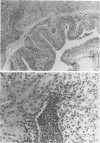
Abstract
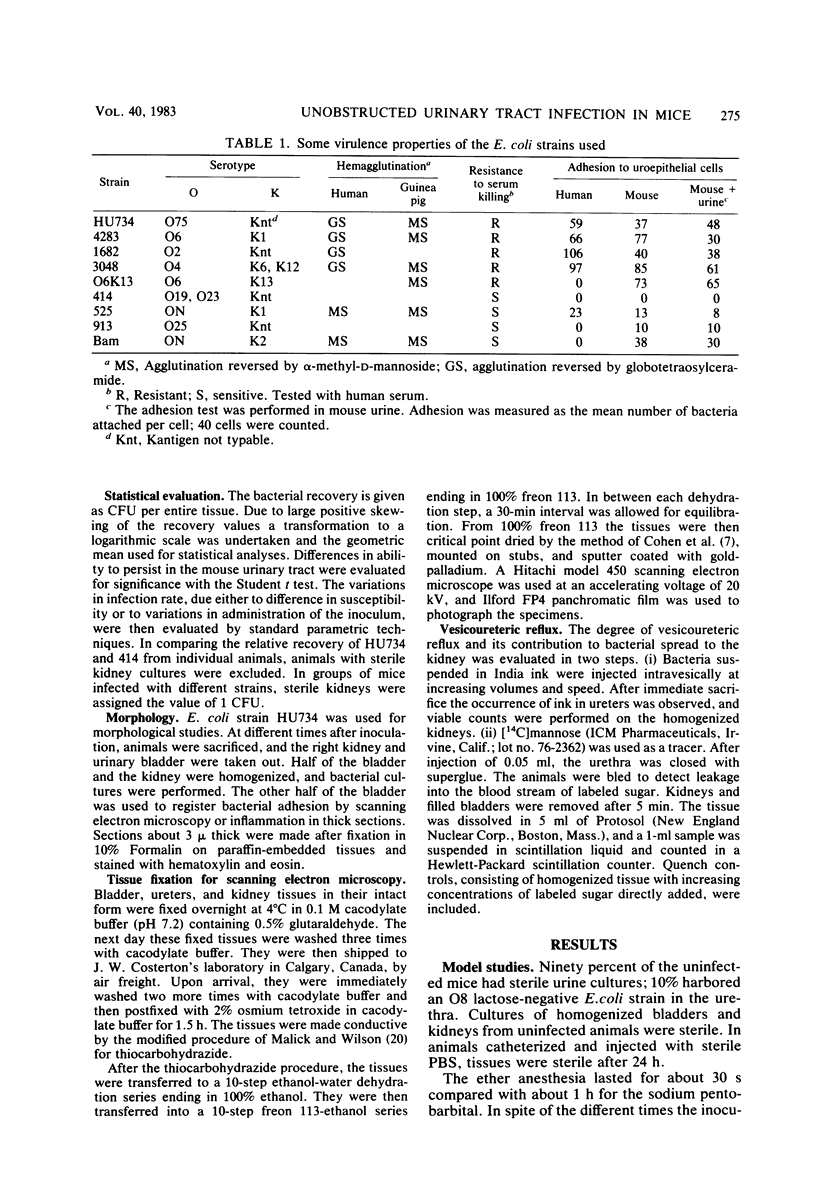
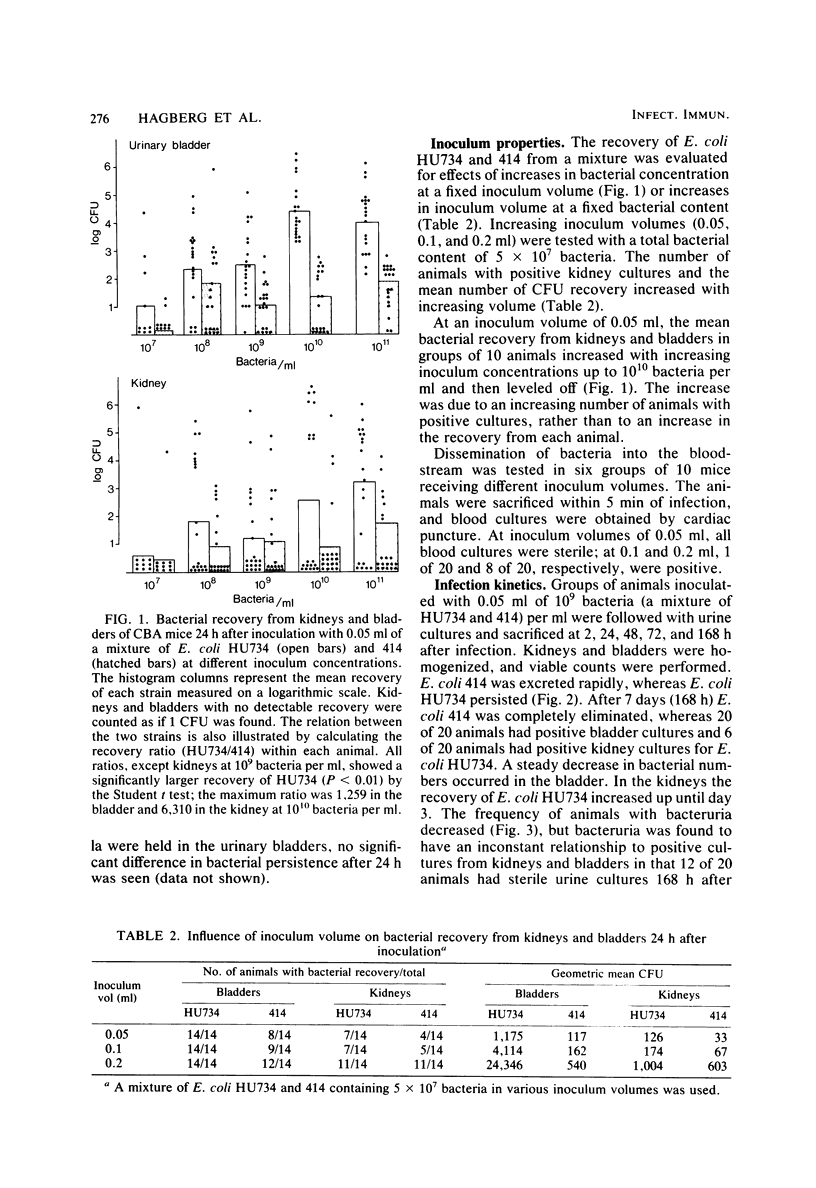
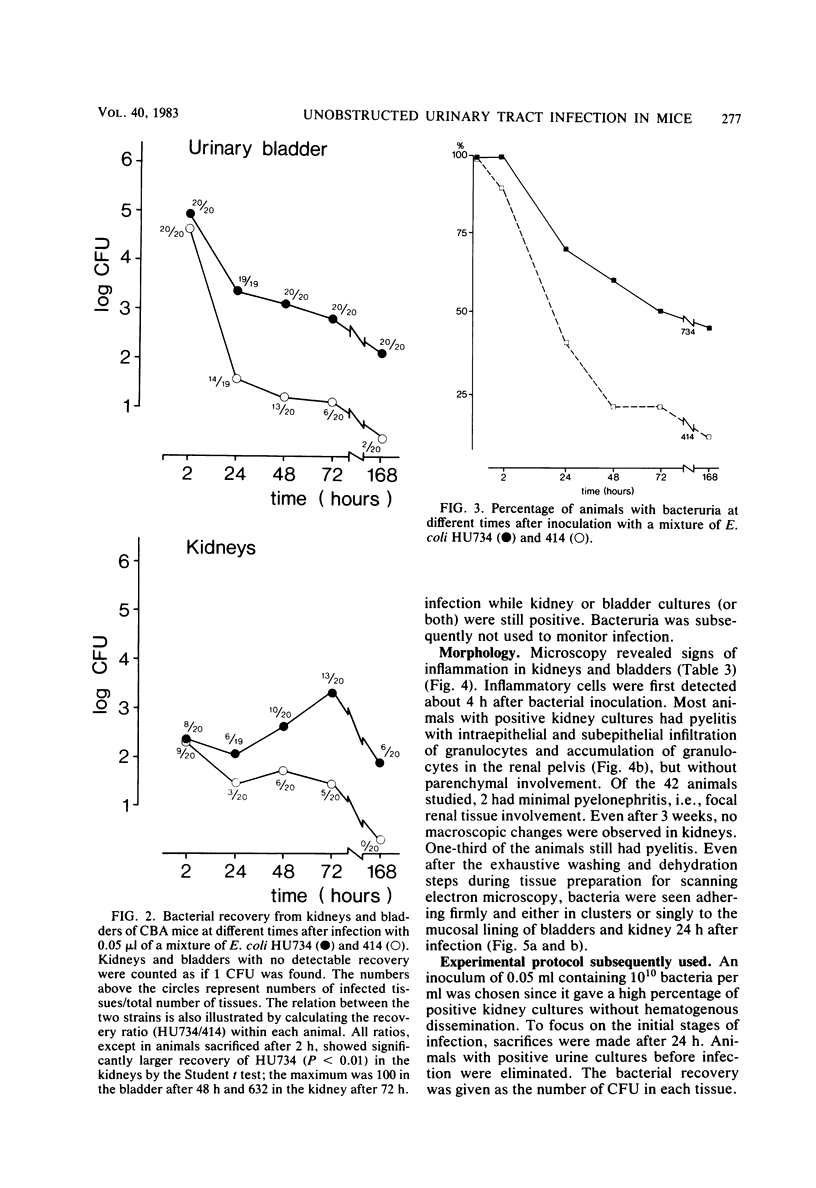
A model for ascending unobstructed urinary tract infection was developed in mice to study the pathogenesis of urinary tract infection induced by Escherichia coli associated with urinary tract infection in humans. Specifically, the model was designed to monitor the initial stages of the infectious process, e.g., bacterial adhesion. Mice were selected since the specificity and intensity of bacterial attachment of pyelonephritogenic E. coli strains to human and mouse uroepithelial cells were similar. Female mice were infected by urethral catheterization and installation of bacteria in the urinary bladder. To maximize clearance of unattached bacteria, no obstructive manipulations were performed. After sacrifice, the persistence of bacteria in kidneys and bladder was determined by viable counts on homogenized tissues. The experimental infection was standardized by using one pyelonephritis (HU734) and one normal fecal (414) E. coli isolate. With both strains all of the bladders became infected, but E. coli 414 was eliminated more rapidly than HU734. The percentage of positive kidney cultures increased with the bacterial inoculum concentration and volume. An inoculum of 0.05 ml containing 10(10) bacteria per ml was selected, giving the highest percentage of positive kidney cultures without detectable bacterial spread to the blood stream. The variation in the percentage of positive kidney cultures possibly depended on the degree of vesicoureteric reflux in the individual animals. Both in the kidneys and in the urinary bladders, strain HU734 yielded higher numbers of bacteria at 24 h and persisted longer than did strain 414. Several E. coli pyelonephritis isolates with properties associated with virulence in the human urinary tract consistently were recovered from mouse kidneys and bladders in higher numbers than E. coli strains of human fecal origin lacking those properties. The role of bacterial adhesion per se is the topic of the accompanying paper.
Full text
PDF

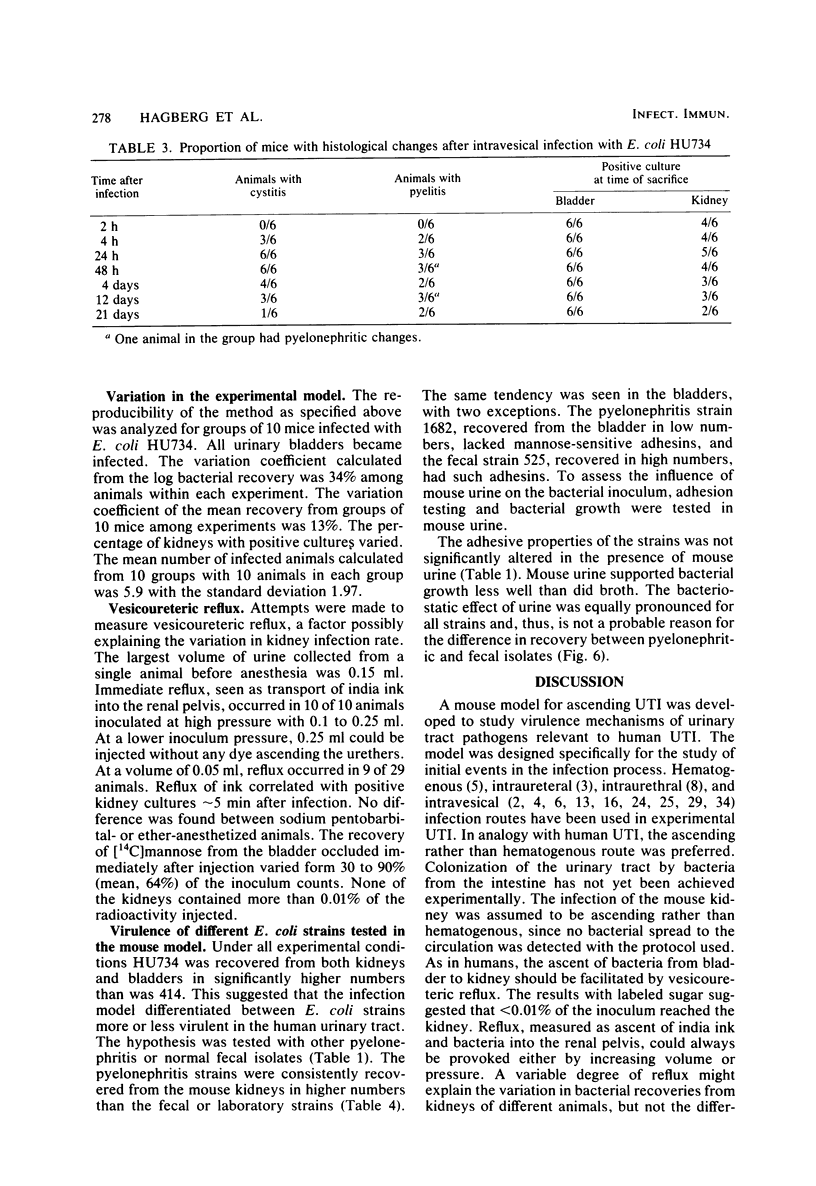
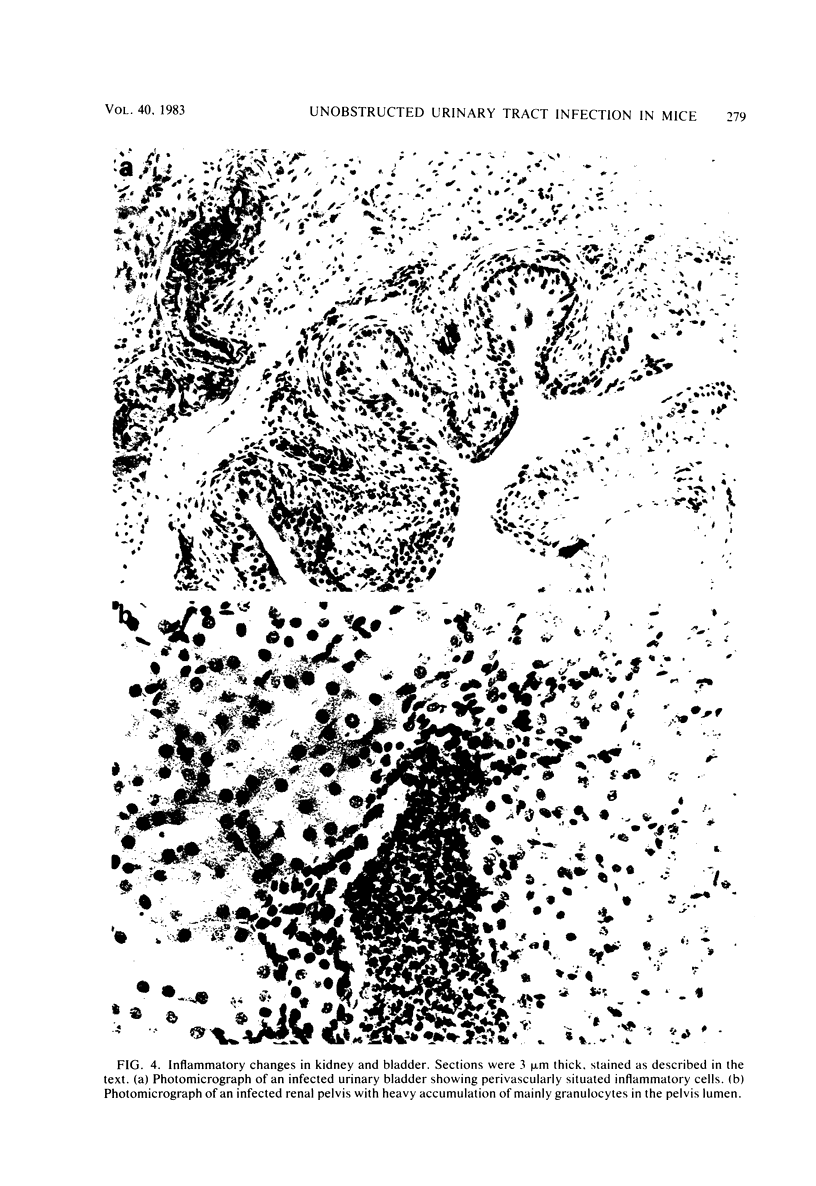
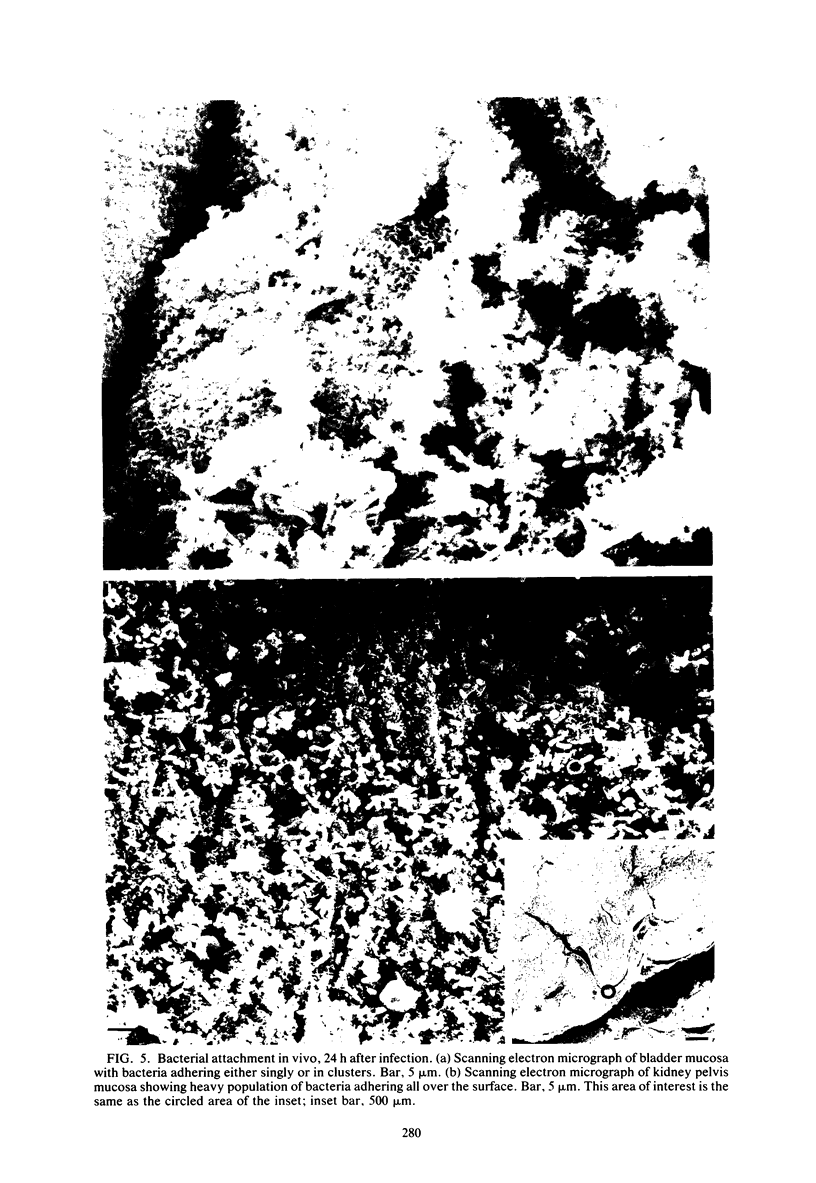
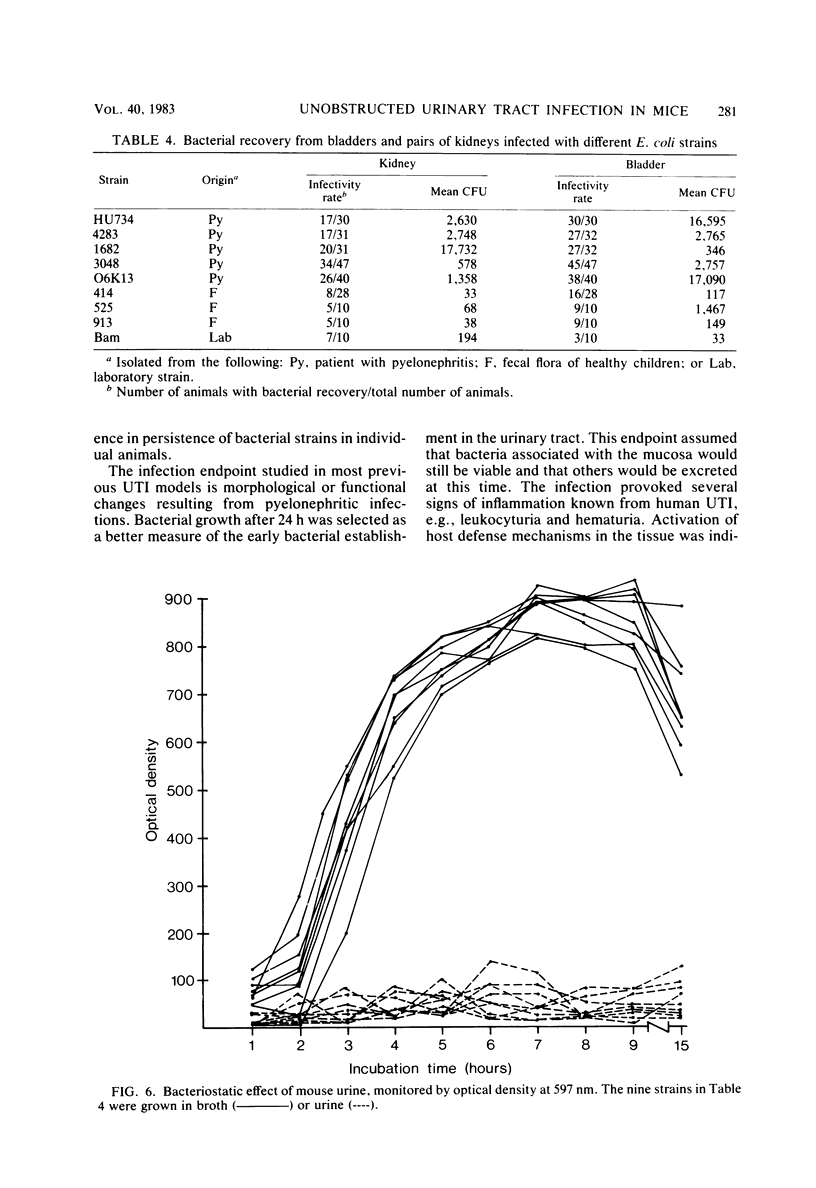


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN B. R., JACKSON G. G. Pyelitis, an important factor in the pathogenesis of retrograde pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 Sep 1;114:375–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams E. P., Gray G. M. The carbohydrate structures of the neutral ceramide glycolipids in kidneys of different mouse strains with special reference to the ceramide dihexosides. Chem Phys Lipids. 1968 Jun;2(2):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(68)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel J. R., Smith T. W., Jr, Roberts J. A. The hydrodynamics of pyelorenal reflux. J Urol. 1979 Jul;122(1):20–26. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson M., Medalia O., Schori L., Mirelman D., Sharon N., Ofek I. Prevention of colonization of the urinary tract of mice with Escherichia coli by blocking of bacterial adherence with methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):329–332. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SHAPIRO A. P., SIEMIENSKI J. Hematogenous pyelonephritis in rats. I. Its pathogenesis when produced by a simple new method. J Clin Invest. 1955 Oct;34(10):1489–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI103200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. J., Lyons J. M., Braude A. I. Immunization against retrograde pyelonephritis. I. Production of an experimental model of severe ascending Escherichia coli pyelonephritis without bacteremia in rats. Am J Pathol. 1974 Feb;74(2):345–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTRAN R. S., VIVALDI E., ZANGWILL D. P., KASS E. H. Retrograde Proteus pyelonephritis in rats. Bacteriologic, pathologic and fluorescent-antibody studies. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jul;43:1–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. E., HINMAN F., Jr Experiments with induced bacteriuria, vesical emptying and bacterial growth on the mechanism of bladder defense to infection. J Urol. 1961 Dec;86:739–748. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)65257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Kaijser B., Janson G. L., Lindberg U., Olling S. Adhesion to normal human uroepithelial cells of Escherichia coli from children with various forms of urinary tract infection. J Pediatr. 1978 Sep;93(3):398–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Freter R., Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Leffler H., Schoolnik G. Inhibition of experimental ascending urinary tract infection by an epithelial cell-surface receptor analogue. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):560–562. doi: 10.1038/298560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hagberg L., Hanson L. A., Korhonen T., Leffler H., Olling S. Adhesion of Escherichia coli in urinary tract infection. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:161–187. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPTINSTALL R. H. EXPERIMENTAL PYELONEPHRITIS. BACTERIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ASCENDING ROUTE OF INFECTION IN THE RAT. Nephron. 1964;1:73–92. doi: 10.1159/000179321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Falkow S., Freter R., Svanborg Edén C. Contribution of adhesion to bacterial persistence in the mouse urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.265-272.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Freedman L. R. Experimental pyelonephritis. XIV. Pyelonephritis in normal mice produced by inoculation of E. coli into the bladder lumen during water diuresis. Yale J Biol Med. 1967 Dec;40(3):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Källenius G., Möllby R., Svenson S. B., Helin I., Hultberg H., Cedergren B., Winberg J. Occurrence of P-fimbriated Escherichia coli in urinary tract infections. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1369–1372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P., Kaijser B., Baltzer I. M., Olling S. An experimental model for ascending acute pyelonephritis caused by Escherichia coli or proteus in rats. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Apr;33(4):408–412. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.4.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidin-Janson G., Hanson L. A., Kaijser B., Lincoln K., Lindberg U., Olling S., Wedel H. Comparison of Escherichia coli from bacteriuric patients with those from feces of healthy schoolchildren. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):346–353. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Mäkelä P. H., Sarvas M. Effect of polymyxin on the ultrastructure of the outer membrane of wild-type and polymyxin-resistant strain of Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1400-1407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. The applicability of the hypothesis of independent action to fatal infections in mice given Salmonella typhimurium by mouth. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Apr;16(2):396–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-2-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malick L. E., Wilson R. B. Modified thiocarbohydrazide procedure for scanning electron microscopy: routine use for normal, pathological, or experimental tissues. Stain Technol. 1975 Jul;50(4):265–269. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Snyder I. S. Mannose-sensitive interaction of Escherichia coli with human peripheral leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):520–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.520-527.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Tuddenham W. J., Howard E. B., Morrow J. W. Pseudomonas urinary tract infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.267-270.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Tsuchiya K. Experimental urinary tract infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):508–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.508-515.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Green G. M., Kass E. H. Antibacterial mechanisms of the urinary bladder. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2689–2700. doi: 10.1172/JCI105952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olling S., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Jodal U., Lincoln K., Lindberg U. The bactericidal effect of normal human serum on E. coli strains from normals and from patients with urinary tract infections. Infection. 1973;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01638251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Birch-Andersen A. Comparison of Escherichia coli fimbrial antigen F7 with type 1 fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.657-666.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Observations on the pathogenic properties of the K88, Hly and Ent plasmids of Escherichia coli with particular reference to porcine diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):467–485. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehling D. T., Mizutani K., Balish E. Effect of immunization of bacterial adherence to urothelium. Invest Urol. 1978 Sep;16(2):145–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]