Abstract
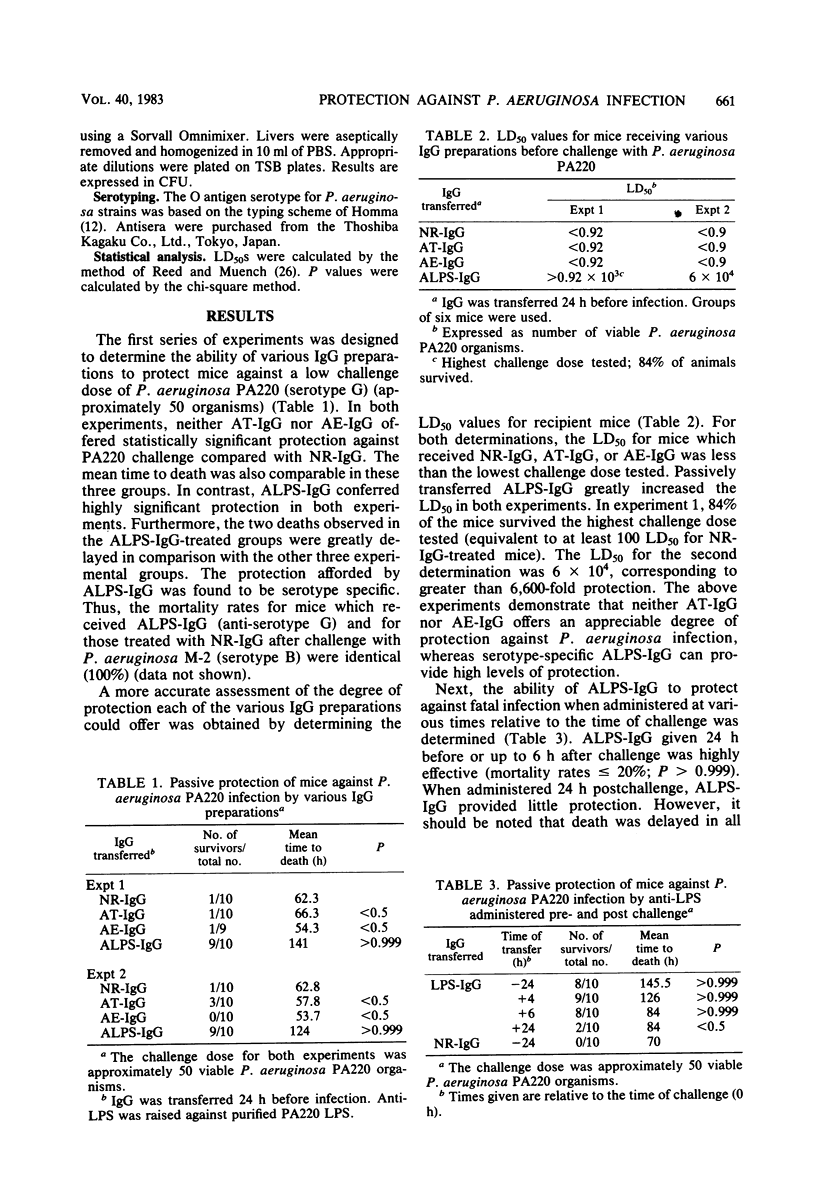
An experimental leukopenic mouse model was used to evaluate the protective capacities of immunoglobulin G (IgG) fractions directed against toxin A (AT-IgG), elastase (AE-IgG), and lipopolysaccharide (ALPS-IgG) against fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Statistically significant protection, as measured by long-term survival, was observed only when mice were treated with serotype-specific ALPS-IgG. The mean lethal dose for P. aeruginosa could be increased by as much as 6,600-fold for mice given ALPS-IgG as compared to mice which received only normal rabbit IgG. ALPS-IgG afforded high levels of protection, even when administered up to 6 h postchallenge. Experiments designed to monitor the growth and spread of a locally administered challenge showed that ALPS-IgG prevented bacteremia and organ colonization, which were pronounced in control animals. The effectiveness of combined antibiotic and immune therapy was tested. Gentamicin alone or in combination with AT-IgG or AE-IgG provided no detectable protection. However, its use with ALPS-IgG afforded substantially higher levels of protection than ALPS-IgG alone.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe K. E., Bass J. A., Young V. M., Straus D. C. Antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts in cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):115–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.115-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Simple model for the study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in leukopenic mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1067–1071. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1067-1071.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. B., Waxman F. J., Bennett B. T., Andersen B. R. Pseudomonas septicemia in neutropenic dogs. I. Treatment with granulocyte transfusions. Transfusion. 1974 Jan-Feb;14(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1974.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürer E., Cryz S. J., Jr, Dorner F., Nicolet J., Wanner M., Germanier R. Protection against colibacillosis in neonatal piglets by immunization of dams with procholeragenoid. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.887-894.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghbin M., Armstrong D., Murphy M. L. Controlled prospective trial of Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in children with acute leukemia. Cancer. 1973 Oct;32(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197310)32:4<761::aid-cncr2820320405>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian S., Regan W., Watson D., Haskell T. H. Isolation and characterization of antigenic components of a new heptavalent Pseudomonas vaccine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 17;229(7):209–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio229209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Andersen B. R., Amirault H. J. Passive immunity against pseudomonas sepsis during granulocytopenia. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1151–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1151-1155.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Andersen B. R. Evaluation of type-specific and non-type-specific pseudomonas vaccine for treatment of pseudomonas sepsis during granulocytopenia. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1139–1143. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1139-1143.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Andersen B. R., Zander A. R., Epstein R. B. Combined pre-immunization and granulocyte transfusion therapy for treatment of pseudomonas septicemia in neutropenic dogs. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 May;87(5):840–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. E., Alexander J. W., Fisher M. Clinical evaluation of Pseudomonas hyperimmune globulin. J Surg Res. 1973 Feb;14(2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(73)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Okada K., Morihara K. Effects of protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on skin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierowski J. A., Reynolds H. Y., Kauffman J. C., Durbin W. A., Graw R. G., Jr, Devlin H. B. Experimental pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in leukopenic dogs: prolongation of survival by combined treatment with passive antibody to Pseudomonas and granulocyte transfusions. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):438–446. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Burns R. P., Iglewski B. H. Corneal infections in mice with toxin A and elastase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):547–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Wood R. E., Robinson R. A., Levine A. S. Use of a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vaccine in pateints with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Sadoff J. C. High-molecular-weight polysaccharide antigen from Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):461–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.461-468.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S., Satterlee W., Young V. M., Serpick A. Empiric therapy with carbenicillin and gentamicin for febrile patients with cancer and granulocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 13;284(19):1061–1065. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105132841904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seid R. C., Jr, Sadoff J. C. Preparation and characterization of detoxified lipopolysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7305–7310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Meyer R. D., Armstrong D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Oct;79(4):518–527. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-4-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Douglas H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa vasculitis and bacteremia following conjunctivitis: a simple model of fatal pseudomonas infection in neutropenia. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):288–296. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


