Abstract
The virulence of two previously described Staphylococcus epidermidis strains was examined in an experimental model of foreign body infection in mice. Animals challenged with the slime-producing strain developed three times as many infections as animals challenged with the strain that did not produce slime (P less than 0.001). Bacterial isolates recovered from the infected sites retained the characteristics of the inoculated strain. Animals without foreign bodies but challenged in a similar manner with either staphylococcal strain did not become infected. Thus, the presence of a foreign body predisposed the animals to S. epidermidis infection. These results indicate that the production of slime by S. epidermidis is a stable characteristic retained after animal passage and may be important in the pathogenesis of these infections.
Full text
PDF
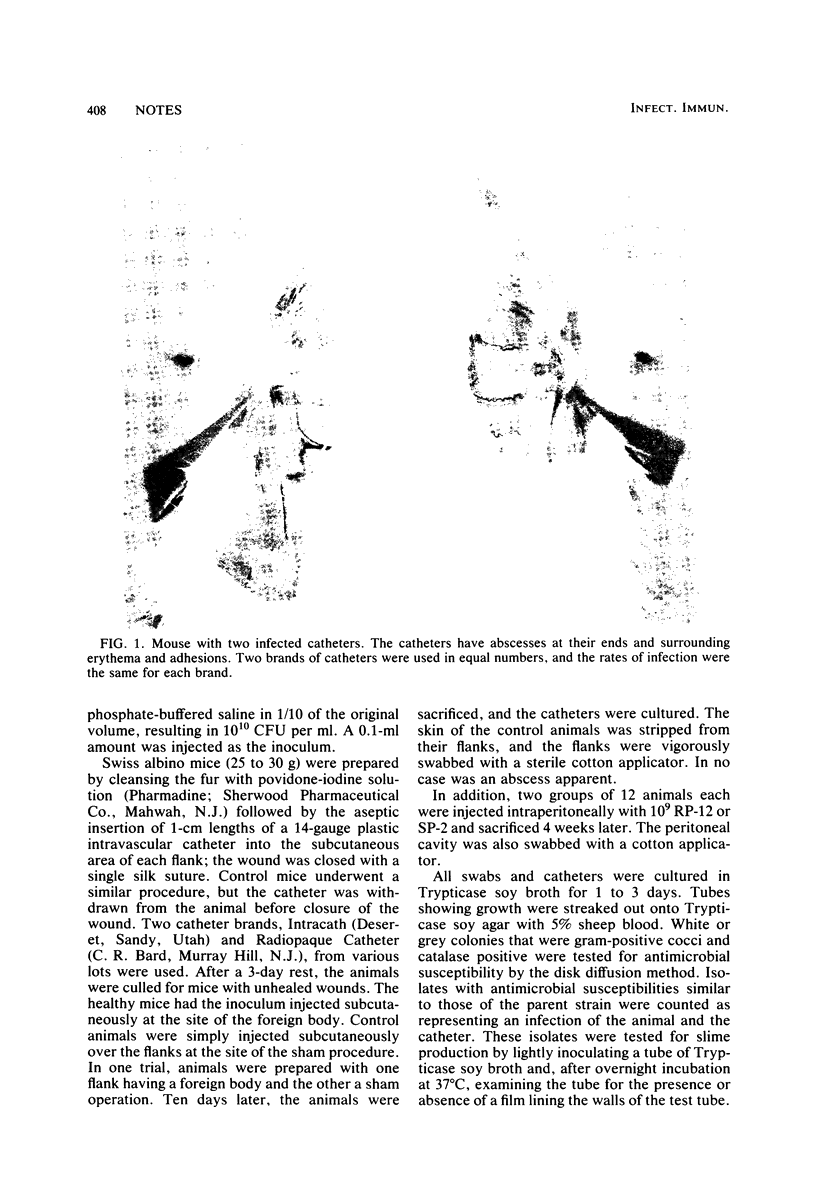

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriole V. T., Lyons R. W. Coagulase-negative staphylococcus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):533–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Vazquez G. J., Johnston J. L. Antibiotic prophylaxis of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):725–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellbusch L. C., Moiel R. H., Cheek W. R. Growing skull fractures. South Med J. 1977 May;70(5):555–558. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197705000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiman Y., Yoshida K. The relationship of capsular-type of Staphylococcus epidermidis to virulence and induction of resistance in the mouse. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;51(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb01237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Walsh J. A., Mayers M. M., Klein R. S., Steigbigel N. H. Antibiotic activity in vitro against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and therapy of an experimental infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):314–321. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Gardner P., Shillito J. Infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):543–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thörig L., Thompson J., Eulderink F. Effect of warfarin on the induction and course of experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):504–509. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.504-509.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez G. J., Archer G. L. Antibiotic therapy of experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):280–285. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Minegishi Y. Isolation of an encapsulated strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;47(2):299–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Waldvogel F. A., Vaudaux P., Nydegger U. E. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):487–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]