Abstract
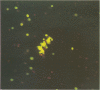
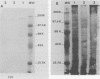
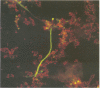
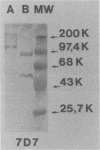
Because Pneumocystis carinii may be related to fungi, we evaluated the reactivities of monoclonal antibodies raised against P. carinii with a variety of fungi. Fifty-two fungi and six protozoa were evaluated by immunofluorescence. One of three monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) tested (MAb 7D7) reacted with 15 fungi but no protozoa. Saccharomyces cerevisiae showed the strongest reactivity by immunofluorescence. The reactive antigen was characterized for four fungi by the immunoblot technique. In all cases the antigen that was reactive with MAb 7D7 was larger than the P. carinii antigens that reacted with 7D7. In further studies with P. carinii, Aspergillus species, and S. cerevisiae, we found that MAb 7D7 reacted with a carbohydrate component in all organisms. The presence of an epitope that is common to P. carinii and a number of fungi further supports the fungal nature of P. carinii.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton E. G., Jr, Campbell W. G., Jr Pneumocystis carinii in lungs of rats treated with cortisone acetate. Ultrastructural observations relating to the life cycle. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):209–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Body B. A., Schwartzman J. D., Brown H., Gröschel D. H. Possible confusion of Aspergillus fumigatus and Pneumocystis carinii. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):603–604. doi: 10.1007/BF02014265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E., Hamilton J. G., Harkin J. C. Comparative study of the cell walls of the yeastlike and mycelial phases of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.466-474.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Edman U., Cao M., Lundgren B., Kovacs J. A., Santi D. V. Isolation and expression of the Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8625–8629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A., Masur H., Santi D. V., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):519–522. doi: 10.1038/334519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman U., Edman J. C., Lundgren B., Santi D. V. Isolation and expression of the Pneumocystis carinii thymidylate synthase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6503–6507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Stokes D. C., Cheatham A. B., Davis D. S., Hughes W. T. Development of murine monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):315–322. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill V. J., Evans G., Stock F., Parrillo J. E., Masur H., Kovacs J. A. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii by fluorescent-antibody stain using a combination of three monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1837–1840. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1837-1840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Ivey M. H., Worley M. A. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.125-133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Swan J. C., Drake J. C., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B. A., Masur H. Potent antipneumocystis and antitoxoplasma activities of piritrexim, a lipid-soluble antifolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):430–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Gill V., Swan J. C., Ognibene F., Shelhamer J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Prospective evaluation of a monoclonal antibody in diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Lundgren B., Swan J. C., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii: identification of specific antigens and characterization of antigenic differences between rat and human isolates. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):60–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Ng V. L., Masur H., Leoung G., Hadley W. K., Evans G., Lane H. C., Ognibene F. P., Shelhamer J., Parrillo J. E. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: improved detection in sputum with use of monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 10;318(10):589–593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803103181001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Cotton R., Lundgren J. D., Edman J. C., Kovacs J. A. Identification of Pneumocystis carinii chromosomes and mapping of five genes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1705–1710. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1705-1710.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Yoshida Y. Sporogony in Pneumocystis carinii: synaptonemal complexes and meiotic nuclear divisions observed in precysts. J Protozool. 1984 Aug;31(3):420–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. H., Schekman R. Lyticase: endoglucanase and protease activities that act together in yeast cell lysis. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):414–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.414-423.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R., Blase M. A., Walzer P. D., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: sequence from ribosomal RNA implies a close relationship with fungi. Exp Parasitol. 1989 May;68(4):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trull A. K., Warren R. E., Thiru S. Novel immunofluorescence test for Pneumocystis carinii. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):271–271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra J., Kucera K. Pneumocystis carinii delanoë, its ultrastructure and ultrastructural affinities. J Protozool. 1970 Aug;17(3):463–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J. M., Coleman D. L., Wofsy C. B., Luce J. M., Blumenfeld W., Hadley W. K., Ingram-Drake L., Volberding P. A., Hopewell P. C. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or pentamidine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):37–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]