Abstract
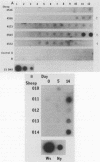
The DNA probe pCS20, which was cloned from the DNA of the Crystal Springs heartwater strain from Zimbabwe, cross-reacted with DNAs of heartwater strains from all endemic areas, including four heartwater strains from Zimbabwe, two strains from South Africa, one strain from Nigeria, and the Gardel strain from the Caribbean island of Guadeloupe. By nucleic acid hybridization, the pCS20 DNA probe detected Cowdria ruminantium DNA in all DNA preparations made from plasma samples from infected sheep before and during the febrile reaction. Synthetic oligonucleotides were prepared for amplification of specific C. ruminantium DNA sequences by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Amplification of two DNA products (181 and 279 bp) from pCS20 DNA and C. ruminantium genomic DNA of heartwater strains was demonstrated. In contrast, amplification of these products or any other products was not possible from genomic DNAs of Anaplasma marginale, Babesia bigemina, Trypanosoma brucei brucei, Escherichia coli, and bovine endothelial cells. The cross-reactivities of the 32P-labeled PCR products with genomic DNAs from several heartwater strains were similar to those with the pCS20 DNA probe. A nucleic acid-based test that uses hybridization assays and PCR provides a sensitive method for the detection of heartwater in both animals and ticks and has applications in epidemiological studies for the disease, which may allow for improved disease control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew H. R., Norval R. A. The carrier status of sheep, cattle and African buffalo recovered from heartwater. Vet Parasitol. 1989 Dec;34(3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(89)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Webb L., Carl M., Dasch G. A. Detection of rickettsiae in arthropod vectors by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. H., Jr, Suebsaeng L., Rooney W., Alecrim G. C., Dourado H. V., Wirth D. F. Specific DNA probe for the diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1434–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.3513309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezuidenhout J. D. Natural transmission of heartwater. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1987 Sep;54(3):349–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrom B., Yunker C. E. Improved culture conditions for Cowdria ruminantium (Rickettsiales), the agent of heartwater disease of domestic ruminants. Cytotechnology. 1990 Nov;4(3):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00563789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassol S. A., Poon M. C., Pal R., Naylor M. J., Culver-James J., Bowen T. J., Russell J. A., Krawetz S. A., Pon R. T., Hoar D. I. Primer-mediated enzymatic amplification of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA. Application to the early diagnosis of CMV infection in marrow transplant recipients. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1109–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI113990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P. A., Iams K., Brown W. C., Sohanpal B., ole-MoiYoi O. K. DNA probes detect genomic diversity in Theileria parva stocks. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Oct;25(3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Plessis J. L. A method for determining the Cowdria ruminantium infection rate of Amblyomma hebraeum: effects in mice injected with tick homogenates. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1985 Jun;52(2):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff W., Barbet A., Stiller D., Palmer G., Knowles D., Kocan K., Gorham J., McGuire T. Detection of Anaplasma-marginale-infected tick vectors by using a cloned DNA probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):919–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H., Feinstone S. M., Unoura M., Kobayashi K., Hattori N., Purcell R. H. Detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):312–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser D. R., Cook G. A., Ochs D. E., Bailey C. P., McKane M. R., Donelson J. E. Detection of Trypanosoma congolense and Trypanosoma brucei subspecies by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Parasitology. 1989 Aug;99(Pt 1):57–66. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000061023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prozesky L. Diagnosis of heartwater at post-mortem in ruminants and the confirmation of Cowdria ruminantium in mice. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1987 Sep;54(3):301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savva D., Morris J. C., Johnson J. D., Holliman R. E. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of Toxoplasma gondii. J Med Microbiol. 1990 May;32(1):25–31. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shompole S., Waghela S. D., Rurangirwa F. R., McGuire T. C. Cloned DNA probes identify Anaplasma ovis in goats and reveal a high prevalence of infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2730–2735. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2730-2735.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirasophon W., Ponglikitmongkol M., Wilairat P., Boonsaeng V., Panyim S. A novel detection of a single Plasmodium falciparum in infected blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uilenberg G. Heartwater (Cowdria ruminantium infection): current status. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1983;27:427–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waghela S. D., Rurangirwa F. R., Mahan S. M., Yunker C. E., Crawford T. B., Barbet A. F., Burridge M. J., McGuire T. C. A cloned DNA probe identifies Cowdria ruminantium in Amblyomma variegatum ticks. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2571–2577. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2571-2577.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]