Abstract
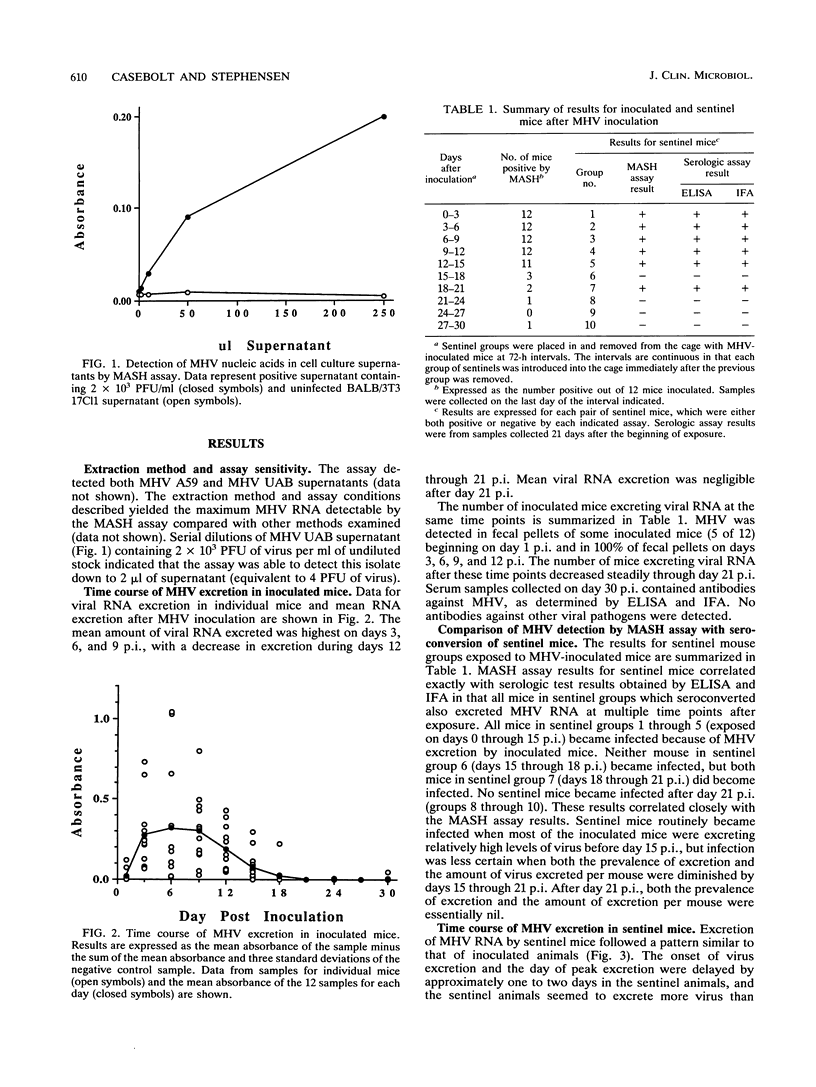
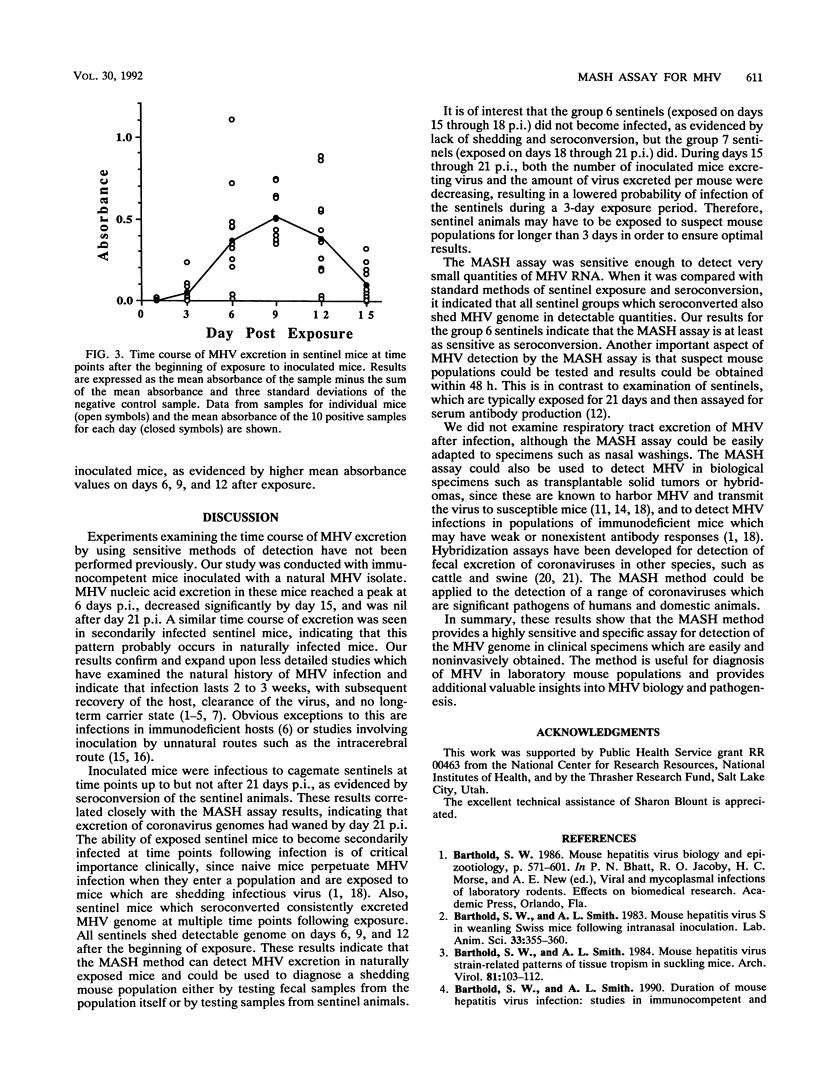
A monoclonal antibody solution hybridization (MASH) assay was developed to detect fecal excretion of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV). The assay used a biotinylated cDNA probe to detect viral RNA target sequences by hybridization in solution, capture of hybrids on the solid phase with antibiotin antibody, and immunoassay with an enzyme-labelled monoclonal antibody specific for DNA-RNA hybrids. The MASH assay was used to monitor the time course of enterotropic MHV excretion after oronasal inoculation. Infectivity of the inoculated mice was simultaneously monitored with sentinel animals. The MASH assay detected MHV excretion in all inoculated mice, with the highest mean excretion levels occurring from day 3 through day 9 postinoculation. Mean excretion then decreased gradually to below detection limits by day 21 postinoculation. Sentinels became infected on exposure to inoculated mice up to but not after day 21 postinoculation. Infected sentinel mice showed a time course of virus excretion similar to that of inoculated mice. These results indicate that the MASH assay is useful for rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of MHV in clinical specimens from laboratory mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIGGERS D. C., KRAFT L. M., SPRINZ H. LETHAL INTESTINAL VIRUS INFECTION OF MICE (LIVIM). AN IMPORTANT NEW MODEL FOR STUDY OF THE RESPONSE OF THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA TO INJURY. Am J Pathol. 1964 Sep;45:413–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L., Lord P. F., Bhatt P. N., Jacoby R. O., Main A. J. Epizootic coronaviral typhlocolitis in suckling mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1982 Aug;32(4):376–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L. Mouse hepatitis virus S in weanling Swiss mice following intranasal inoculation. Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Aug;33(4):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L. Mouse hepatitis virus strain--related patterns of tissue tropism in suckling mice. Arch Virol. 1984;81(1-2):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01309300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L., Povar M. L. Enterotropic mouse hepatitis virus infection in nude mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1985 Dec;35(6):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguslawski S. J., Smith D. E., Michalak M. A., Mickelson K. E., Yehle C. O., Patterson W. L., Carrico R. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 1;89(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casebolt D. B., Lindsey J. R., Cassell G. H. Prevalence rates of infectious agents among commercial breeding populations of rats and mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Jun;38(3):327–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casebolt D. B., Spalding D. M., Schoeb T. R., Lindsey J. R. Suppression of immune response induction in Peyer's patch lymphoid cells from mice infected with mouse hepatitis virus. Cell Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;109(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90295-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. J., Jr, Parker J. C. Murine virus contaminants of leukemia viruses and transplantable tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Oct;49(4):1139–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillehay D. L., Lehner N. D., Huerkamp M. J. The effectiveness of a microisolator cage system and sentinel mice for controlling and detecting MHV and Sendai virus infections. Lab Anim Sci. 1990 Jul;40(4):367–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon M. T., Schoeb T. R., Benjamin W. H., Jr, Lindsey J. R., Briles D. E. Modulation of resistance to Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice by mouse hepatitis virus (MHV). Microb Pathog. 1989 Feb;6(2):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90011-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Tunison L. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Selected mutants of mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (JHM strain) induce different CNS diseases. Pathobiology of disease induced by wild type and mutants ts8 and ts15 in BALB/c and SJL/J mice. Am J Pathol. 1982 Nov;109(2):157–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi E., Gilden D. H., Highkin M. K., Weiss S. R. Persistence of mouse hepatitis virus A59 RNA in a slow virus demyelinating infection in mice as detected by in situ hybridization. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):563–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.563-566.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Patterson W. L., Johnson P. K., Swartzell C. T., Wogoman F., Albarella J. P., Carrico R. J. Detection of bacteria by hybridization of rRNA with DNA-latex and immunodetection of hybrids. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1271-1276.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockley L. J., Kapke P. A., Lapps W., Brian D. A., Potgieter L. N., Woods R. Diagnosis of porcine and bovine enteric coronavirus infections using cloned cDNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1591-1596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek A., Dea S., Tijssen P. Detection of bovine enteric coronavirus in clinical specimens by hybridization with cDNA probes. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Apr;4(2):107–120. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90012-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., O'Meara C., Farzadegan H., Yolken R. Monoclonal antibody solution hybridization assay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.120-125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir E. C., Bhatt P. N., Barthold S. W., Cameron G. A., Simack P. A. Elimination of mouse hepatitis virus from a breeding colony by temporary cessation of breeding. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Aug;37(4):455–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


