Abstract
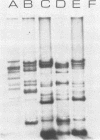
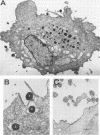
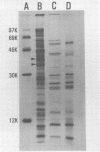
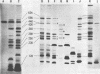
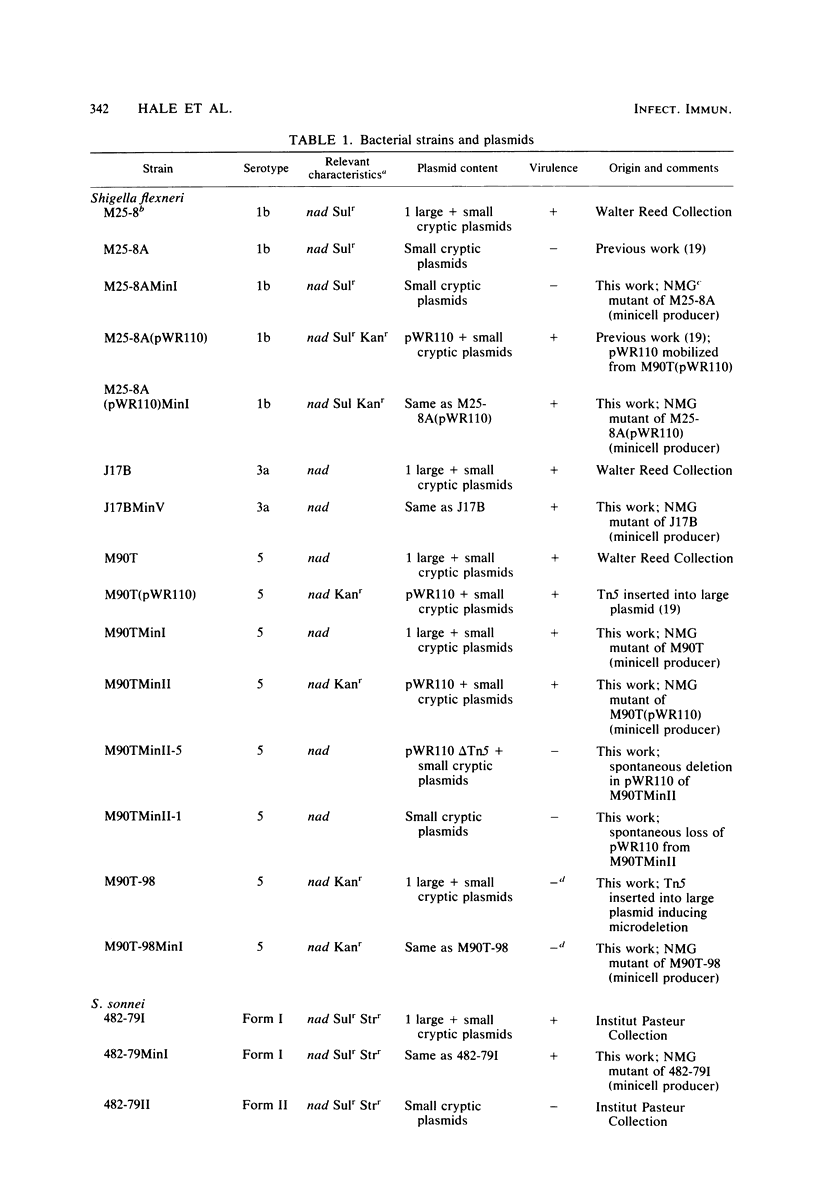
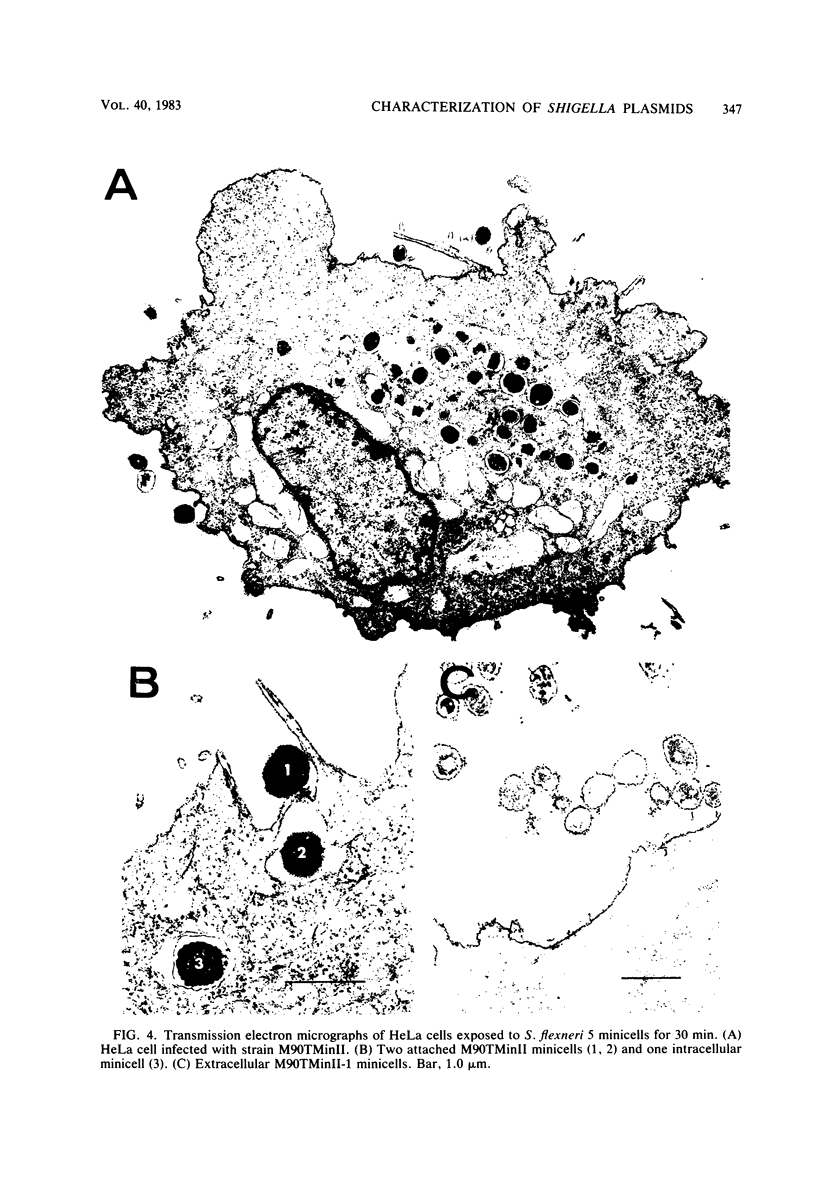
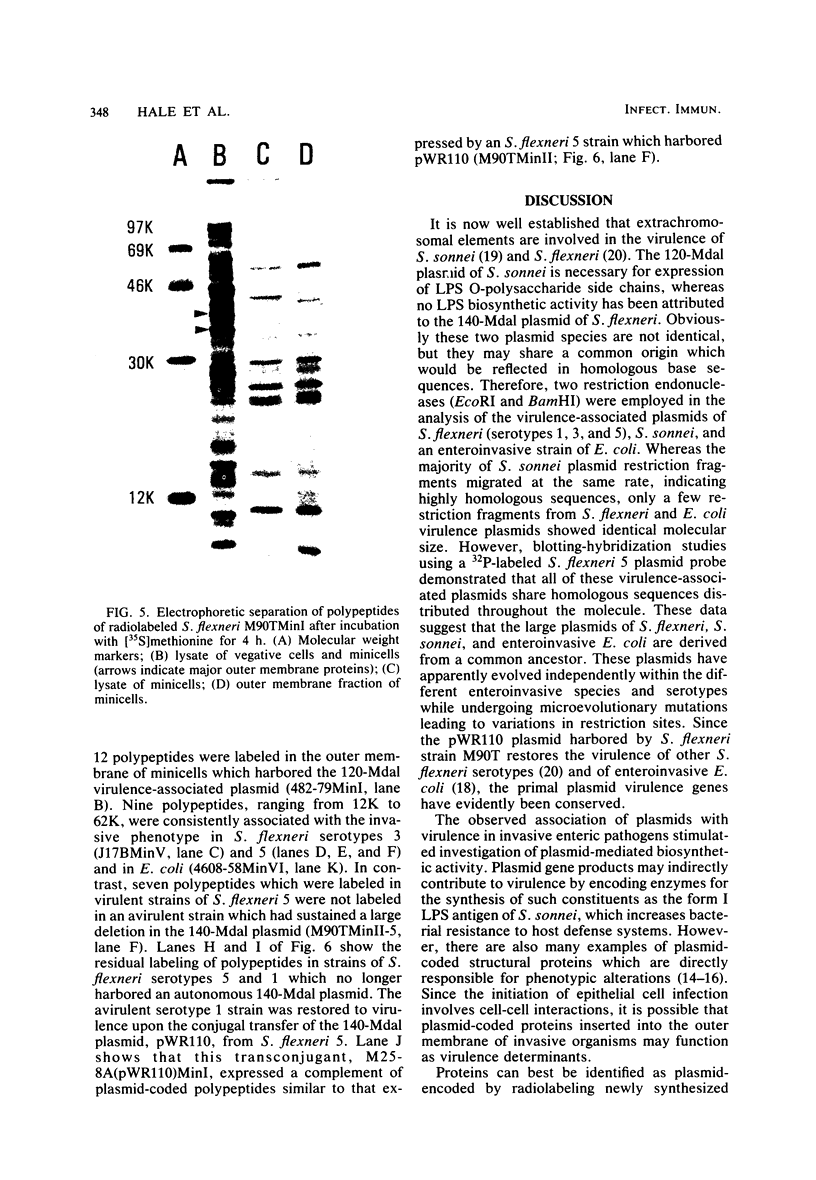
The 140-megadalton plasmids of Shigella flexneri serotypes 1, 3, and 5, in addition to the 120-megadalton plasmid of Shigella sonnei, are associated with virulence. The present study showed that a 140-megadalton plasmid is also associated with virulence in Escherichia coli. When these plasmids were cleaved with EcoRI or BamHI restriction endonucleases, considerable homology was evident in plasmids from S. sonnei strains, whereas only a few common fragments were observed among the S. flexneri and enteroinvasive E. coli plasmids. Nitrocellulose filter hybridization demonstrated that, despite variations in restriction sites, all these plasmids shared a considerable complement of homologous sequences. Minicell-producing strains were obtained by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. Transmission electron microscopy of infected HeLa cells showed that minicells from invasive strains retained the invasive phenotype. Sixteen polypeptides were labeled when S. flexneri 5 minicells were incubated with [35S]methionine. Fourteen of these plasmid-coded polypeptides were associated with the outer membrane in invasive strains of S. flexneri 5, and nine polypeptides of similar molecular weight were labeled in the outer membrane of invasive strains of S. flexneri 3, S. sonnei, and E. coli. Seven of the S. flexneri 5 polypeptides were not labeled in a noninvasive strain which had sustained a large deletion in the virulence-associated plasmid, and none were labeled in minicells which no longer harbored this plasmid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Rownd R., Baron L. S. GENETIC HOMOLOGY BETWEEN ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12 AND SALMONELLA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1303–1312. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1303-1312.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrazza D., Levy S. B. Biochemical and immunological characterization of an R plasmid-encoded protein with properties resembling those of major cellular outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):149–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.149-158.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Gemski P., Baron L. S., Labrec E. H. A Chromosomal Locus Which Controls the Ability of Shigella flexneri to Evoke Keratoconjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.73-79.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Production, properties and utility of bacterial minicells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:1–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Griffin D. E. Isolation and characterization of minicell-producing mutants of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):297–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.297-302.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Sheahan D. G., Washington O., Formal S. B. Virulence of Shigella flexneri hybrids expressing Escherichia coli somatic antigens. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):104–111. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.104-111.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the host cell. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.887-894.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Washington O., Formal S. B. Genetic and physical evidence for plasmid control of Shigella sonnei form I cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.207-214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B., McMurry L., Palmer E. R factor proteins synthesized in Escherichia coli minicells: membrane-associated R factor proteins. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1464–1471. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1464-1471.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. R factor proteins synthesized in Escherichia coli minicells: incorporation studies with different R factors and detection of deoxyribonucleic acid-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1451–1463. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1451-1463.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll A., Manning P. A., Timmis K. N. Plasmid-determined resistance to serum bactericidal activity: a major outer membrane protein, the traT gene product, is responsible for plasmid-specified serum resistance in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):359–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.359-367.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., d'Hauteville H., Formal S. B., Toucas M. Plasmid-mediated invasiveness of "Shigella-like" Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 May-Jun;133(3):351–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P., David M., Toucas M. Corrélation entre la perte d'ADN plasmidique et le passage de la phase I virulente à la phase II avirulente chez Shigella sonnei. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Mar 31;290(13):879–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C., Deutch C. E., Soffer R. L. Transfer of methionyl residues by leucyl, phenylalanyl-tRNA-protein transferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):584–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]