Abstract
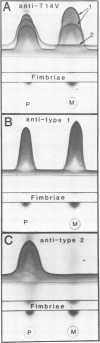
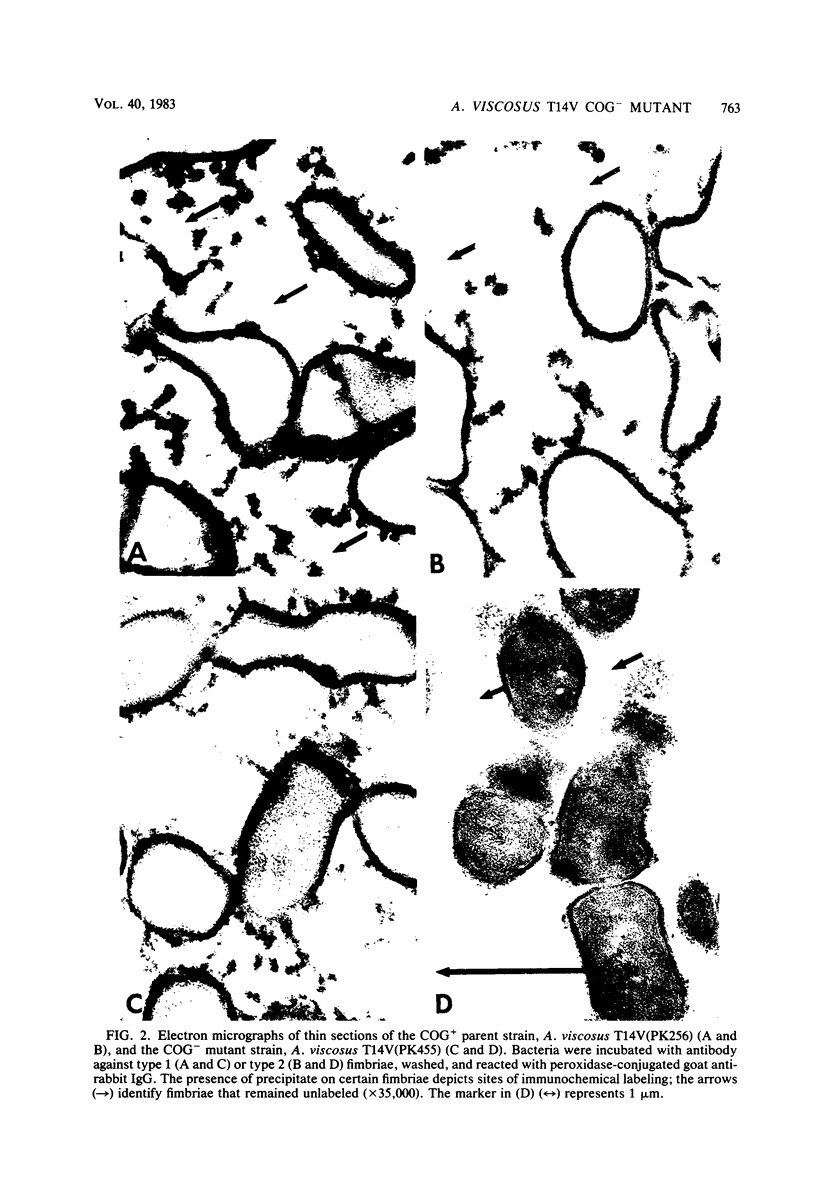
The coaggregation-defective (COG-) mutant Actinomyces viscosus T14V(PK455), which is unable to participate in lactose-sensitive adherence, and its COG+ parent were compared to structurally define the mutational loss of cell-associated lectin activity. Immunoelectrophoretic comparisons of crude extracts or isolated fimbriae from both strains demonstrated type 2 fimbriae (previously designated Ag2) in preparations obtained from the parent but none in those obtained from the mutant. This result was verified by the immunoelectron-microscopic identification of type 1 (previously designated Ag1 or VAl) and type 2 fimbriae on the parent organism but only type 1 fimbriae on the mutant. A comparison of the amounts of extractable fimbriae of each type and the capacity of the cells to bind 14C-labeled monoclonal antibodies specific for each fimbrial component showed that the mutational loss of type 2 fimbriae had no significant quantitative effect on fimbriation of the COG- mutant with type 1 structures. Cells of A. viscosus T14AV, a mutant with various adherence defects that include the COG- phenotype, displayed fimbriae of both types, but in greatly reduced amounts. Thus, the properties of mutant strain T14V(PK455) associated the lectin activity with type 2 fimbriae, whereas those of strain T14AV provided little insight into the mechanism of lactose-sensitive adherence. In addition, the precise nature of the cell surface modification displayed by strain T14V(PK455) provides clear evidence for the existence of distinct and independent fimbriae on A. viscosus T14V.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brecher S. M., van Houte J., Hammond B. F. Role of colonization in the virulence of Actinomyces viscosus strains T14-Vi and T14-Av. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):603–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.603-614.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. The use of monoclonal antibodies in the study of lactose-sensitive adherence of Actinomyces viscosus T14V. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Dec;28(Suppl):73s–79s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Vatter A. E., McIntire F. C. Identification of the virulence-associated antigen on the surface fibrils of Actinomyces viscosus T14. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):312–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.312-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Webb E. L., Wheeler T. T., Fischlschweiger W., Birdsell D. C., Mansheim B. J. Role of surface fimbriae (fibrils) in the adsorption of Actinomyces species to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):908–917. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.908-917.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. H., Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., Gabriel O. Neuraminidase-dependent hamagglutination of human erythrocytes by human strains of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):563–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.563-572.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Fillery E. D., Chan K. H., Grove D. A. Sialidase-enhanced lectin-like mechanism for Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.335-343.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond B. F., Steel C. F., Peindl K. S. Antigens and surface components associated with virulence of Actinomyces viscosus. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A19–A25. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500111011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N., Dearborn D. G. Labeling of proteins by reductive methylation using sodium cyanoborohydride. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4359–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective mutants of Actinomyces viscosus, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1200–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1200-1208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Williams B. L. Lactose-reversible coaggregation between oral actinomycetes and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.95-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Crosby L. K., Vatter A. E. Inhibitors of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34: beta-galactosides, related sugars, and anionic amphipathic compounds. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):371–378. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.371-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T., Fischlschweiger W., Birdsell D. C. Modification of surface composition of Actinomyces viscosus T14V and T14AV. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):934–944. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.934-944.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Berg R., Martin G. R., Foidart J. M., Robey P. G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revis G. J., Vatter A. E., Crowle A. J., Cisar J. O. Antibodies against the Ag2 fimbriae of Actinomyces viscosus T14V inhibit lactose-sensitive bacterial adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1217–1222. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1217-1222.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B., Birdsell D. C. Adherence of Actinomyces viscosus T14V and T14AV to hydroxyapatite surfaces in vitro and human teeth in vivo. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1066–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1066-1074.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B. Fibril-mediated adherence of Actinomyces viscosus to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.577-584.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]