Abstract
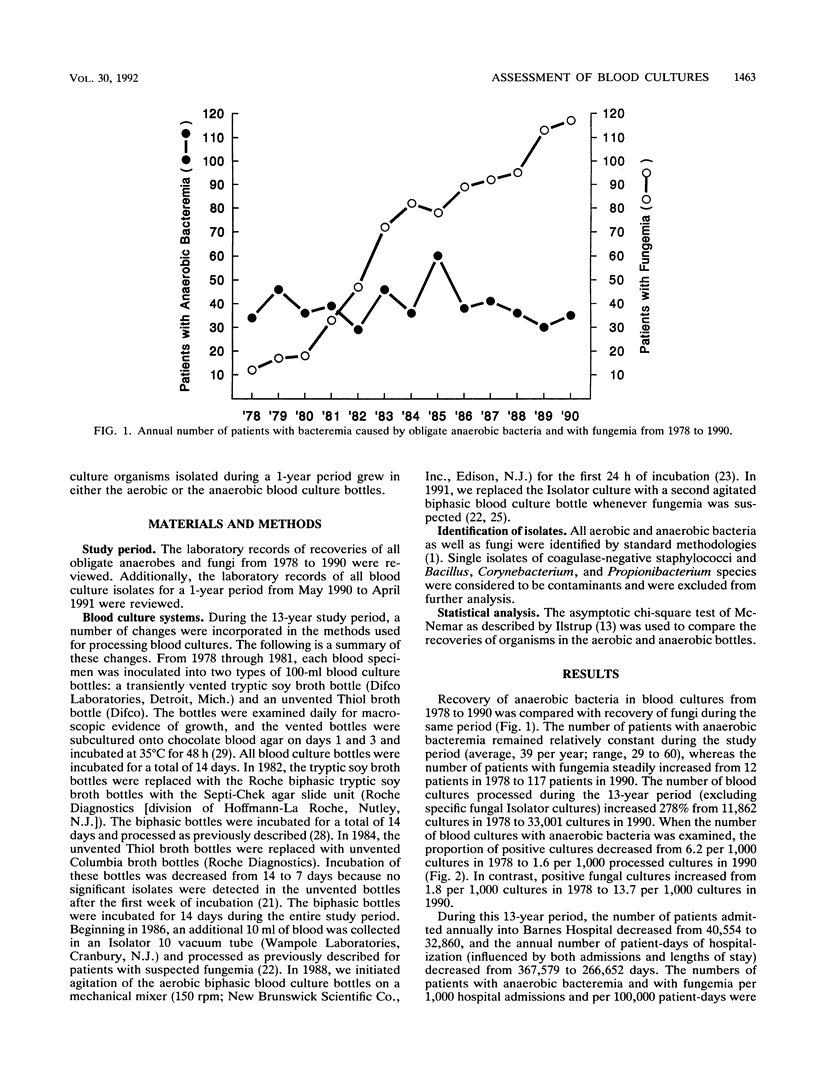
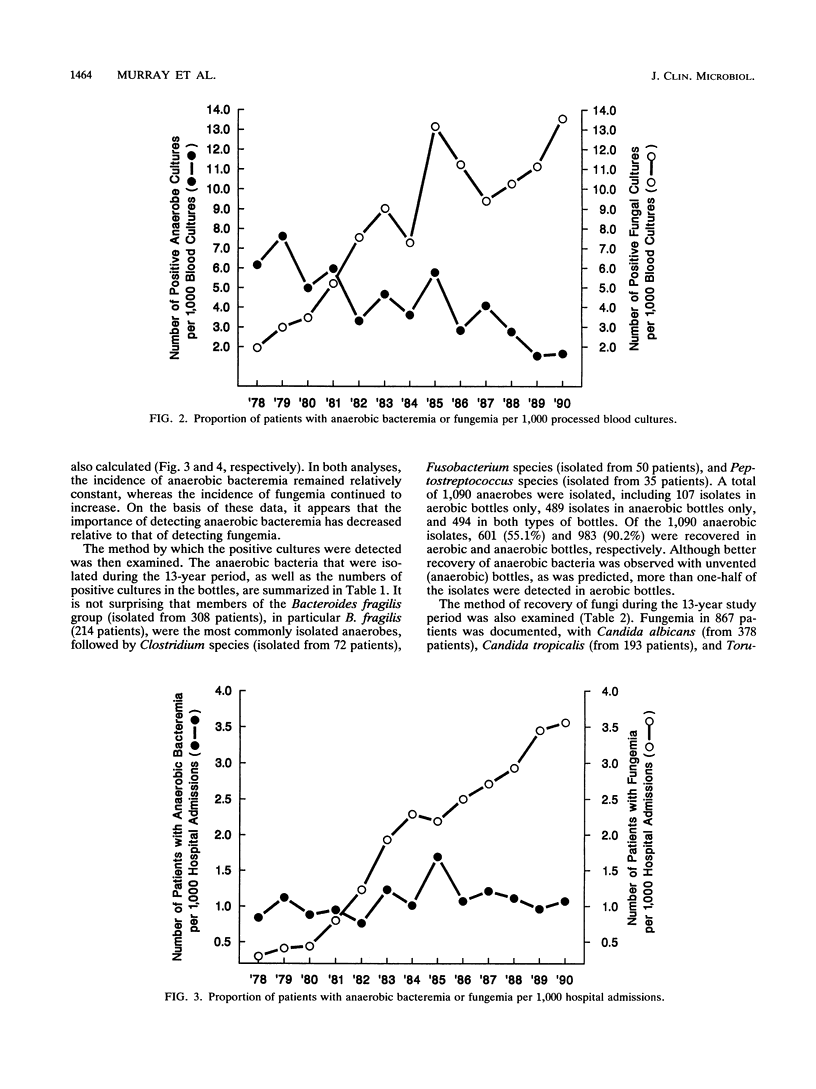
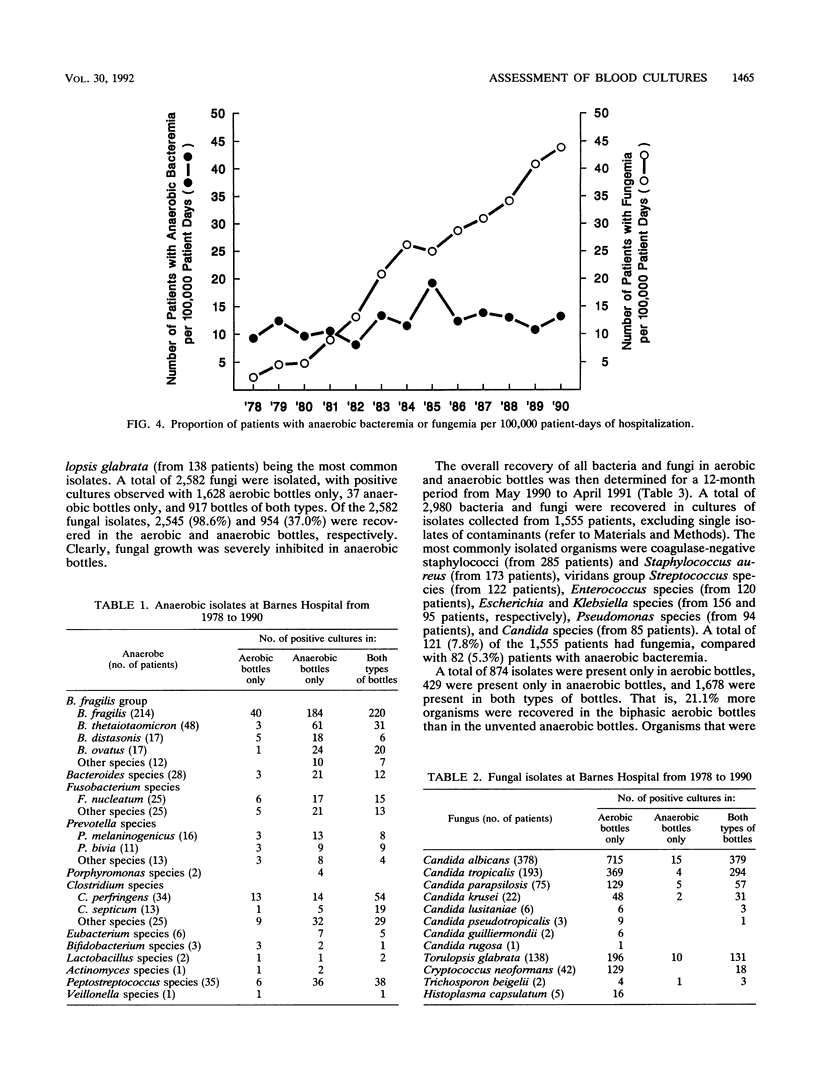
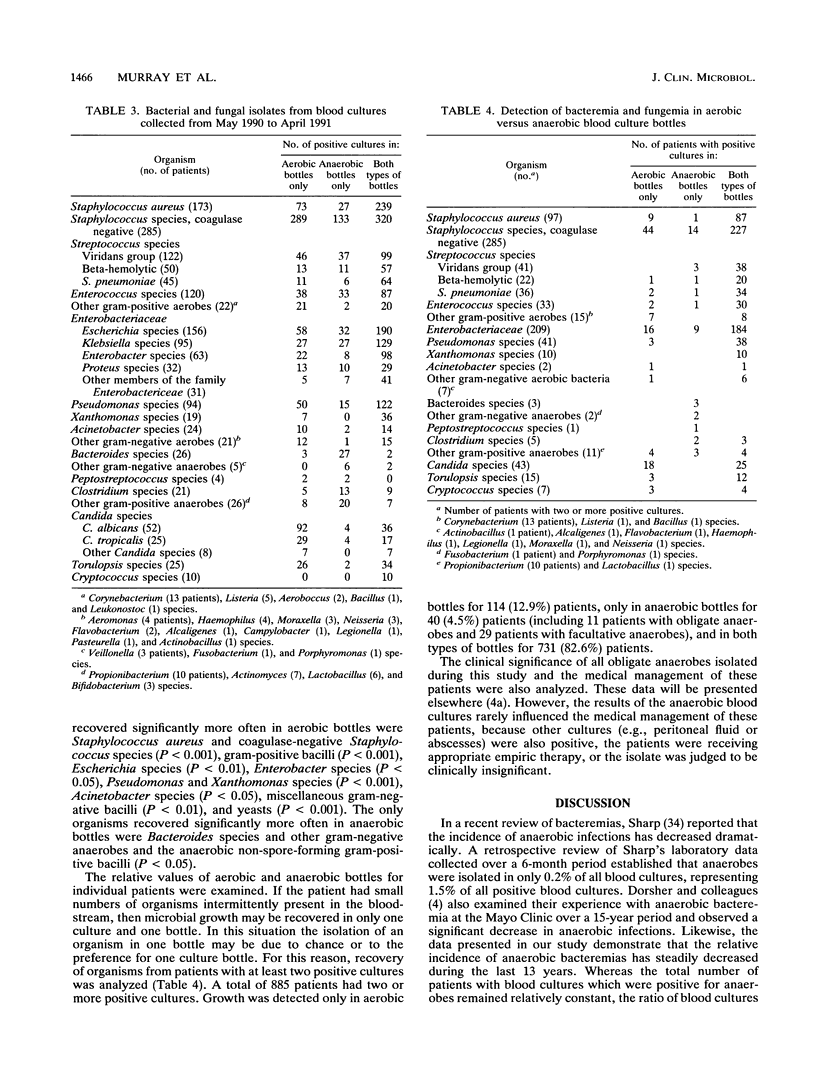
Recent reports have documented a decrease in anaerobic bacteremias and have questioned the need for routine anaerobic blood cultures. At the same time, we and others have noted an increase in fungal bloodstream infections. In this two-part study, we first compared recoveries of obligate anaerobic bacteria with those of fungi over a 13-year period and then examined the recoveries of all bacteria and fungi in aerobic and anaerobic blood culture bottles during a 12-month period. During the 13-year period, the number of patients with anaerobic bacteremia remained relatively constant (average, 39 patients per year), while the incidence of fungemia steadily increased, from 12 patients in 1978 to 117 patients in 1990. Of the 1,090 anaerobic isolates, 55.1 and 90.2% were recovered in aerobic and anaerobic bottles, respectively, compared with 98.6 and 37.0% of the 2,582 fungi. During the 12-month period of evaluation, 2,980 bacteria and fungi were recovered in cultures collected from 1,555 patients. Overall, 21.1% more organisms were recovered in aerobic bottles than in anaerobic bottles, including significantly more Staphylococcus species; gram-positive aerobic bacilli; Escherichia, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Xanthomonas, and Acinetobacter species; miscellaneous gram-negative bacilli; and yeasts. Only anaerobic gram-negative bacilli and non-spore-forming gram-positive bacilli were isolated more commonly in anaerobic bottles. These data support the concepts that bacteremia caused by obligate anaerobic bacteria is decreasing relative to sepsis caused by other bacteria and fungi and that the routine use of unvented anaerobic blood culture bottles reduces the recovery of common aerobic bloodstream pathogens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blazevic D. J., Stemper J. E., Matsen J. M. Effect of aerobic and anaerobic atmospheres on isolation of organisms from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):154–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.154-156.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannon P., Kiehn T. E. Large-scale clinical comparison of the lysis-centrifugation and radiometric systems for blood culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):951–954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.951-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsher C. W., Rosenblatt J. E., Wilson W. R., Ilstrup D. M. Anaerobic bacteremia: decreasing rate over a 15-year period. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):633–636. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Kiehn T. E., Beebe J. L., McCarthy L. R. Critical analysis of hypertonic medium and agitation in detection of bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):216–224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.216-224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Romero L., Telenti A., Thompson R. L., Roberts G. D. Polymicrobial fungemia: microbiology, clinical features, and significance. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11(2):208–212. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of three blood culture media with tryptic soy broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):299–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.299-301.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Effect of volume of blood cultured on detection of bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.643-645.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness J. L., Hall M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Effects of atmosphere of incubation and of routine subcultures on detection of bacteremia in vacuum blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):296–299. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.296-299.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins B. L., Peterson E. M., de la Maza L. M. Improvement of positive blood culture detection by agitation. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., McLimans C. A., Wright A. J., Thompson R. L., Wilson W. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Microbiological and clinical evaluation of the isolator lysis-centrifugation blood culture tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):864–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.864-869.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Wong B., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Fungemia in a cancer hospital: changing frequency, earlier onset, and results of therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):646–655. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.5.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilstrup D. M. Statistical methods in microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):219–226. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd The importance of volume of blood cultured in the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;1(2):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. J., Gottschall R. L., Schwabe L. D., Randall E. L. Effect of agitation and frequent subculturing on recovery of aerobic and facultative pathogens by Roche Septi-Chek and BACTEC blood culture systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):312–315. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.312-315.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. J., Watanakunakorn C. Hospital-acquired fungemia. Its natural course and clinical significance. Am J Med. 1979 Jul;67(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komshian S. V., Uwaydah A. K., Sobel J. D., Crane L. R. Fungemia caused by Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata in the hospitalized patient: frequency, characteristics, and evaluation of factors influencing outcome. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):379–390. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koontz F. P., Flint K. K., Reynolds J. K., Allen S. D. Multicenter comparison of the high volume (10 ml) NR BACTEC PLUS system and the standard (5 ml) NR BACTEC system. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;14(2):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90044-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Carpentier F., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Fungemia in the immunocompromised host. Changing patterns, antigenemia, high mortality. Am J Med. 1981 Sep;71(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. J., Jr, Freer C. V., Searcy M. A., Landry S. M., Wenzel R. P. Nosocomial bloodstream infections: secular trends in a statewide surveillance program in Virginia. Infect Control. 1986 Nov;7(11):550–553. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700065309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R. Comparison of the lysis-centrifugation and agitated biphasic blood culture systems for detection of fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):96–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.96-98.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R. Determination of the optimum incubation period of blood culture broths for the detection of clinically significant septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):481–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.481-485.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Niles A. C., Heeren R. L., Curren M. M., James L. E., Hoppe-Bauer J. E. Comparative evaluation of the oxoid signal and Roche Septi-Chek blood culture systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2526–2530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2526-2530.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Sondag J. E. Evaluation of routine subcultures of macroscopically negative blood cultures for detection of anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):427–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.427-430.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Spizzo A. W., Niles A. C. Clinical comparison of the recoveries of bloodstream pathogens in Septi-Chek brain heart infusion broth with saponin, Septi-Chek tryptic soy broth, and the isolator lysis-centrifugation system. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):901–905. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.901-905.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paisley J. W., Rosenblatt J. E., Hall M., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of a routine anaerobic subculture of blood cultures for detection of anaerobic bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):764–766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.764-766.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Sibley T. K., Westfall L. M., Hoppe-Bauer J. E., Keating M. A., Murray P. R. Clinical laboratory comparison of a slide blood culture system with a conventional broth system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.525-530.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Westfall L. M., Murray P. R. Value of routine aerobic subculturing of unvented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):601–604. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.601-604.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G., Murray P. R. Current controversies in the detection of septicemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;5(5):487–491. doi: 10.1007/BF02017688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plorde J. J., Tenover F. C., Carlson L. G. Specimen volume versus yield in the BACTEC blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):292–295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.292-295.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of fungi in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.309-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Reller L. B., Mirrett S., Wang W. L., Weinstein M. P. Controlled evaluation of the volume of blood cultured in detection of bacteremia and fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.558-561.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Reller L. B., Mirrett S., Weinstein M. P., Wang W. L. Controlled evaluation of the effect of atmosphere of incubation on detection of bacteremia and fungemia in supplemented peptone broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.437-442.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Ilstrup D. M. Blood cultures: issues and controversies. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):792–802. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Mirrett S., Reimer L. G., Reller L. B. Effect of agitation and terminal subcultures on yield and speed of detection of the Oxoid Signal blood culture system versus the BACTEC radiometric system. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):427–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.427-430.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P., Pfaller M. A. Candida species: emerging hospital bloodstream pathogens. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1991 Sep;12(9):523–524. doi: 10.1086/646403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whimbey E., Kiehn T. E., Brannon P., Blevins A., Armstrong D. Bacteremia and fungemia in patients with neoplastic disease. Am J Med. 1987 Apr;82(4):723–730. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Martin W. J., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Anaerobic bacteremia. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Sep;47(9):639–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


