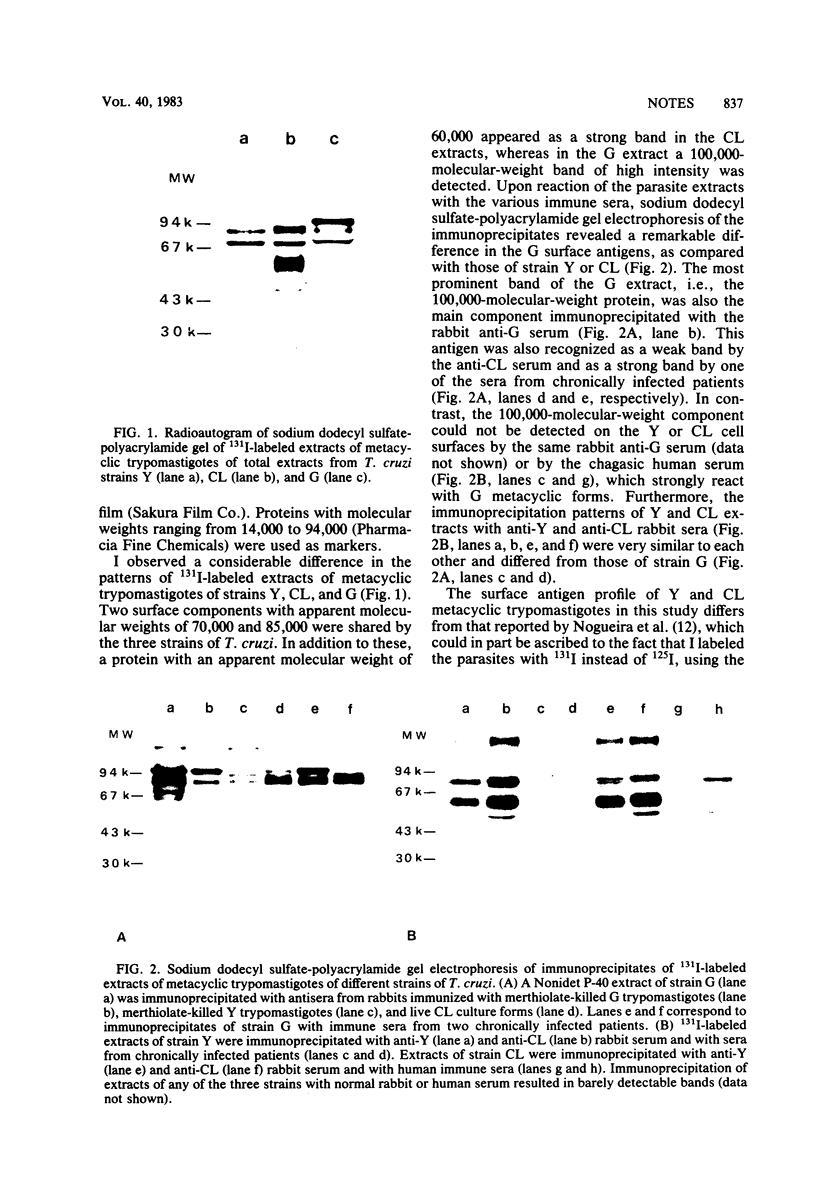
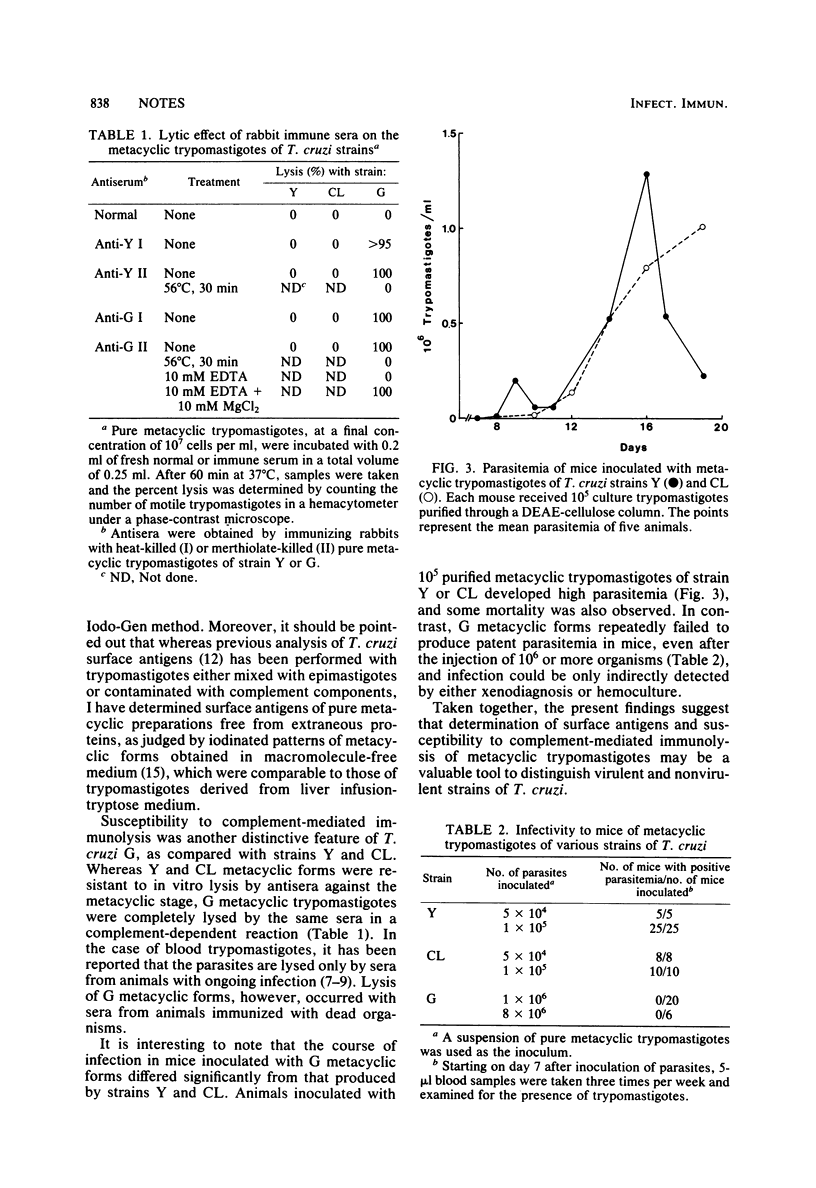
Abstract
The surface antigen makeup of metacyclic trypomastigote forms of strain G of Trypanosoma cruzi, which produce a subpatent infection in mice, differed from those of the virulent strains Y and CL. A 100,000-molecular-weight protein, barely detectable on the Y or CL cell surface, appeared as the main surface antigen of the G metacyclic trypomastigotes. In addition, the G metacyclic forms differed from those of the virulent strains in their susceptibility to complement-mediated immunolysis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Characterization of stages and strains of Trypanosoma cruzi by analysis of cell membrane components. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):855–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENER Z., CHIARI E. VARIA C OES MORFOL'OGICAS OBSERVADAS EM DIFERENTES AMOSTRAS DE TRYPANOSOMA CRUZI. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1963 Sep-Oct;5:220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMARGO E. P. GROWTH AND DIFFERENTIATION IN TRYPANOSOMA CRUZI. I. ORIGIN OF METACYCLIC TRYPANOSOMES IN LIQUID MEDIA. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1964 May-Jun;6:93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo E. P., Mattei D. M., Barbieri C. L., Morel C. M. Electrophoretic analysis of endonuclease-generated fragments of k-DNA, of esterase isoenzymes, and of surface proteins as aids for species identification of insect trypanosomatids. J Protozool. 1982 May;29(2):251–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb04022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. Cross-reactivity of lytic antibodies against blood forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Parasitol. 1976 Feb;62(1):134–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettli A. U., Brener Z. Resistance against Trypanosoma cruzi associated to anti-living trypomastigote antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2009–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Chaplan S., Tydings J. D., Unkeless J., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi. Surface antigens of blood and culture forms. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D. Trypanosoma cruzi: antigenic invariance of the cell surface glycoprotein. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Feb;49(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N. A macromolecule-free partially defined medium for Trypanosoma cruzi. J Protozool. 1975 Feb;22(1):128–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb00957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Potocnjak P., Nussenzweig V., Nussenzweig R. S. Biosynthesis of Pb44, the protective antigen of sporozoites of Plasmodium berghei. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1225–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




