Abstract
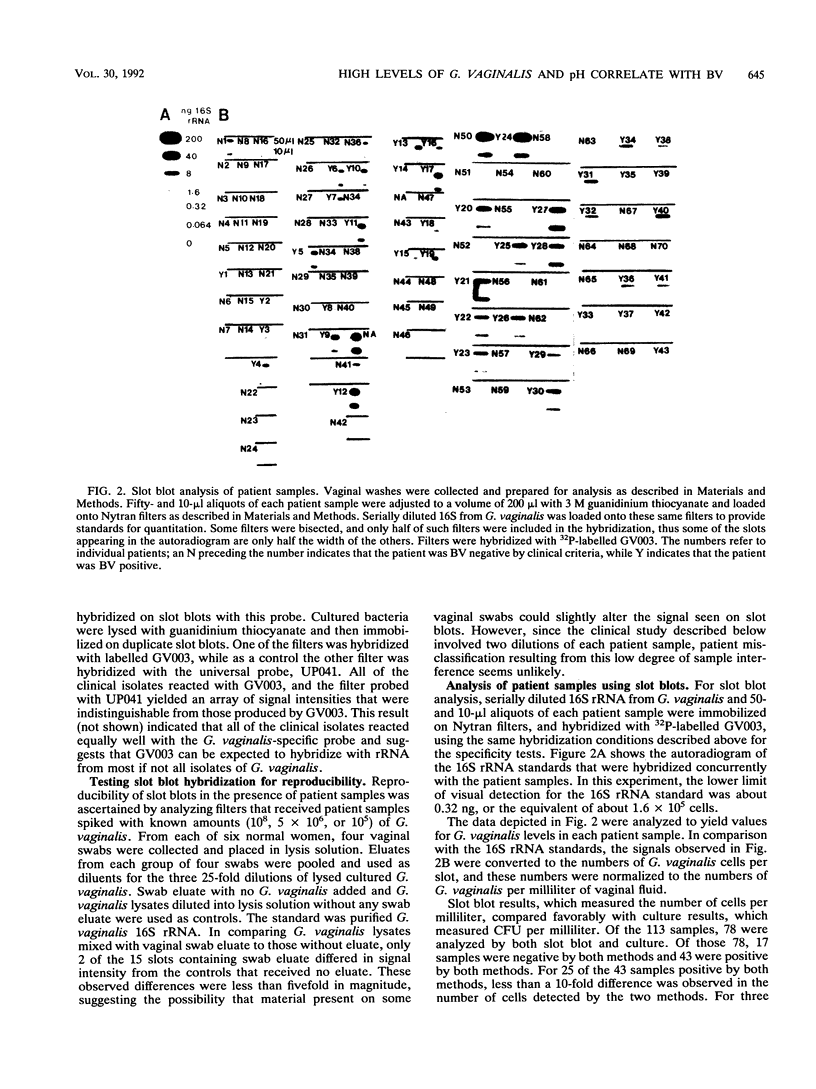
We have demonstrated a new approach to diagnosing bacterial vaginosis (BV) that is based on measuring the concentration of Gardnerella vaginalis in vaginal fluid with DNA probes. G. vaginalis is virtually always present at high concentrations in women who have BV but is also detected frequently in normal women, usually at concentrations of less than 10(7) CFU/ml of vaginal fluid. Elevated vaginal pH is another sensitive indicator of BV, although it can occur in conjunction with other conditions. We have proposed that quantitative measurements of G. vaginalis using specific DNA probes can serve as a useful aid in diagnosing BV, provided the vaginal pH is above 4.5. To test this hypothesis, a group of 113 women were first evaluated for BV by the standard set of clinical signs. Vaginal washes were collected, and aliquots were analyzed by quantitative culture for the concentration of G. vaginalis. Portions of these same samples were immobilized on nylon filters, along with standards for quantitation. The filters were incubated with a radiolabelled oligonucleotide specific for G. vaginalis 16S rRNA, and the subsequent autoradiographs were examined to determine levels of G. vaginalis in each sample. G. vaginalis at concentrations of greater than or equal to 2 x 10(7) CFU/ml and vaginal pH of greater than 4.5 were then analyzed for concurrence with the diagnoses based on clinical criteria. Results of this slot blot analysis gave a sensitivity of 95%, correctly categorizing 41 of 43 BV-positive specimens, and a specificity of 99%, correctly identifying 69 of 70 BV-negative specimens, compared with diagnosis based on clinical criteria.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsel R., Totten P. A., Spiegel C. A., Chen K. C., Eschenbach D., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis. Diagnostic criteria and microbial and epidemiologic associations. Am J Med. 1983 Jan;74(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Onderdonk A. B., Drude E., Goldstein C., Anderka M., Alpert S., McCormack W. M. Quantitative bacteriology of the vaginal flora. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):271–277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristiano L., Coffetti N., Dalvai G., Lorusso L., Lorenzi M. Bacterial vaginosis: prevalence in outpatients, association with some micro-organisms and laboratory indices. Genitourin Med. 1989 Dec;65(6):382–387. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.6.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNKELBERG W. E., Jr DIAGNOSIS OF HEMOPHILUS VAGINALIS VAGINITIS BY GRAM-STAINED SMEARS. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Apr 1;91:998–1000. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(65)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix K., Watanabe S. M., McArdle S., Lee D. I., Randolph C., Moncla B., Schwartz D. E. Species-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the identification of periodontal bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):319–323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.319-323.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbach D. A., Gravett M. G., Chen K. C., Hoyme U. B., Holmes K. K. Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy. An association with prematurity and postpartum complications. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1984;86:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbach D. A., Hillier S., Critchlow C., Stevens C., DeRouen T., Holmes K. K. Diagnosis and clinical manifestations of bacterial vaginosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Apr;158(4):819–828. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravett M. G., Hummel D., Eschenbach D. A., Holmes K. K. Preterm labor associated with subclinical amniotic fluid infection and with bacterial vaginosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Feb;67(2):229–237. doi: 10.1097/00006250-198602000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier S. L., Martius J., Krohn M., Kiviat N., Holmes K. K., Eschenbach D. A. A case-control study of chorioamnionic infection and histologic chorioamnionitis in prematurity. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 13;319(15):972–978. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810133191503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier S., Krohn M. A., Watts D. H., Wolner-Hanssen P., Eschenbach D. Microbiologic efficacy of intravaginal clindamycin cream for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Sep;76(3 Pt 1):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst E., Wathne B., Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A. Bacterial vaginosis: microbiological and clinical findings. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):536–541. doi: 10.1007/BF02014242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohn M. A., Hillier S. L., Eschenbach D. A. Comparison of methods for diagnosing bacterial vaginosis among pregnant women. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1266–1271. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1266-1271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livengood C. H., 3rd, Thomason J. L., Hill G. B. Bacterial vaginosis: diagnostic and pathogenetic findings during topical clindamycin therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Aug;163(2):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)91187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martius J., Krohn M. A., Hillier S. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K., Eschenbach D. A. Relationships of vaginal Lactobacillus species, cervical Chlamydia trachomatis, and bacterial vaginosis to preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;71(1):89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. M., Hayes C. H., Rosner B., Evrard J. R., Crockett V. A., Alpert S., Zinner S. H. Vaginal colonization with Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis). J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):740–745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. A., French J. I., Richter R., Franco-Buff A., Johnson A., Hillier S., Judson F. N., Todd J. K. Antenatal microbiologic and maternal risk factors associated with prematurity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;163(5 Pt 1):1465–1473. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90607-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkoff H., Grunebaum A. N., Schwarz R. H., Feldman J., Cummings M., Crombleholme W., Clark L., Pringle G., McCormack W. M. Risk factors for prematurity and premature rupture of membranes: a prospective study of the vaginal flora in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Dec 15;150(8):965–972. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(84)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent R. P., Krohn M. A., Hillier S. L. Reliability of diagnosing bacterial vaginosis is improved by a standardized method of gram stain interpretation. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.297-301.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Lin S. S., Hsieh T. T. The detection of Gardnerella vaginalis DNA sequences in uncultured clinical specimens with cloned G. vaginalis DNA as probes. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Oct;4(5):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90027-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E., Godts P., Vanderheyden J. The vaginal microbial flora in non-specific vaginitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;1(5):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02019976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver H. M., Sperling R. S., St Clair P. J., Gibbs R. S. Evidence relating bacterial vaginosis to intraamniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Sep;161(3):808–812. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Amsel R., Eschenbach D., Schoenknecht F., Holmes K. K. Anaerobic bacteria in nonspecific vaginitis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):601–607. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Amsel R., Holmes K. K. Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis by direct gram stain of vaginal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Blackwell A. L., Barlow D., Phillips I. Gardnerella vaginalis, anaerobes, and vaginal discharge. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1376–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92498-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason J. L., Gelbart S. M., Wilcoski L. M., Peterson A. K., Jilly B. J., Hamilton P. R. Proline aminopeptidase activity as a rapid diagnostic test to confirm bacterial vaginosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Apr;71(4):607–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason J. L., Schreckenberger P. C., Spellacy W. N., Riff L. J., LeBeau L. J. Clinical and microbiological characterization of patients with nonspecific vaginosis associated with motile, curved anaerobic rods. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):801–809. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Amsel R., Hale J., Piot P., Holmes K. K. Selective differential human blood bilayer media for isolation of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):141–147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.141-147.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. H., Krohn M. A., Hillier S. L., Eschenbach D. A. Bacterial vaginosis as a risk factor for post-cesarean endometritis. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jan;75(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]