Abstract
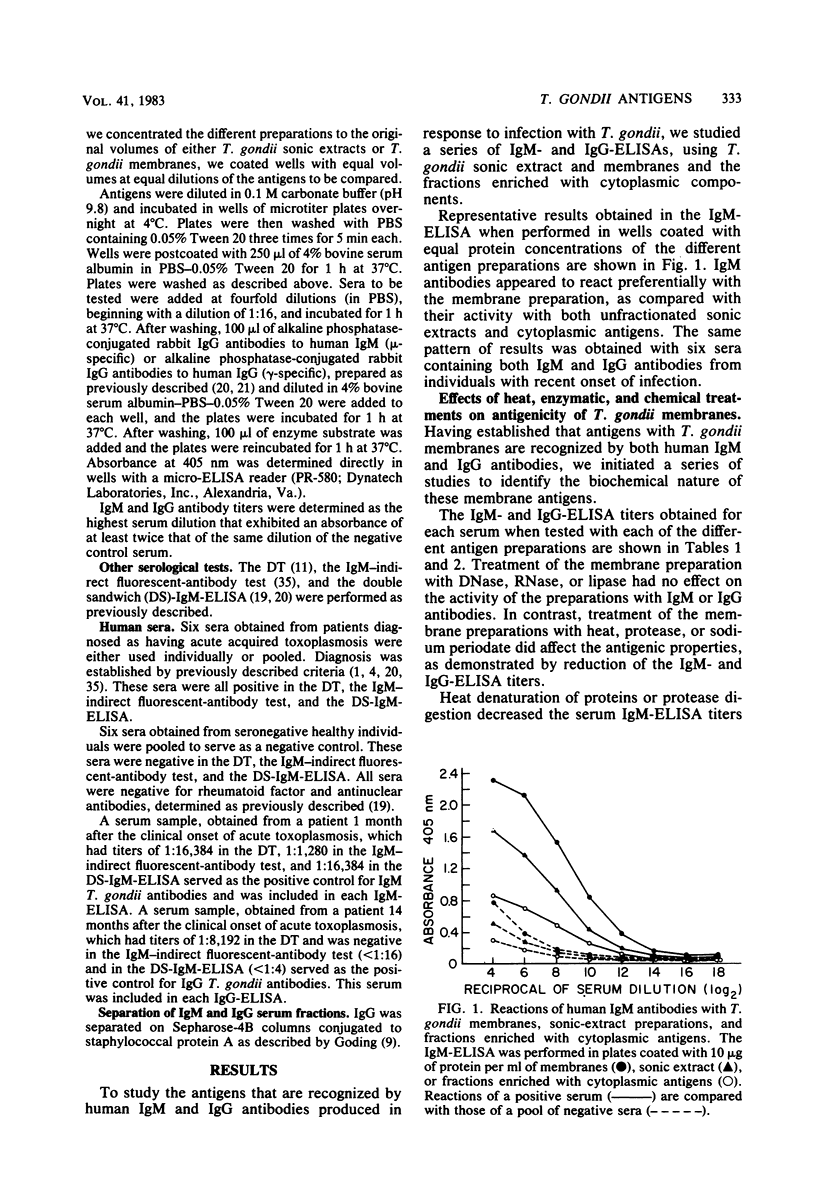
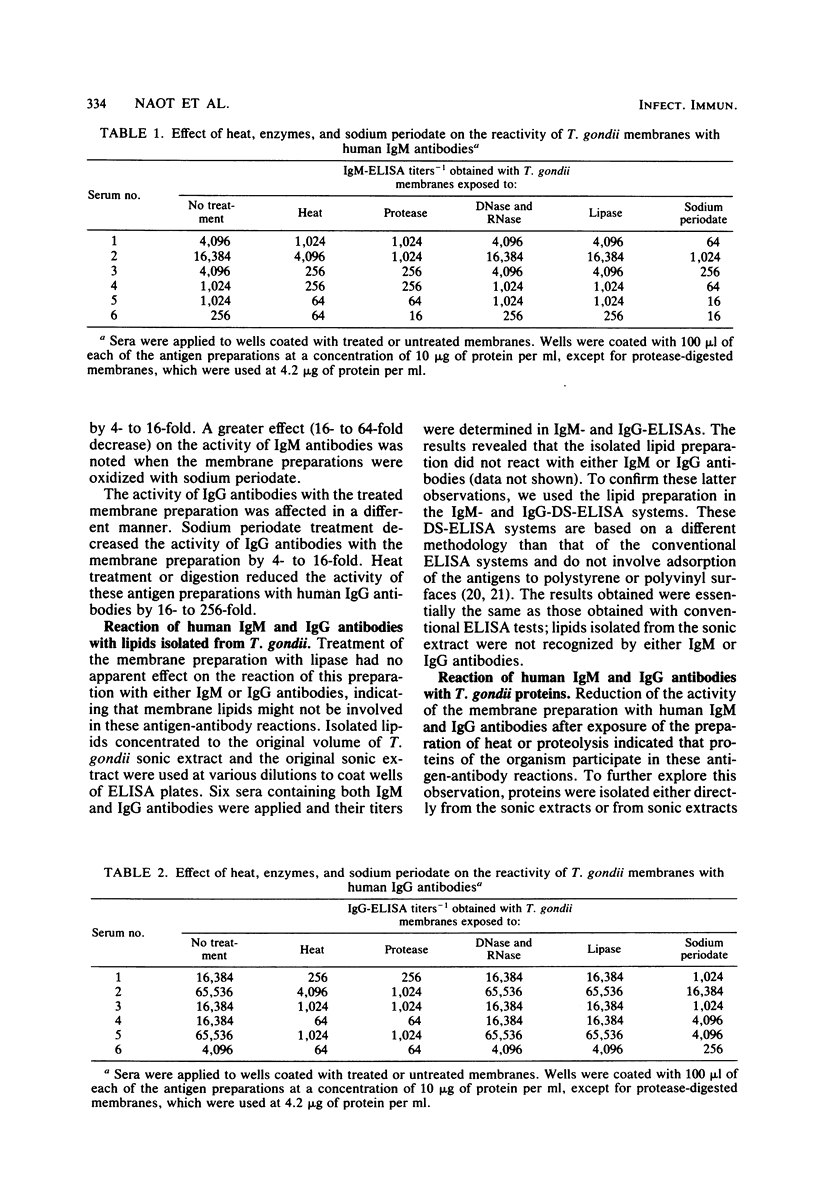
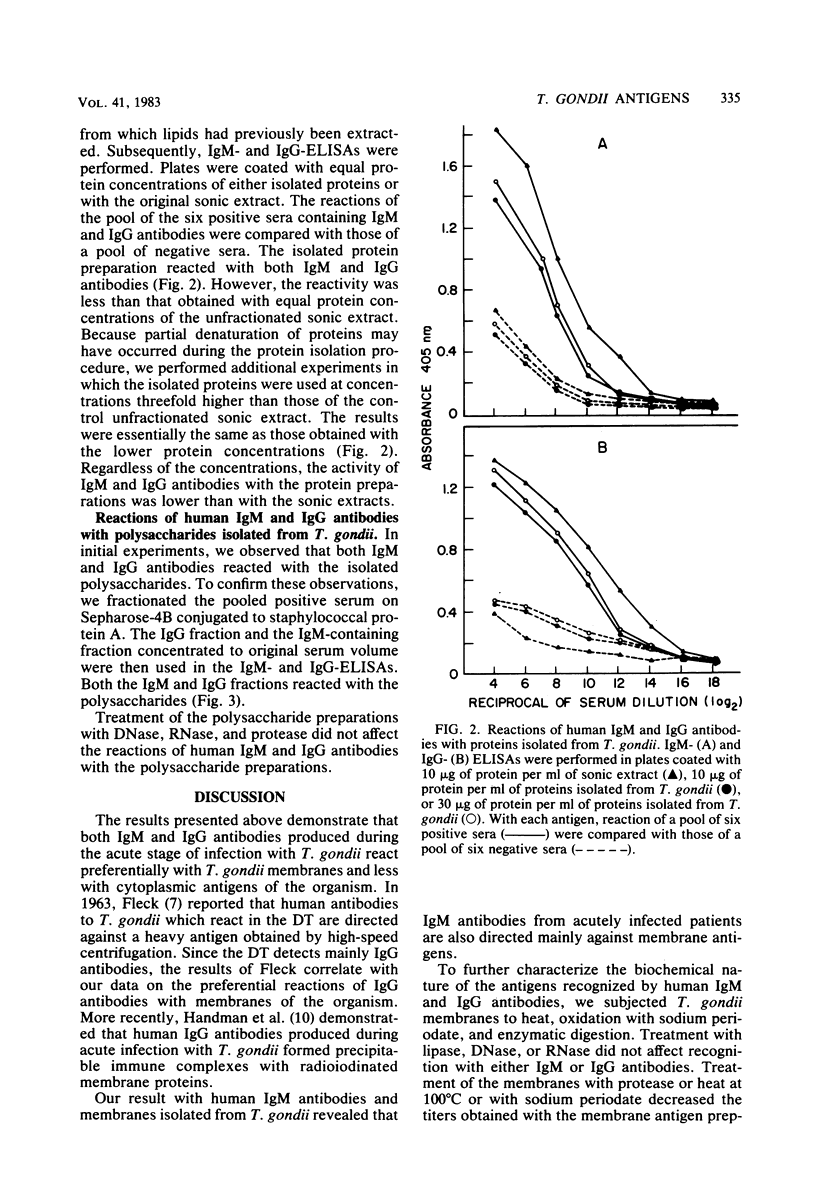
Studies were performed to define the nature of the Toxoplasma gondii antigens that are recognized by human immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG antibodies. Both IgM and IgG antibodies were found to be directed mainly against T. gondii membrane antigens in sera obtained from patients with acute toxoplasmosis. Treatment of the membrane preparation with DNase, RNase, or lipase had no apparent effect on the reactivity of the membrane antigens with IgM and IgG antibodies. Lipids isolated from tachyzoites were not recognized by either IgM or IgG antibodies. Exposure of T. gondii membranes to heat, proteolysis, or oxidation with sodium periodate decreased the reactivity of the membrane preparations with both IgM and IgG antibodies. A preparation of T. gondii proteins and polysaccharides were recognized by both immunoglobulin classes. T. gondii polysaccharides reacted with human IgG antibodies produced during both the acute and chronic phases of the infection. We concluded that, after infection with T. gondii, IgM and IgG antibodies are elicited in response to both protein and carbohydrate constituents of the invading parasite.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Remington J. S. The diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. South Med J. 1975 Nov;68(11):1433–1443. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197511000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIDDLE R. S., BOCK R. M., GREEN D. E., TISDALE H. Physical characteristics of proteins of the electron transfer system and interpretation of the structure of the mitochondrion. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:827–842. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M. E., Ferreira A. W., Mineo J. R., Takiguti C. K., Nakahara O. S. Immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and defined toxoplasmosis serological patterns. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.55-58.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DYER J. R. Use of periodate oxidations in biochemical analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:111–152. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Remington J. S. Value of lymph-node biopsy in the diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 25;289(17):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310252891702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK D. G. Antibodies of Toxoplasma gondii. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Mar;61:53–60. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK D. G. Serological tests for toxoplasmosis. Nature. 1961 Jun 10;190:1018–1019. doi: 10.1038/1901018b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W., Remington J. S. Detection and characterization of membrane antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2578–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Remington J. S. Serological and immunochemical characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasin M., Rottem S., Razin S. The outer membrane of Proteus mirabilis. I. Isolation and characterization of the outer and cytoplasmic membrane fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 14;375(3):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Balfour A. H. An investigation of the antigenic structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Autumn;3(3):235–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., McDonald P. J., Neoh S. H. Molecular weight analysis of the major polypeptides and glycopeptides of Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):934–943. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauras G., Dodeur M., Laget P., Senet J. M., Bourrillon R. Partial resolution of the sugar content of Toxoplasma gondii membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):906–912. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mineo J. R., Camargo M. E., Ferreira A. W. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii polysaccharides in human toxoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):283–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.283-287.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for detection of monoclonal antibodies: experience with antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Complement fixation test in toxoplasmosis and persistence of the antibody in human beings. Pediatrics. 1949 Oct;4(4):443–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEEN E., KASS E. A new toxoplasma antigen for complement fixation test. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1951;28(1):36–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1951.tb04999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Rahman A., Pelster B., Brandis H. Search for the presence of lectin-binding sites on Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1977 Dec;63(6):1076–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Lipid composition of Mycoplasma neurolyticum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):554–558. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.554-558.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THALHAMMER O. Uber ein neues haltbares Antigen für KBR und Hauttest auf Toxoplasmose. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1956 Mar;104(3):110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryon J. C. Toxoplasma gondii: ultrastructure and antigenicity of purified tachyzoite pellicle. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Oct;48(2):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN J., RUSS S. B. Cultivation of toxoplasma in embryonated egg; an antigen derived from chorioallantoic membrane. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1948 Jan;67(1):85–89. doi: 10.3181/00379727-67-16213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Bullock S. L., English D. K. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and its microadaptation for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):273–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.273-277.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch P. C., Masur H., Jones T. C., Remington J. S. Serologic diagnosis of acute lymphadenopathic toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):256–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


