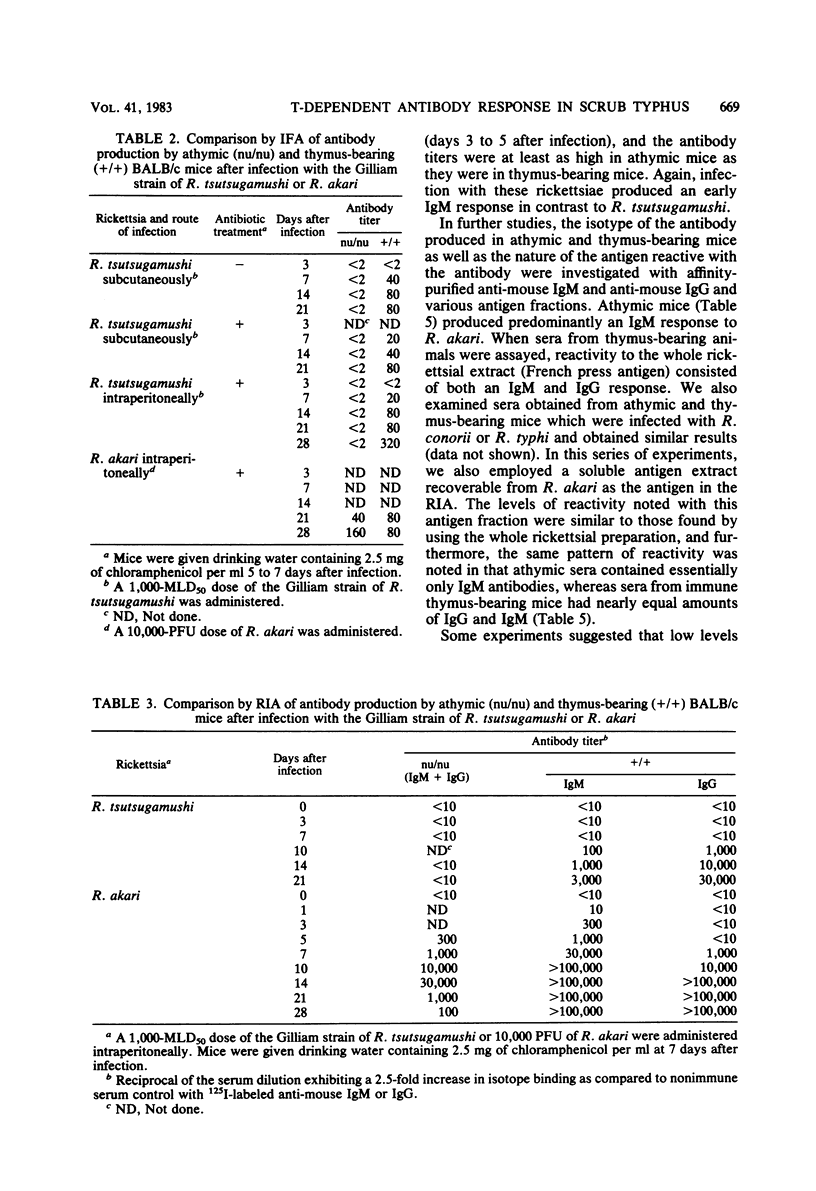
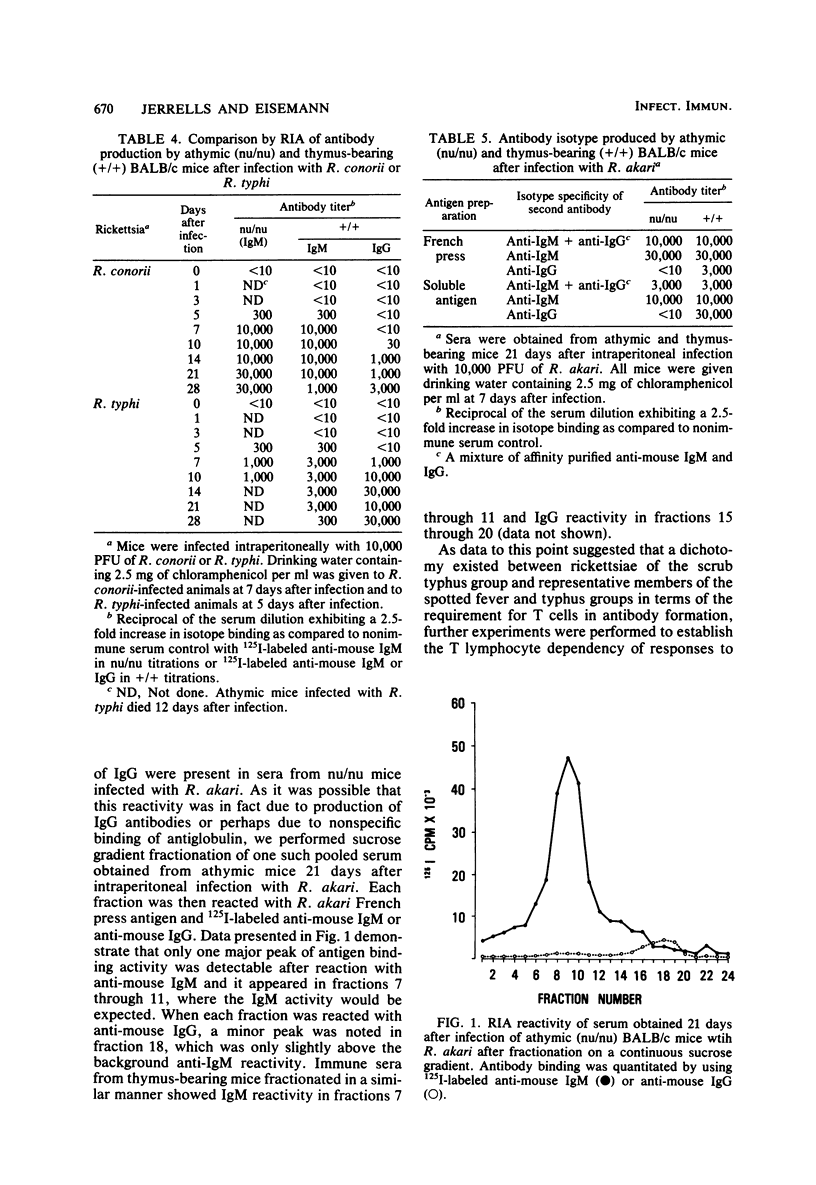
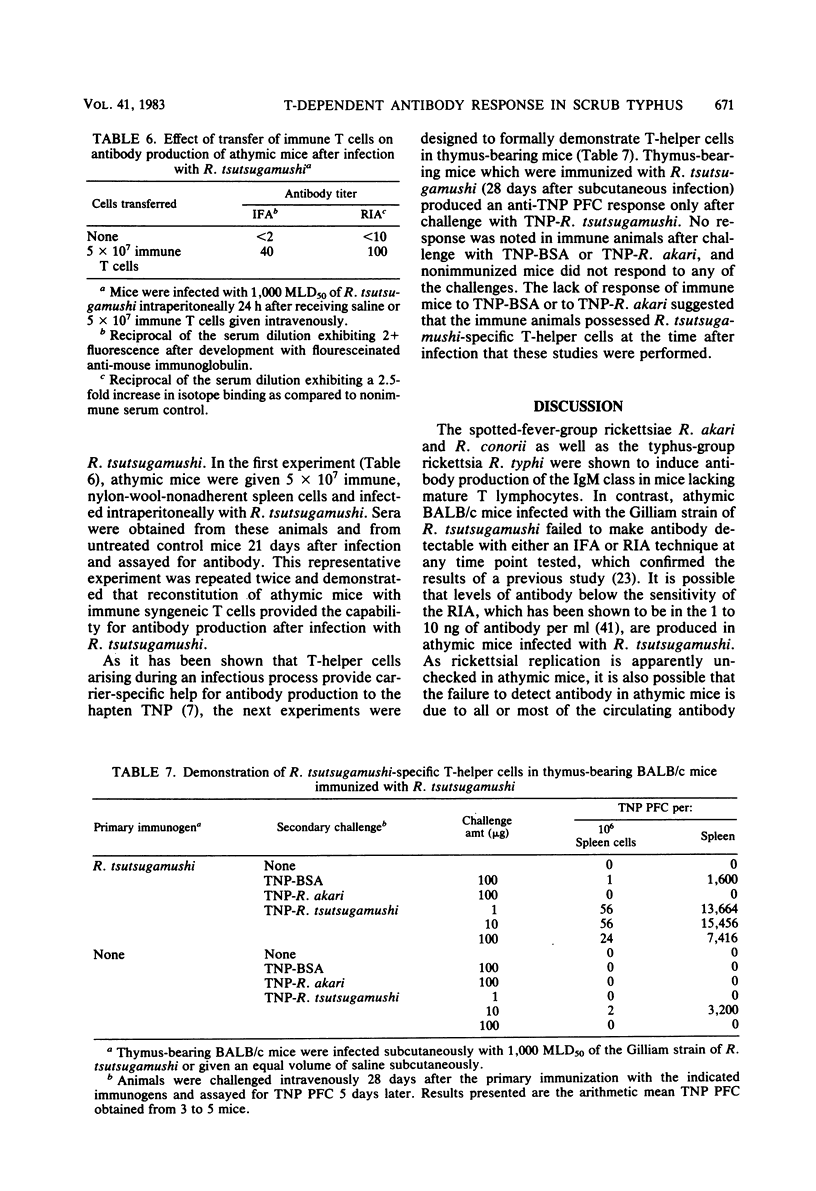
Abstract
The requirement of thymus-dependent lymphocytes for antibody production to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia akari, Rickettsia conorii, and Rickettsia typhi was investigated by comparing antibody production in athymic (nu/nu) or thymus-bearing BALB/c mice. Athymic BALB/c mice produced antibody after infection with R. akari, R. conorii, and R. typhi as measured by indirect fluorescent antibody titration or radioimmunoassay. Antibody production in these mice was a great or greater than in the thymus-bearing mice and demonstrated similar kinetics. In contrast, athymic BALB/c mice infected either intraperitoneally or subcutaneously with the Gilliam strain of R. tsutsugamushi failed to produce demonstrable antibody. The requirement of thymus-dependent lymphocytes for antibody production to R. tsutsugamushi was further suggested by the demonstration of antibody production after transfer of immune thymus-dependent lymphocytes to athymic mice and the demonstration of R. tsutsugamushi-specific T helper cells in immune thymus-bearing mice. The antibody produced in athymic mice after infection with R. akari, R. conorii, and R. typhi was predominantly immunoglobulin M, based on isotype-specific radioimmunoassays and sucrose gradient fractionation. Furthermore, the antibody produced by athymic mice in response to R. akari infection reacted with a carbohydrate-containing outer membrane component.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. H., Stashak P. W. Quantitative and qualitative studies on the primary antibody response to pneumococcal polysaccharides at ehe cellular level. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1342–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Reed N. D., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Regulation of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. I. Nature of regulatory cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1431–1441. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. I. Dose-response studies and the effect of prior immunization on the magnitude of the antibody response. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):469–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. F., Patt J. K., Hopps H. E. Titration and neutralization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):825–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. E., Kuhn R. E., Carlson K. S. Induction of parasite-specific helper T lymphocytes during Trypanosoma cruzi infections in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2092–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.155-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg G. H., Jr, Osterman J. V. Gamma-irradiated scrub typhus immunogens: development and duration of immunity. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):80–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.80-86.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing E. P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Shirai A., Osterman J. V. Experimental infection of mouse peritoneal mesothelium with scrub typhus rickettsiae: an ultrastructural study. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1068–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1068-1075.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C., Möller G. Immunological unresponsiveness to thymus-independent antigens: two fundamentally different genetic mechanisms of B-cell unresponsiveness to dextran. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1663–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Rittenberg M. B. In vitro and in vivo allogeneic effects: differential modulation of B cell subpopulations. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1625–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Christie G. H., Courtenay B. M., Leuchars E., Davies A. J. Studies on immunological paralysis. VI. Thymic-independence of tolerance and immunity to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1971 Dec;2(6):614–626. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphres R. C., Hinrichs D. J. Role of antibody in Coxiella burnetii infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):641–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.641-645.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Mallavia L. P., Hinrichs D. J. Detection of long-term cellular immunity to Coxiella burneti as assayed by lymphocyte transformation. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.280-286.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: delayed-type hypersensitivity responses of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.117-123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Palmer B. A., Osterman J. V. Gamma-irradiated scrub typhus immunogens: development of cell-mediated immunity after vaccination of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):262–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.262-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura A., Jr, Murata M., Osono M., Nogami S., Shirasaka A., Tanaka H., Sudo K., Suzuki K., Miyairi T., Kijima H. Studies on inapparent infection of tsutsugamuschi disease in Izu Shichito Islands: seroepidemiology and demonstration of an avirulent Rickettsia strain for mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1980 Apr;50(2):91–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon R. H., Pedersen C. E., Jr Immune responses to Rickettsia akari infection in congenitally athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):310–313. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.310-313.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Andersson J., Lernhardt W., Schreier M. H. Roles of surface-bound immunoglobulin molecules in regulating the replication and maturation to immunoglobulin secretion of B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1980;52:89–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Paul W. E. T cell regulation of the IgG2a response to TNP-Ficoll: evidence that allotype congenic mice contain both helper cells that preferentially enhance IgG2a synthesis and suppressor cells that specifically suppress IgG2 synthesis. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Stein K. E., Paul W. E. T cell regulation of IgG subclass antibody production in response to T-independent antigens. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):1–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Zitron I. M., Mond J. J., Ahmed A., Scher I., Paul W. E. Surface immunoglobulin D as a functional receptor for a subclass of B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:89–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Michael G. Frequency of antigen-sensitive cells to thymus-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of normal and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.744-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks S. C., Jr, Hetrick F. M., Osterman J. V. A plaque reduction assay for studying antigenic relationships among strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):998–1006. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks S. C., Jr, Osterman J. V., Hetrick F. M. Plaque assay and cloning of scrub typhus rickettsiae in irradiated L-929 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):76–80. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.76-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. V., Eisemann C. S. Rickettsial indirect hemagglutination test: isolation of erythrocyte-sensitizing substance. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.189-196.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Hansburg D., Briles D. E., Nicolotti R. A., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine anti-carbohydrate antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pratt K. L. Antitrinitrophenyl (TNP) plaque assay. Primary response of Balb/c mice to soluble and particulate immunogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):575–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. M., Brown G., Gan E., Huxsoll D. L. Adaptation of a microimmunofluorescence test to the study of human Rickettsia tsutsugamuskh antibody. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Nov;25(6):900–905. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Catanzaro P. J., Eisenberg G. H., Jr, Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: effect of chloramphenicol. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):324–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.324-329.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Catanzaro P. J., Phillips S. M., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of cellular immunity in heterologous protection. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.39-46.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein K. E., Zopf D. A., Johnson B. M., Miller C. B., Paul W. E. The immune response to an isomaltohexosyl-protein conjugate, a thymus-dependent analogue of alpha(1 replaced by 6) dextran. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1350–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. W., Bever C. T., Rollwagen F. M., Evans C. B., Asofsky R. The rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium yoelii lacks both types 1 and 2 T-independent antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1854–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Peenen P. F., Ho C. M., Bourgeois A. L. Indirect immunofluorescence antibodies in natural and acquired Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infections of Philippine rodents. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):813–816. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.813-816.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Trenkner E., Cohn M. The use of bacterial lipopolysaccharides to show that two signals are required for the induction of antibody synthesis. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):699–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Dalrymple J. M., Artenstein M. S. Analysis of parameters affecting the solid phase radioimmunoassay quantitation of antibody to meningococcal antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1788–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Glasebrook A. L. Requirement for three signals in "T-independent" (lipopolysaccharide-induced) as well as in T-dependent B cell responses. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):666–680. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


