Abstract
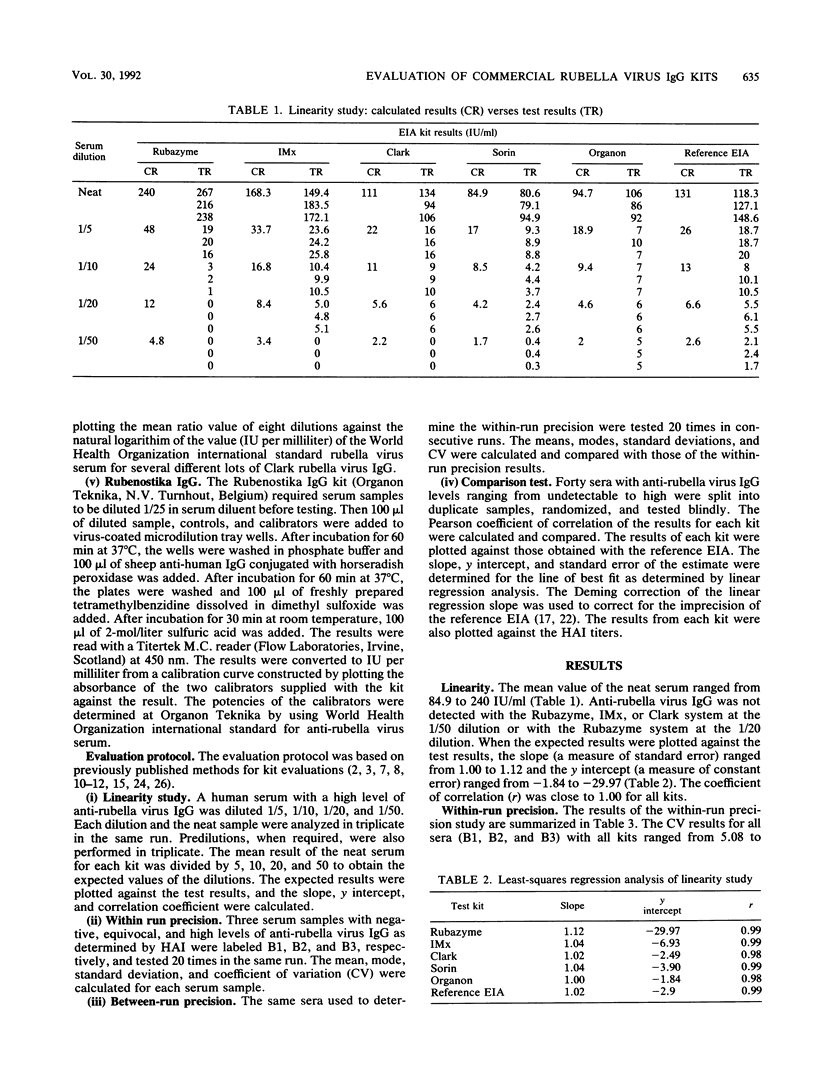
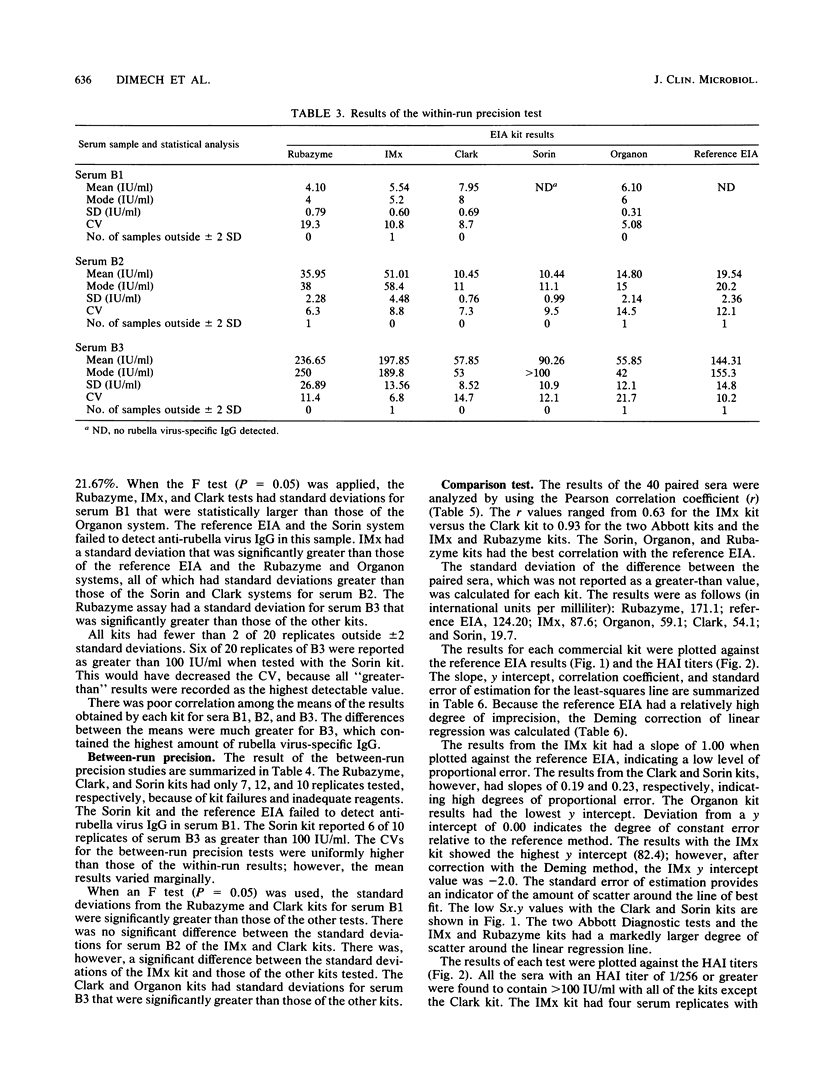
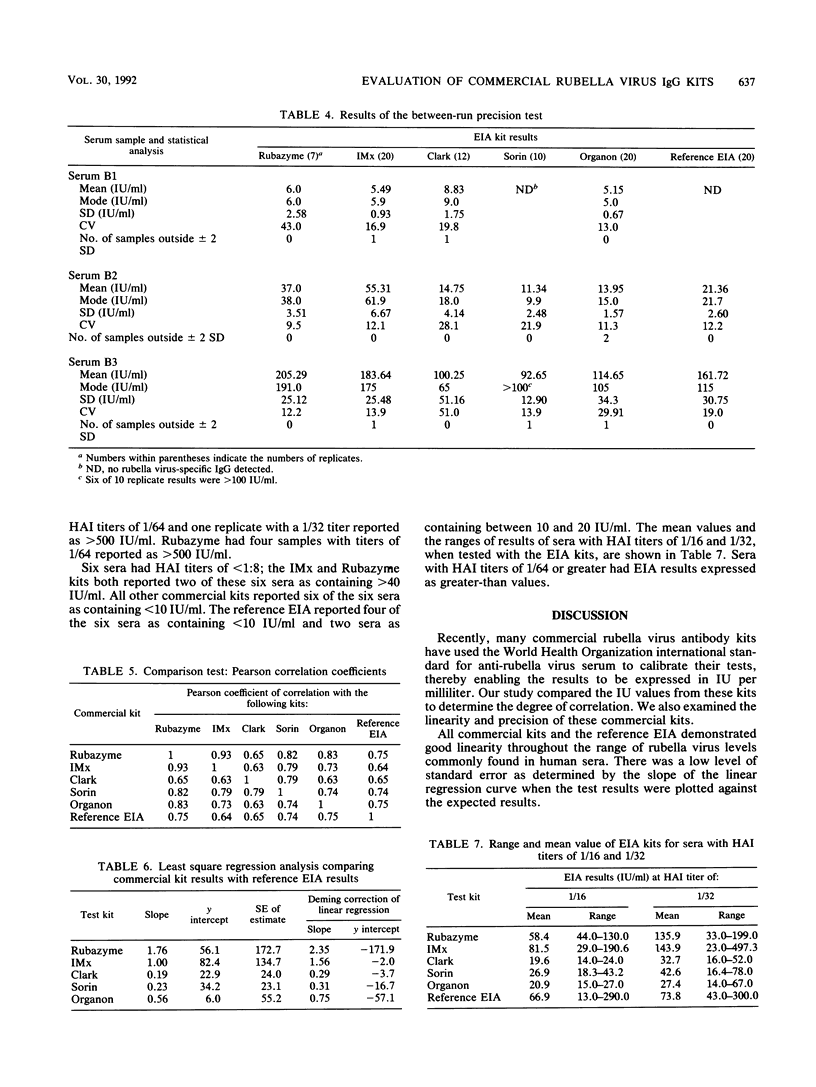
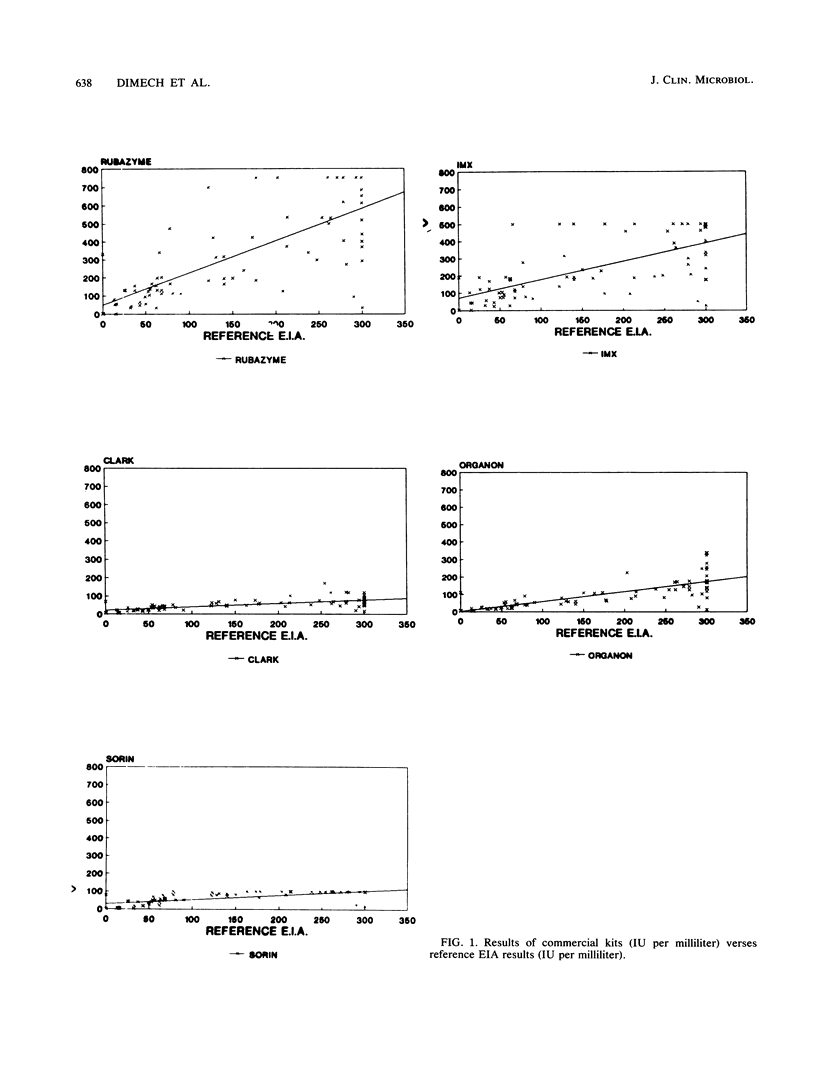
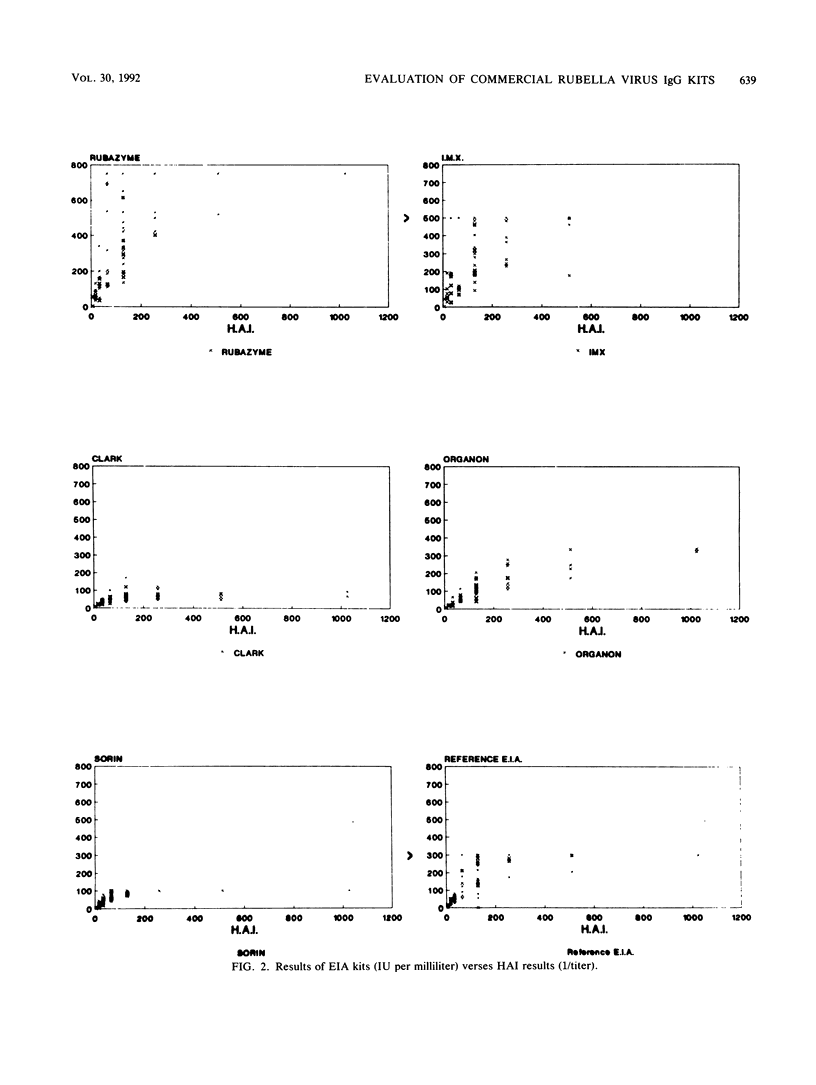
In a multicenter study, the consistency of international units expressed by five commercially available rubella virus immunoglobulin G kits was evaluated. The linearity and within-run and between-run precision were determined for each kit. All kits demonstrated good linearity and had within-run and between-run precision coefficients of variation ranging from 5.1 to 21.7% and from 9.5 to 51.0%, respectively. To compare the international units expressed, the results from 40 samples tested in duplicate were compared with the results of a reference enzyme immunoassay calibrated with World Health Organization international standard serum and a hemagglutination inhibition test. The results of the kits were plotted against those of the reference tests, and linear regression analysis was applied. The Pearson correlation coefficient ranged from 0.64 to 0.75 when the commercial kit results were compared with those of the reference enzyme immunoassay, indicating only a moderate degree of correlation. Therefore, the international units expressed by the commercial kits are insufficiently consistent to be of practical use in diagnostic clinical microbiology.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott G. G., Safford J. W., MacDonald R. G., Craine M. C., Applegren R. R. Development of automated immunoassays for immune status screening and serodiagnosis of rubella virus infection. J Virol Methods. 1990 Feb;27(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornbleet P. J., Gochman N. Incorrect least-squares regression coefficients in method-comparison analysis. Clin Chem. 1979 Mar;25(3):432–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. B., Thompson J. E., Pardue H. L. Characteristics of statistical parameters used to interpret least-squares results. Clin Chem. 1978 Apr;24(4):611–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Ho D. W., Cunningham A. L. Evaluation of rubella immune status by three commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):990–994. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.990-994.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore M., Mitchell J., Doan T., Nelson R., Winter G., Grandone C., Zeng K., Haraden R., Smith J., Harris K. The Abbott IMx automated benchtop immunochemistry analyzer system. Clin Chem. 1988 Sep;34(9):1726–1732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis B. H., Hatherley L. I., Walstab J. E., Taft L. I. Rubella screening and vaccination programme at a Melbourne maternity hospital. A five-year review. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 12;1(12):502–504. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. G., Singer R. Better laboratory evaluations of instruments and kits are required. Clin Chem. 1985 May;31(5):667–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney J. R., Cembrowski G. S. Need for improved instrument and kit evaluations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Sep;86(3):391–393. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleeman K. T., Kiefer D. J., Halbert S. P. Rubella antibodies detected by several commercial immunoassays in hemagglutination inhibition-negative sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1131–1137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1131-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P. H. A scheme for the evaluation of diagnostic kits. Ann Clin Biochem. 1978 May;15(3):136–145. doi: 10.1177/000456327801500129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J. E. Revised recommendation (1983) on evaluation of diagnostic kits. Part 2. Guidelines for the evaluation of clinical chemistry kits. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1983 Dec;21(12):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Evans B. K., Horstmann D. M. Use of enzyme immunoassays and the latex agglutination test to measure the temporal appearance of immunoglobulin G and M antibodies after natural infection or immunization with rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):745–748. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.745-748.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy-Robb I. W., Broughton P. M., Jennings R. D., McCormack J. J., Neill D. W., Saunders R. A., Warner M. A recommended scheme for the evaluation of kits in the clinical laboratory. Ann Clin Biochem. 1980 Sep;17(5):217–226. doi: 10.1177/000456328001700501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer L. E., Dyke J. W., Meglio F. D., Murray P. R., Crafts W., Niles A. C. Evaluation of microparticle enzyme immunoassays for immunoglobulins G and M to rubella virus and Toxoplasma gondii on the Abbott IMx automated analyzer. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2410–2413. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2410-2413.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall R. F., Jr, Kern C. W., Tenoso H. J. Test data matrix and results for linear regression analysis by method of W. E. Deming. Clin Chem. 1980 Feb;26(2):352–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simor A. E., Chua R., Low D. E. Evaluation of a new latex test and a new enzyme immunoassay for determination of rubella immunity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1582–1583. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1582-1583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P., Wilcox K. R., Edson D. C. Evaluation of assays for the detection of antibodies to rubella. A report based on data from the College of American Pathologists Surveys of 1982. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4 Suppl):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurrie I. J., Gilbert G. L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rubella immunoglobulin G: new method for attachment of antigens to microtiter plates. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):738–743. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.738-743.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. S., Pourfarzaneh M., Kamel R. S. Linear regression analysis by Deming's method. Clin Chem. 1980 Jun;26(7):1105–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steece R. S., Talley M. S., Skeels M. R., Lanier G. A. Problems in determining immune status in borderline specimens in an enzyme immunoassay for rubella immunoglobulin G antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):923–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.923-925.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westgard J. O., Hunt M. R. Use and interpretation of common statistical tests in method-comparison studies. Clin Chem. 1973 Jan;19(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


