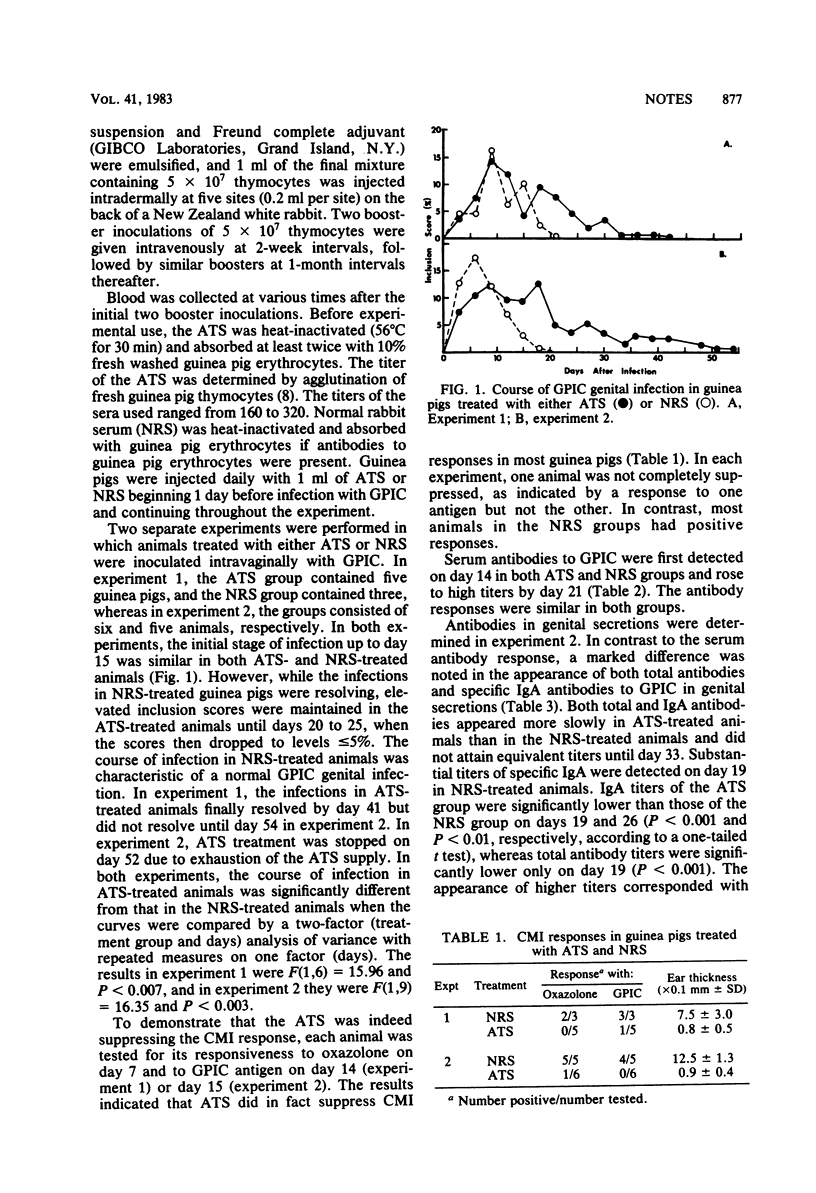
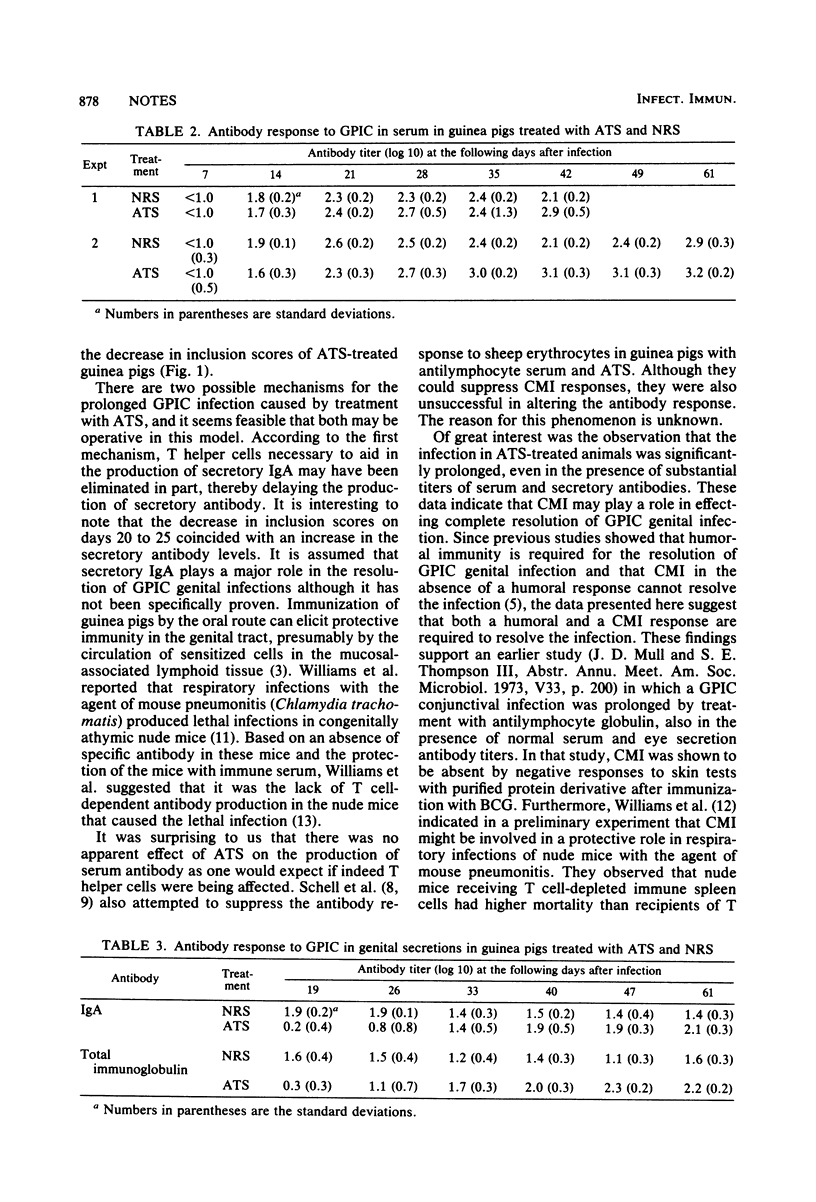
Abstract
The treatment of female guinea pigs, infected in the genital tract with the chlamydial agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis, with rabbit anti-guinea pig thymocyte serum extended the course of the infection by 20 to 30 days. The rabbit anti-guinea pig thymocyte serum was shown to suppress delayed hypersensitivity responses to the guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis agent and the contact allergen oxazolone. The appearance of antibody in genital secretions was delayed, but the infection persisted at low levels even when normal serum and secretory antibody titers were attained, indicating that cell-mediated immunity may play a role in the resolution of chlamydial genital infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kuo C., Chen W. J. A mouse model of Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):198–202. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Murray E. S., Nisson P. E. Use of enteric vaccines in protection against chlamydial infections of the genital tract and the eye of guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):742–746. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Barron A. L. Humoral immune response in acquired immunity to chlamydial genital infection of female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):463–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.463-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Barron A. L. Humoral immunity in the resolution of genital infection in female guinea pigs infected with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):573–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.573-579.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Hough A. J., Jr, Pasley J. N., Barron A. L. Effect of estradiol on chlamydial genital infection of female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):699–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.699-705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Soloff B. L., Barron A. L. Cystitis associated with chlamydial infection of the genital tract in male guinea pigs. Sex Transm Dis. 1981 Jul-Sep;8(3):203–210. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell K., Daniel K., Blazkovec A. A. Effects of anti-lymphocyte, anti-macrophage and anti-thymocyte serum IgG on the immune response. II. Immediate-type and delayed-type cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions in outbred guinea pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(2):302–320. doi: 10.1159/000230528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell K., Daniel K., Blazkovec A. A. Effects of anti-lymphocyte, anti-macrophage and anti-thymocyte serum IgG on the immune response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(2):286–301. doi: 10.1159/000230527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffrey M., Falder P., Taylor-Robinson D. Genital-tract infection and disease in nude and immunologically competent mice after inoculation of a human strain of Chlamydia trachomatis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Oct;63(5):539–546. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Drutz D. J., Sumaya C. V. Pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the immunocompromised (nude) mouse. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):238–241. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B., Sumaya C. V. The role of antibody in host defense against the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


