J. Binding properties of immunoglobulin combining sites specific for terminal or nonterminal antigenic determinants in dextran. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):435–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Austrian R., Cvjetanović B., Robbins J. B. Prospects for the prevention of bacterial meningitis with polysaccharide vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(4):509–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Brandt B. L., Altieri P. L., Pier G. B., Berman S. L. Safety and immunogenicity of group Y and group W135 meningococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccines in adults. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):725–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.725-732.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Sivonen A., Mäkelä H. Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children: a double-blind field study of 100,000 vaccinees 3 months to 5 years of age in Finland. Pediatrics. 1977 Nov;60(5):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Immunoglobulin-producing tumors and myeloma proteins of mice. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):631–719. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press J. L. The CBA/N defect defines two classes of T cell-dependent antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1234–1240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Eidinger D. Antigenic competition: a review of nonspecific antigen-induced suppression. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:133–168. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60309-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B. The relationship between group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides and serum opsonins in man. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):499–513. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Antigenic competition between polypeptidyl determinants in normal and tolerant rabbits. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):237–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. H., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. V. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent and thymus-dependent antigens in athymic and euthymic mice. Cell Immunol. 1982 Mar 15;68(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Zopf D. A., Johnson B. M., Miller C. B., Paul W. E. The immune response to an isomaltohexosyl-protein conjugate, a thymus-dependent analogue of alpha(1 replaced by 6) dextran. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1350–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Zopf D. A., Miller C. B., Johnson B. M., Mongini P. K., Ahmed A., Paul W. E. Immune response to a thymus-dependent form of B512 dextran requires the presence of Lyb-5+ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):657–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Antigenic competition. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;60:125–174. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65502-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. G., Buys J., Hanstede J. G., Hagenaars A. M. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and passive hemagglutination method for quantification of antibodies to lipopolysaccharide and tetanus toxoid in rats. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.798-803.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D., Braley-Mullen H. Antigen requirements for priming of type III pneumococcal polysaccharide-specific IgG memory responses: suppression of memory with the T-independent form of antigen. Cell Immunol. 1981 Oct;64(1):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90468-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


