Abstract
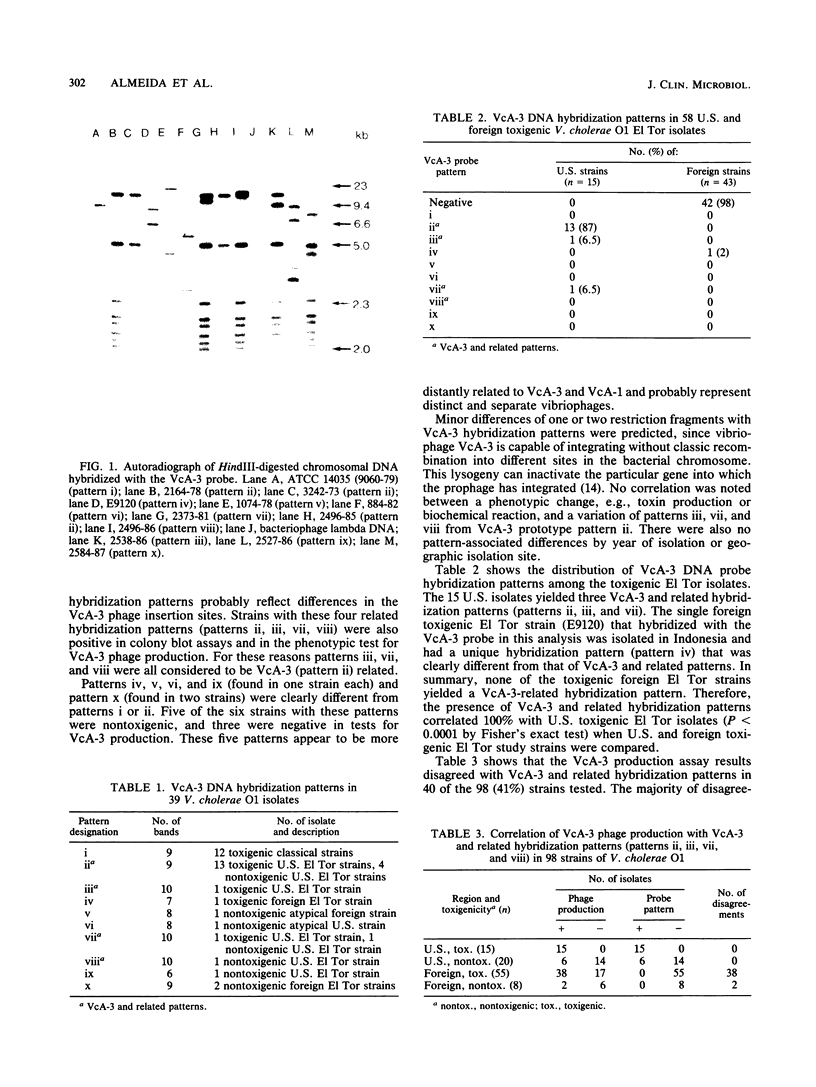
Toxigenic and nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1, El Tor biotype strains, which are endemic to the U.S. Gulf Coast, can be lysogenic for bacteriophage VcA-3. To evaluate the presence of VcA-3 as an indicator of toxigenicity and as an epidemic strain marker, phage production and the presence of phage and cholera toxin genes were assayed in 98 strains of V. cholerae O1 (35 U.S. and 63 foreign strains). By using a HindIII chromosomal digest for Southern blot analysis, 39 of the study strains hybridized with the VcA-3 probe in 10 banding patterns. The 15 toxigenic and 6 of the 20 nontoxigenic U.S. isolates gave four VcA-3-related patterns. Among the foreign isolates, 12 of 12 toxigenic classical biotype strains, 1 of 43 toxigenic El Tor biotype strains, and 3 of 8 nontoxigenic atypical strains gave six patterns that were clearly distinct from that of VcA-3. Compared with Southern blot analysis, the phage production assay had a sensitivity of 1.0 and a specificity of 0.48, while the colony hybridization assay had a sensitivity of 1.0 and a specificity of 0.77 for identification of VcA-3. Neither assay reliably identified the toxigenic Gulf Coast clone. The presence of VcA-3, as defined by Southern blot analysis, always separated toxigenic U.S. from foreign isolates and often from nontoxigenic U.S. isolates of V. cholerae O1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Sowers E. G., Puhr N. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Wachsmuth I. K. Comparison of a latex agglutination assay and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting cholera toxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.128-130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Wachsmuth K., Davis B. R., Bopp C. A., Chaiken B. P., Lee J. V. Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 strain from Mexico identical to United States isolates. Lancet. 1983 Oct 15;2(8355):912–912. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90894-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F., Evins G. M., Cook W. L., Almeida R., Hargrett-Bean N., Wachsmuth K. Genetic diversity among toxigenic and nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 isolated from the Western Hemisphere. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):225–233. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. L., Wachsmuth K., Johnson S. R., Birkness K. A., Samadi A. R. Persistence of plasmids, cholera toxin genes, and prophage DNA in classical Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):222–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.222-226.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. C., Romig W. R. Complete and Defective Bacteriophages of Classical Vibrio cholerae: Relationship to the Kappa Type Bacteriophage. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1231–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1231-1238.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. C., Romig W. R. Genetic basis of toxin production and pathogenesis in Vibrio cholerae: evidence against phage conversion. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):445–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.445-452.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S., Murphy J. R. Molecular epidemiological studies of United States Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae strains: integration site of mutator vibriophage VcA-3. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.224-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Romig W. R. Vibrio cholerae conjugative plasmid pSJ15 contains transposable prophage dVcA1. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):632–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.632-638.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Bradford H. B., Roberts N. C., Falkow S. Molecular epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae in the U.S. Gulf Coast. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.129-134.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Picardi J. L., Lieb S., Lee J. V., Roberts A., Hood M., Gunn R. A., Blake P. A. Isolation of nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae O group 1 from a patient with severe gastrointestinal disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):296–297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.296-297.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Bopp C. A., Fields P. I., Carrillo C. Difference between toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 from South America and US gulf coast. Lancet. 1991 May 4;337(8749):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91744-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K. Molecular epidemiology of bacterial infections: examples of methodology and of investigations of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):682–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]