Abstract
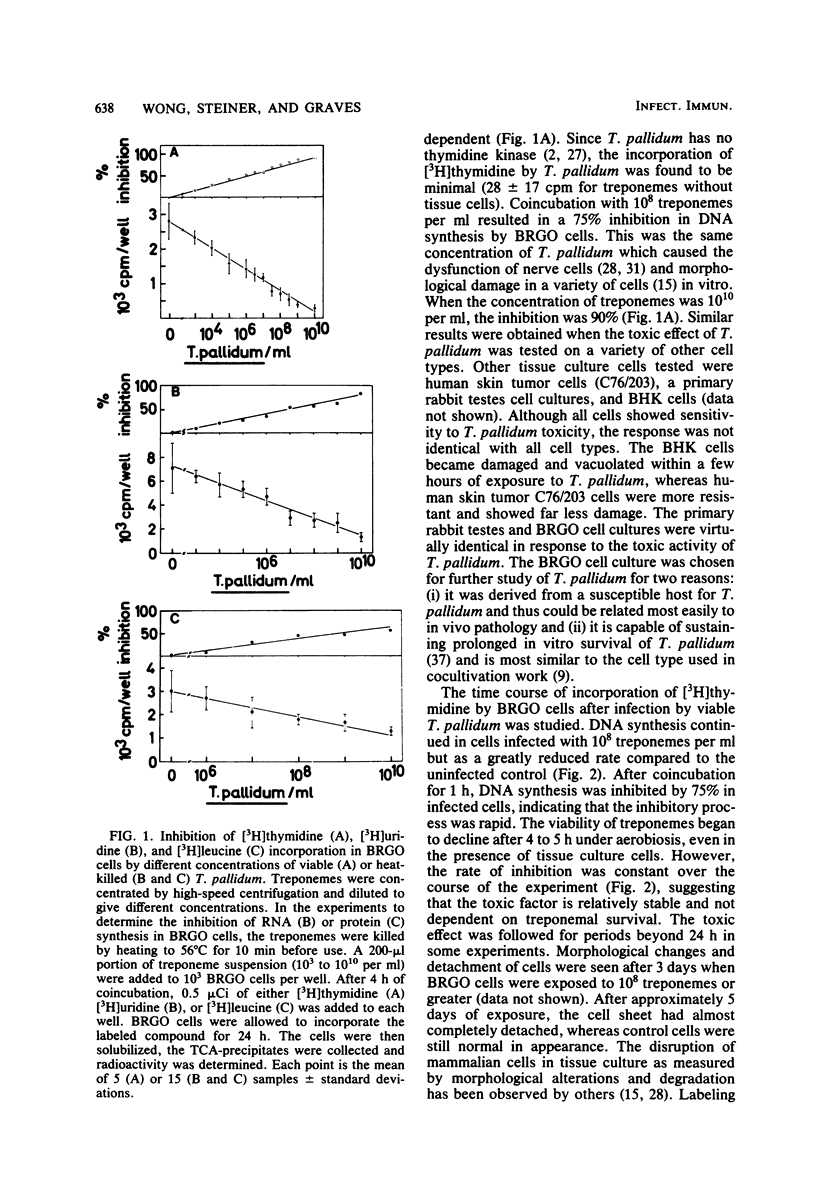
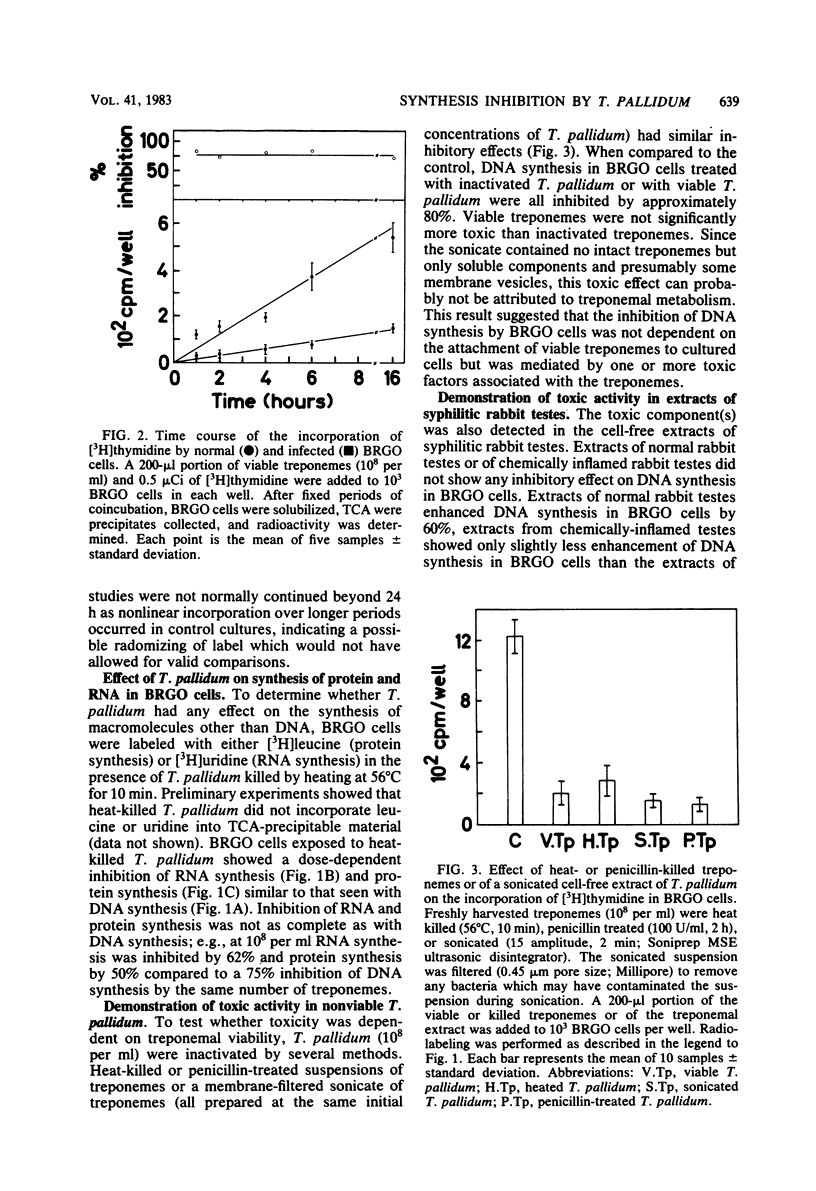
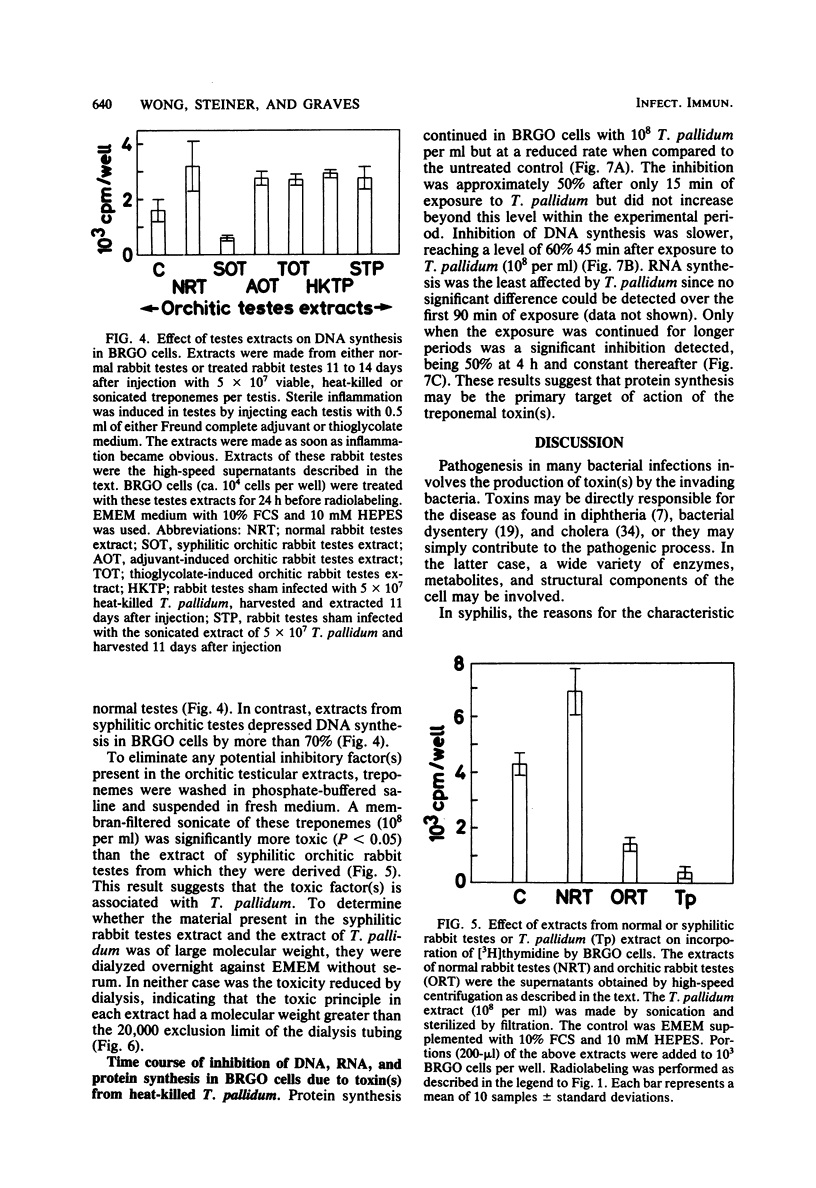
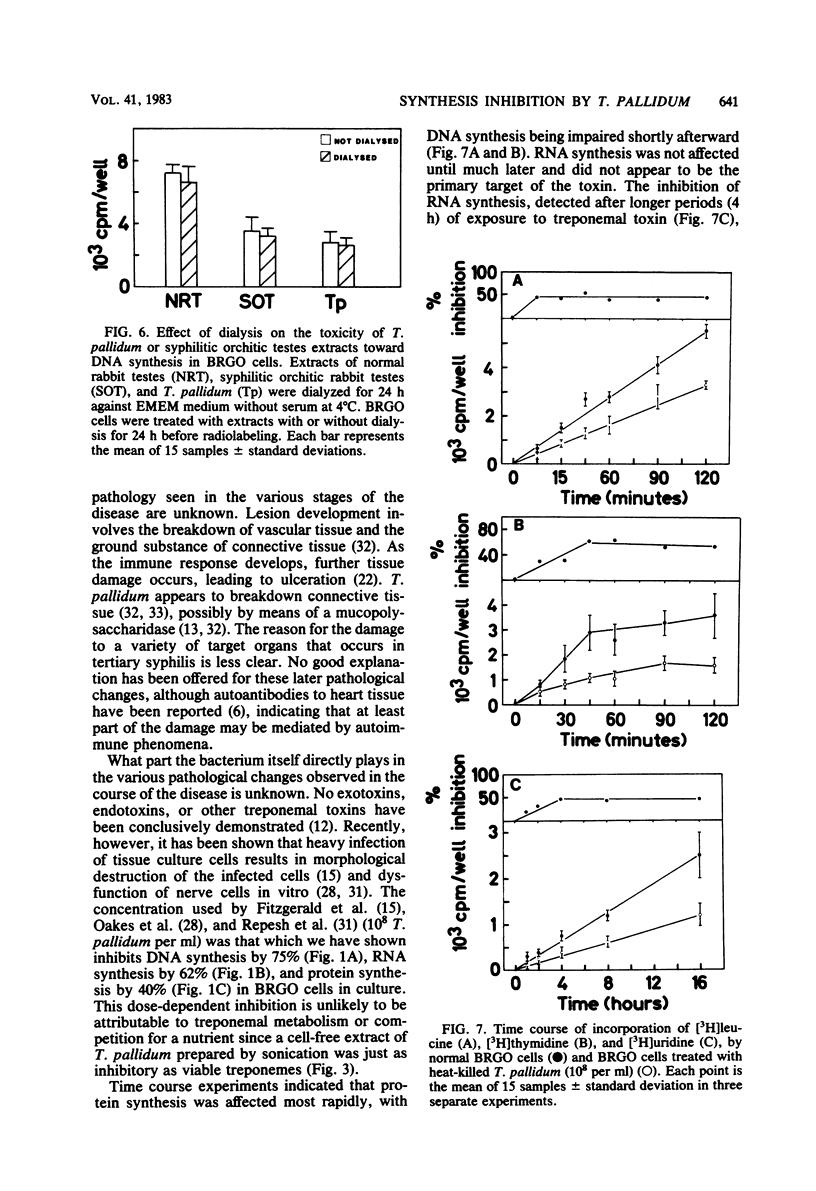
Treponema pallidum partially inhibited the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and protein by rabbit cells in vitro. The inhibition of DNA synthesis was proportional to treponemal concentration and persisted during the period of exposure to T. pallidum. The toxic effect was not dependent on treponemal metabolism or on whole treponemes, since heat- and penicillin-killed treponemes and a cell-free sonicate of treponemes had similar toxicities. The toxic factor(s) was also detected in extracts of syphilitic rabbit testes but not in extracts of normal rabbit testes or testes inflamed by chemical means. The T. pallidum-derived toxic material had a molecular weight greater than 20,000 as determined by dialysis. Protein and DNA synthesis were most rapidly inhibited; RNA synthesis continued at normal rates for up to 2 h after exposure to treponemes. Protein synthesis or a necessary precursor of protein synthesis appeared to be the primary target of the T. pallidum toxin(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Hayes N. S. Protein synthesis by Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit tissue. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1350–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1350-1355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Mogerley S. Capacity of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols) for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):392–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.392-397.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya P., Simet I., Basu S. Inhibition of human neuroblastoma DNA polymerase activities by plant lectins and toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2218–2221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Rothman S. W., Doctor B. P. Inhibition of protein synthesis in intact HeLa cells by Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):98–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.98-107.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Clinical pathology of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):696–704. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavant C. H., Wicher V., Wicher K. Host response to Treponema pallidum infection. III. Demonstration of autoantibodies to heart in sera from infected rabbits. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;56(2):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Cultivation of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):908–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.908-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Mucopolysaccharidase of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.261-268.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Wolff E. T. Sulfhydryl oxidation using procedures and experimental conditions commonly used for Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Jun;56(3):129–136. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.3.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J. Pathogenesis and immunology of Treponema pallidum. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:29–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Oakes S. G. Morphological destruction of cultured cells by the attachment of Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Feb;58(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Elin R. J., Berry F. W., Jr, Frank M. M. Endotoxemia associated with the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 22;295(4):211–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607222950409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg C. R., Melly M. A., Hellerqvist C. G., Coniglio J. G., McGee Z. A. Toxic activity of purified lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae for human fallopian tube mucosa. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):432–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Inhibitors of protein biosynthesis. V. Effects of emetine on protein and nucleic acid biosynthesis in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4089–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. W., Zey P. N. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharide isolated from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.838-844.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene G. M., Turk J. L., Wright D. J., Grimble A. G. Reduced lymphocyte transformation due to a plasma factor in patients with active syphilis. Lancet. 1969 Aug 2;2(7614):246–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Kao W. Y., Tserng K. Y., Chen C. C., Tung T. C. Effect of crystalline abrin on the biosynthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA in experimental tumors. Cancer Res. 1970 Sep;30(9):2431–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Liu K., Chen C. C., Tung T. C. Effect of crystalline ricin on the biosynthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA in experimental tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1971 Jul;31(7):921–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. C., Baseman J. B. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):854–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.854-860.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Long-term incorporation of tritiated adenine into deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid by Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain). Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1040-1049.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes S. G., Repesh L. A., Pozos R. S., Fitzgerald T. J. Electrophysiological dysfunction and cellular disruption of sensory neurones during incubation with Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Aug;58(4):220–227. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.4.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Dubrow R., Hamlin J. L., Kletzien R. F. Animal cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:715–750. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Prather W. Cytotoxicity of ascorbate and other reducing agents towards cultured fibroblasts as a result of hydrogen peroxide formation. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jan;90(1):61–70. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040900109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repesh L. A., Fitzgerald T. J., Oakes S. G., Pozos R. S. Scanning electron microscopy of the attachment of Treponema pallidum to nerve cells in vitro. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Aug;58(4):211–219. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.4.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT V., DAMMIN G. J. Hyaluronidase and experimental syphilis. III. Metachromasia in syphilitic orchitis and its relationship to hyaluronic acid. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1950 Nov;34(6):501–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT V., DAMMIN G. J. Morphologic and histochemical sequences in syphilitic and in tuberculous orchitis in the rabbit. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 May;38(3):189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W. Action of cholera toxin on fluid and electrolyte movement in the small intestine. Annu Rev Med. 1973;24:19–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.24.020173.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Intracellular location of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in the rabbit testis. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):307–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.307-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N., Kalan A. J. Treponema pallidum within cells of a primary chancre from a human female. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Feb;50(1):40–44. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Steiner B. M., Graves S. R. Effects of anaerobic and microaerophilic conditions of extraction and incubation on the survival of Treponema pallidum in vitro. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Jun;58(3):139–142. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.3.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Steiner B. M., Graves S. R. Lack of effect of bicarbonate on the survival of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) in vitro. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Apr;58(2):130–130. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Steiner B., Faine S., Graves S. Factors affecting the attachment of Treponema pallidum to mammalian cells in vitro. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Feb;59(1):21–29. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


