Abstract
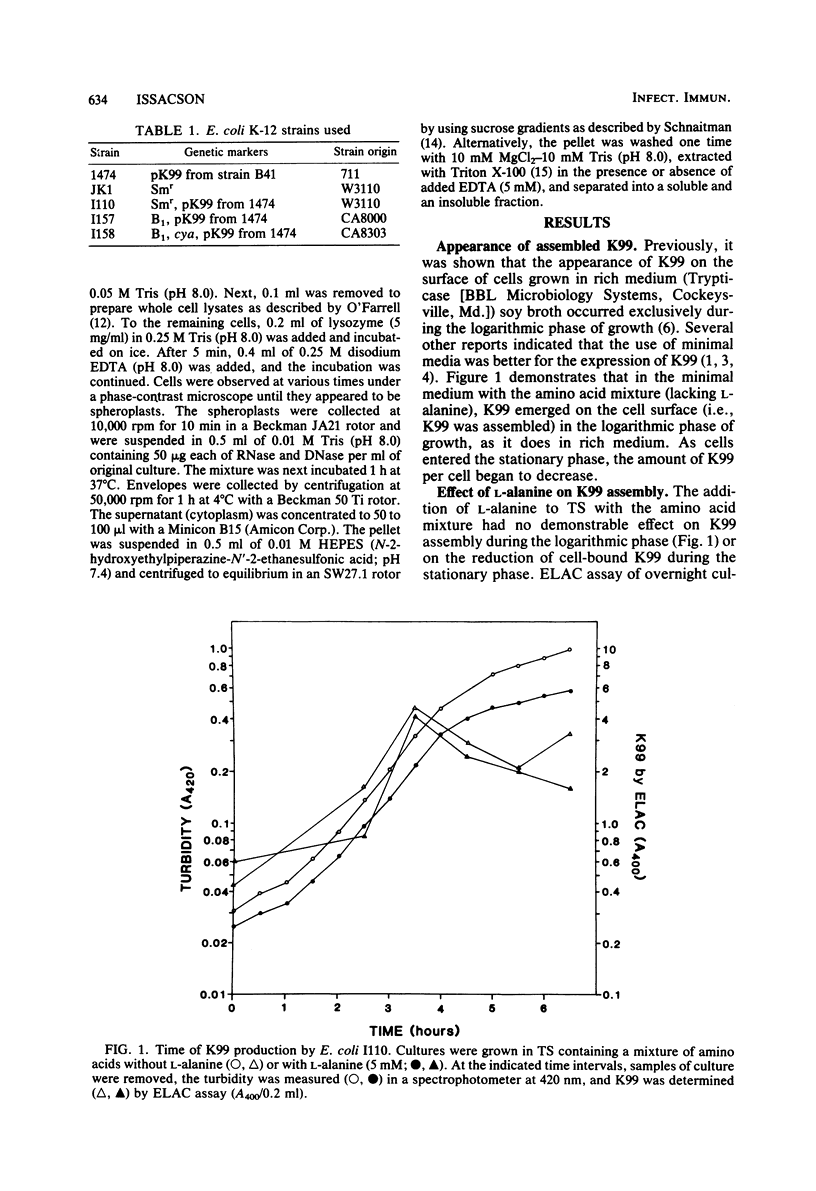
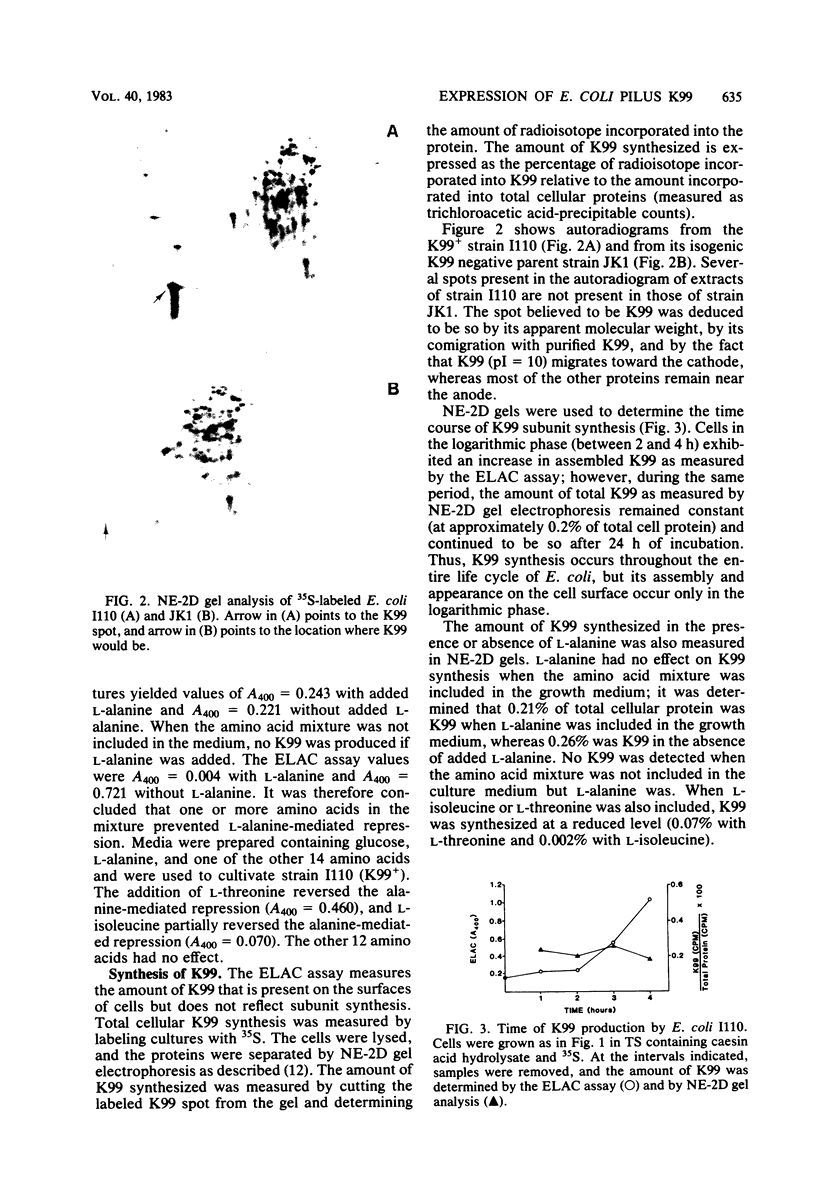
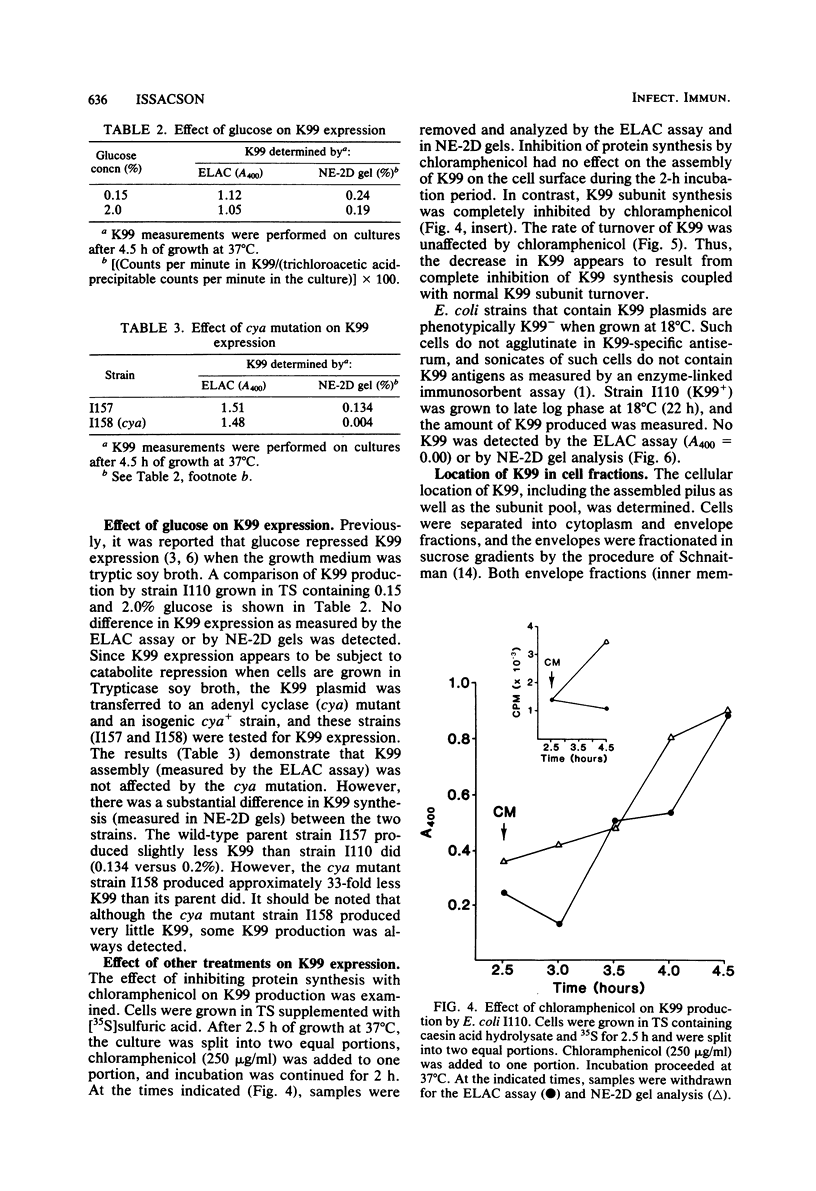
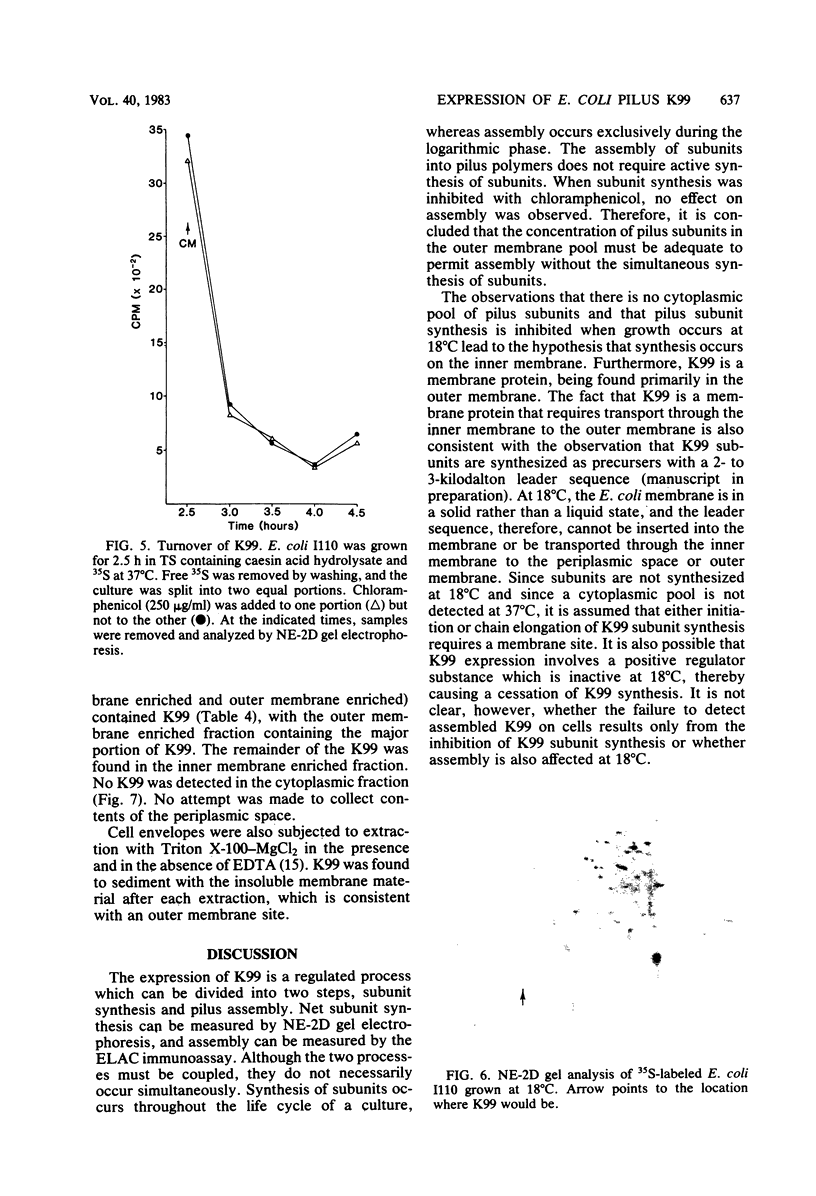
An immunoassay demonstrated that the assembled K99 pilus on the surface of Escherichia coli grown in minimal medium appeared during the logarithmic phase of growth, but the synthesis of K99 subunits, as measured by nonequilibrium two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, occurred throughout the life cycle of the cell. Contrary to other reports, the addition of glucose to the growth medium did not affect K99 pilus assembly or subunit synthesis, although in a K99+ adenyl cyclase (cya) mutant, subunit synthesis was reduced. There was no reduction in the amount of assembled K99 on the cell surface of the cya mutant compared with the wild-type parent. The addition of L-alanine to minimal medium repressed K99 synthesis. However, if L-threonine or L-isoleucine was also included in the growth medium, the effect of L-alanine was reduced. Chloramphenicol caused a complete inhibition of K99 subunit synthesis, but assembly proceeded normally. Growth at 18 degrees C inhibited both subunit synthesis and pilus assembly. Approximately 92% of all cellular K99 was associated with the outer membrane, and 4% was associated with the inner membrane. No K99 was detected in the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd Identification of a mutation affecting an alanine-alpha-ketoisovalerate transaminase activity in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 2;176(1):147–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00334306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Agterberg C. M. Detection of the K99 antigen by means of agglutination and immunoelectrophoresis in Escherichia coli isolates from calves and its correlation with entertoxigenicity. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1369–1377. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1369-1377.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Veldkamp J., Jansen W. H. Improved minca medium for the detection of K99 antigen in calf enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):676–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.676-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E. Factors affecting expression of the Escherichia coli pilus K99. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):190–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.190-194.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E. K99 surface antigen of Escherichia coli: purification and partial characterization. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.272-279.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Nagy B., Moon H. W. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: colonization and adhesion factors of pig enteropathogens that lack K88. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):531–539. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen J., Silverman P. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli K-12 chromosomal mutants defective in expression of F-plasmid functions: identification of genes cpxA and cpxB. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):60–67. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.60-67.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Nagy B., Isaacson R. E., Orskov I. Occurrence of K99 antigen on Escherichia coli isolated from pigs and colonization of pig ileum by K99+ enterotoxigenic E. coli from calves and pigs. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):614–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.614-620.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Regulation of lac operon expression: reappraisal of the theory of catabolite repression. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):947–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.947-954.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen W. A., Berg C. M. Analysis of an avtA::Mu d1(Ap lac) mutant: metabolic role of transaminase C. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.739-746.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Klaasen-Boor P., van Hees J. E. Biosynthesis of the K99 surface antigen is repressed by alanine. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):125–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.125-128.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





