Abstract
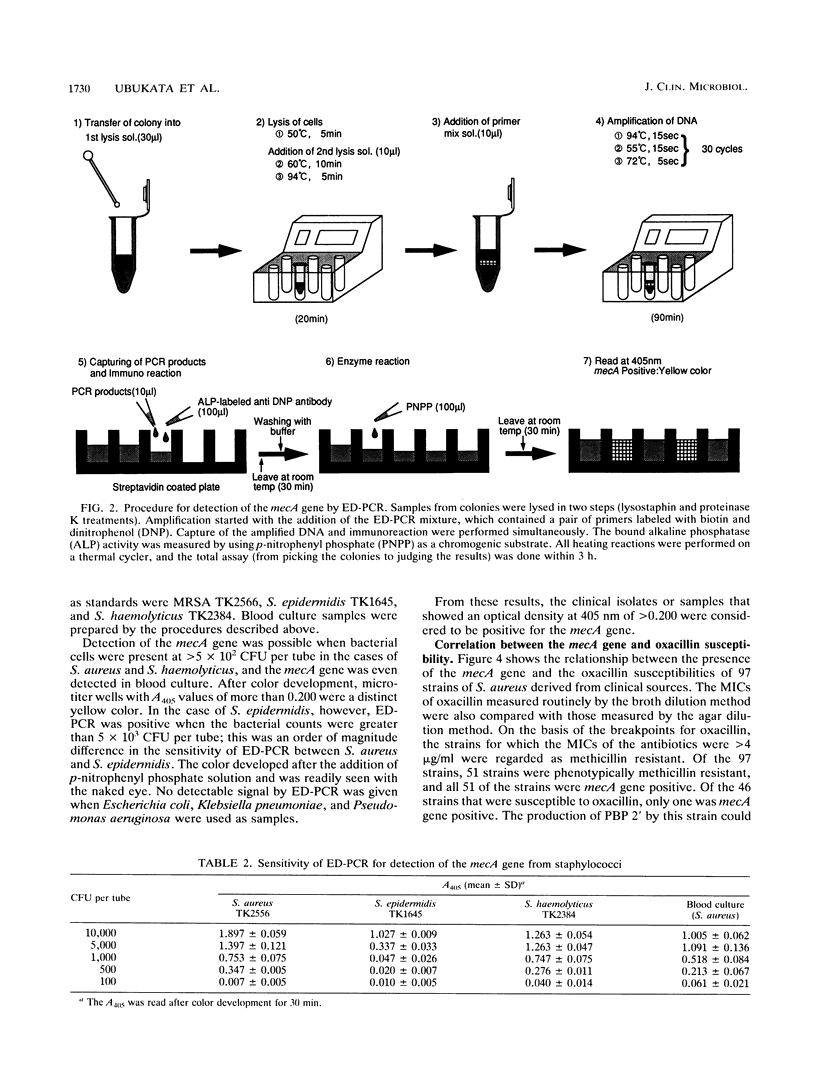
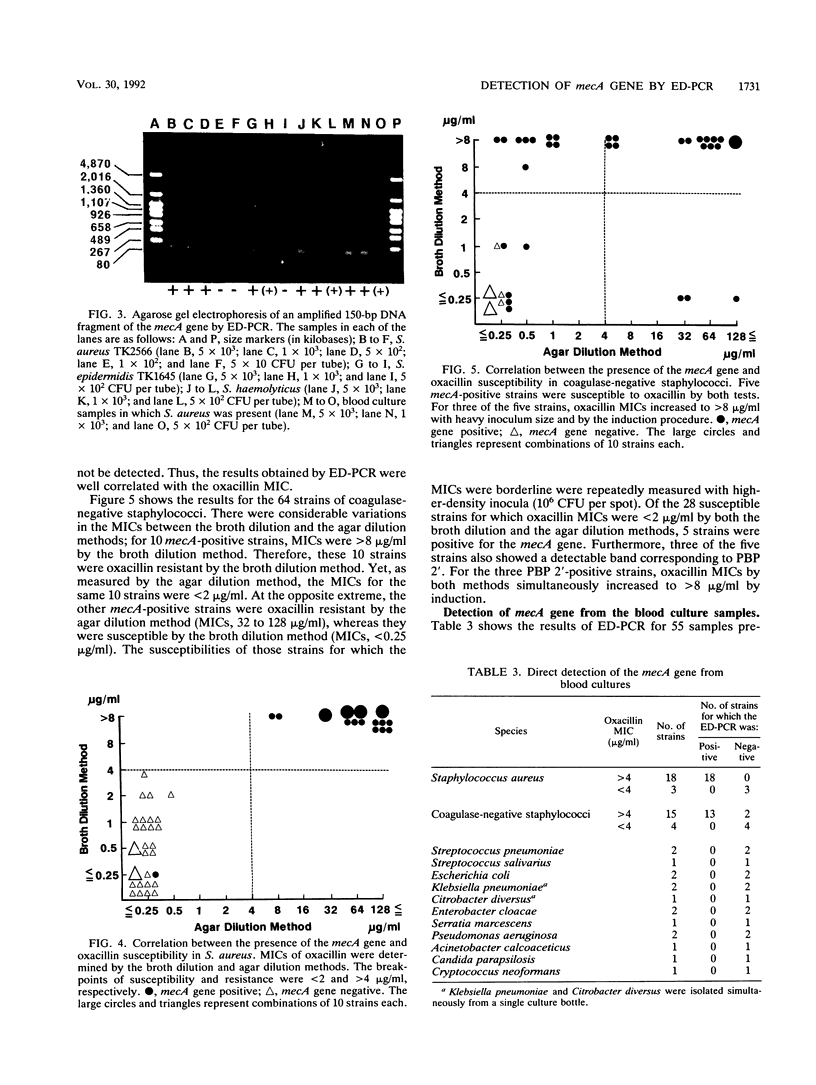
In order to identify methicillin-resistant staphylococci from clinical sources with ease and reliability, enzymatic detection of polymerase chain reaction (ED-PCR) was applied. ED-PCR is based on the capture of amplified products via biotin-streptavidin affinity and the detection of an incorporated hapten in amplified products with an enzyme-linked antibody. In order to identify methicillin-resistant staphylococci of all species, a 150-bp fragment of the mecA gene was targeted for ED-PCR. After PCR was performed with a pair of biotin and dinitrophenol 5'-labeled primers, the reaction mixture was applied to a microtiter well precoated with streptavidin. Thereafter, bound PCR products were detected colorimetrically with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-dinitrophenol antibody. The extraction of DNA from staphylococcal cells for PCR was simplified so that it could be performed within one tube. The total assay, including PCR, took less than 3 h. The sensitivity of mecA gene detection ranged from greater than 5 x 10(2) CFU per tube for Staphylococcus aureus to greater than 5 x 10(3) CFU per tube for Staphylococcus epidermidis. Genotyping results obtained by ED-PCR of 161 tested strains from the colonies (97 strains of S. aureus and 64 strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci) were compared with the phenotypic susceptibilities of the strains to oxacillin. The results of ED-PCR showed excellent agreement with the MICs of oxacillin with very few exceptions; only one strain of S. aureus and two strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci were found to possess the mecA gene, which was discrepant with their phenotypes. Fifty-five blood culture samples were also tested by ED-PCR. For staphylococcal isolates in 33 of the cultures, oxacillin MICs were >4 microgram/ml; 31 of the 33 staphylococcal isolates were determined by ED-PCR to be mecA gene positive. These results suggest that ED-PCR can be used with reasonable confidence in the clinical microbiological laboratory.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Pennell E. Detection of methicillin resistance in staphylococci by using a DNA probe. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1720–1724. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Archer G., Matsuhashi M. Low-level methicillin resistance in strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):424–428. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: detection methods and treatment of infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):995–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Expression of methicillin resistance in heterogeneous strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis B., Matthews P. R., Stewart P. R. The expression in Staphylococcus aureus of cloned DNA encoding methicillin resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1465–1469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligozzi M., Rossolini G. M., Tonin E. A., Fontana R. Nonradioactive DNA probe for detection of gene for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):575–578. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maple P. A., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. World-wide antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1989 Mar 11;1(8637):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Song M. D., Ishino F., Wachi M., Doi M., Inoue M., Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Molecular cloning of the gene of a penicillin-binding protein supposed to cause high resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):975–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.975-980.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Minamide W., Wada K., Nakamura E., Teraoka H., Watanabe S. Identification of methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2240–2244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2240-2244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Nomura K., Doi M., Yoshida T. Production of low-affinity penicillin-binding protein by low- and high-resistance groups of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre J., Williamson R., Bornet M., Gutmann L. Presence of an additional penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, and Staphylococcus simulans with a low affinity for methicillin, cephalothin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1691–1694. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi L., Tonin E., Cheng Y. R., Fontana R. Regulation of penicillin-binding protein activity: description of a methicillin-inducible penicillin-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):828–831. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel C., Tesch W., Birch-Machin I., Reynolds P. E., Barberis-Maino L., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Sequence comparison of mecA genes isolated from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):137–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra-Madero J. G., Knapp C., Karaffa C., Washington J. A. Role of beta-lactamase and different testing conditions in oxacillin-borderline-susceptible staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1754–1757. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song M. D., Wachi M., Doi M., Ishino F., Matsuhashi M. Evolution of an inducible penicillin-target protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by gene fusion. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesch W., Strässle A., Berger-Bächi B., O'Hara D., Reynolds P., Kayser F. H. Cloning and expression of methicillin resistance from Staphylococcus epidermidis in Staphylococcus carnosus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1494–1499. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokue Y., Shoji S., Satoh K., Watanabe A., Motomiya M. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using polymerase chain reaction amplification. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1991 Jan;163(1):31–37. doi: 10.1620/tjem.163.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Drugeon H. B., de Lencastre H. M., Jabes D., McDougall L., Bille J. New mechanism for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: clinical isolates that lack the PBP 2a gene and contain normal penicillin-binding proteins with modified penicillin-binding capacity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1869–1874. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Nonoguchi R., Matsuhashi M., Konno M. Expression and inducibility in Staphylococcus aureus of the mecA gene, which encodes a methicillin-resistant S. aureus-specific penicillin-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2882–2885. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2882-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Nonoguchi R., Matsuhashi M., Song M. D., Konno M. Restriction maps of the regions coding for methicillin and tobramycin resistances on chromosomal DNA in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1624–1626. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Nonoguchi R., Song M. D., Matsuhashi M., Konno M. Homology of mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus simulans to that of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):170–172. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Yokota T. Role of an altered penicillin-binding protein in methicillin- and cephem-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):397–403. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lencastre H., Sá Figueiredo A. M., Urban C., Rahal J., Tomasz A. Multiple mechanisms of methicillin resistance and improved methods for detection in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):632–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



