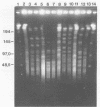
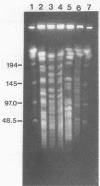
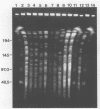
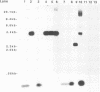
Abstract
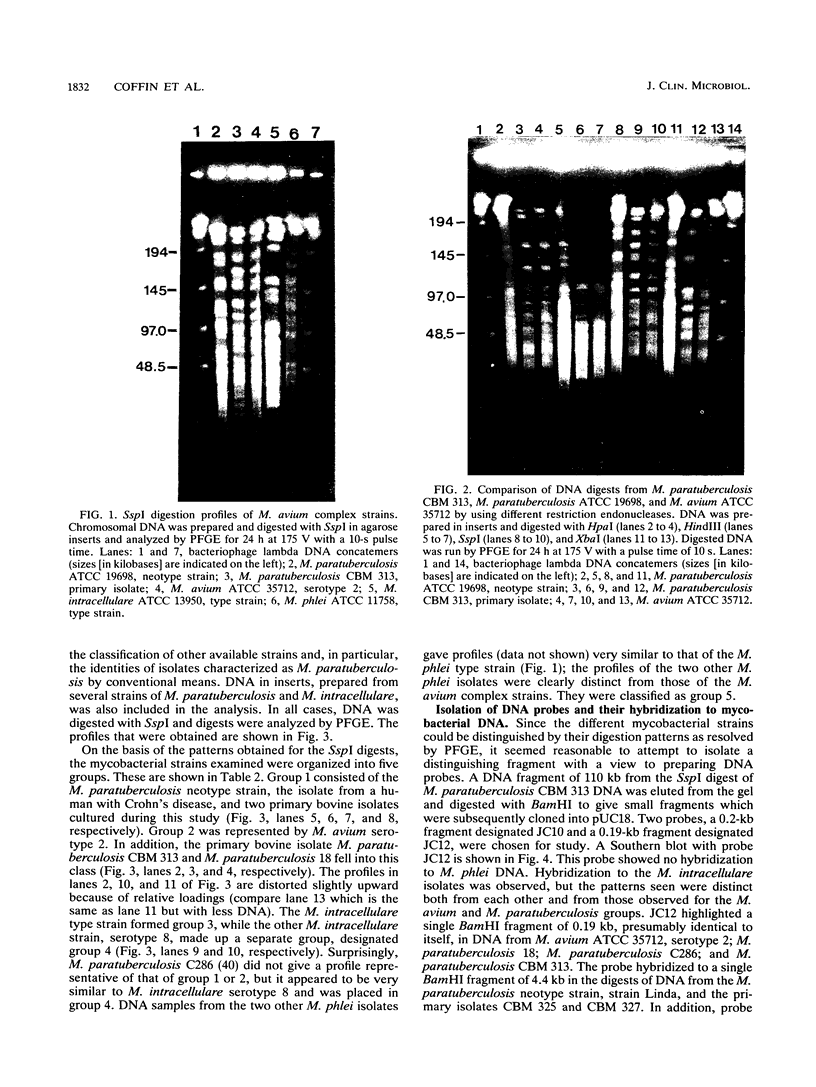
Mycobacterial strains from the Mycobacterium avium complex were compared with each other and with Mycobacterium phlei isolates by restriction endonuclease digestion of chromosomal DNA with SspI and analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Characteristic profiles were observed for known typed strains, and five groups were identified. Primary bovine isolates identified as Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by classical methods were shown to fall into both the M. paratuberculosis- and M. avium-like groups. M. paratuberculosis 18 was in the latter category. Two Mycobacterium intracellulare strains of different Schaefer serotypes had different digestion profiles. In addition, this system was exploited for the preparation of DNA probes by the isolation, digestion, and subcloning of DNA fragments separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Probe JC12 hybridized only to M. avium complex strains, but not to M. phlei, showing characteristic hybridization profiles for each of the groups previously identified by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. The approach taken in the study lends itself to the comparative analysis of members of the M. avium complex and to the isolation and characterization of DNA probes with specificity for these mycobacteria.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anz W., Lauterbach D., Meissner G., Willers I. Vergleich von Sensitin-Testen an Meerschweinchen mit Serotyp und Hühnervirulenz bei M. avium- und M. intracellulare-Stämmen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(4):536–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baess I. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of slowly-growing mycobacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Aug;87(4):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baess I. Deoxyribonucleic acid relationships between different serovars of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Jun;91(3):201–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camphausen R. T., Jones R. L., Brennan P. J. Antigenic relationship between Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Aug;49(8):1307–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Biochemical characteristics of various strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1442–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. Crohn's disease and the mycobacterioses: a review and comparison of two disease entities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):90–117. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J. The genetic relationship between Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and the M. avium complex. Acta Leprol. 1989;7 (Suppl 1):249–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Thayer W. R., Coutu J. A., Merkal R. S. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of a Mycobacterium sp. isolated from patients with Crohn's disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):930–932. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., De Lisle G. W. Identification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., de Lisle G. W. Identification of two groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1591-1596.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. AIDS-related mycobacterial disease. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(4):375–391. doi: 10.1007/BF02053847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Hindler J. A., Berlin O. G., Bruckner D. A. Rapid identification of Mycobacterium avium complex in culture using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1442–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1442-1445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Kiehn T. E., Cammarata R., Hosmer M. Rapid detection and identification of pathogenic mycobacteria by combining radiometric and nucleic acid probe methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1349–1352. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1349-1352.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C. Opportunistic pathogens in the genus Mycobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:347–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson S. J., Portaels F., Thompson J., Green E. P., Moss M. T., Hermon-Taylor J., McFadden J. J. DNA probes demonstrate a single highly conserved strain of Mycobacterium avium infecting AIDS patients. Lancet. 1989 Jan 14;1(8629):65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V. V., Thorel M. F., Varnerot A., Gicquel B. DNA polymorphism in Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, "wood pigeon mycobacteria," and related mycobacteria analyzed by field inversion gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2823–2826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2823-2826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R. J., Hermon-Taylor J. Determination of genome size and DNA homology between an unclassified Mycobacterium species isolated from patients with Crohn's disease and other mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):211–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Schröder K. H., Amadio G. E., Anz W., Chaparas S., Engel H. W., Jenkins P. A., Käppler W., Kleeberg H. H., Kubala E. A co-operative numerical analysis of nonscoto- and nonphotochromogenic slowly growing mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):207–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R., Kvach J. T., Mounts P. Isolation and restriction endonuclease analysis of mycobacterial DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):541–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Plotch S. J., Wang Z., Lin B. C., Donegan J. J., Yang H. L. DNA probes for mycobacteria. I. Isolation of DNA probes for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and for mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT). Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Jun;2(2):111–124. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Tsang A. Y., Yang H. L. Speciation of organisms within the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum (MAIS) complex based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Dec;2(4):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., McMillan C., Coyle M. B. Whole chromosomal DNA probes for rapid identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1239–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1239-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runyon E. H. Pathogenic mycobacteria. Bibl Tuberc. 1965;21:235–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Dawson D. J. Identification of various serovar strains of Mycobacterium avium complex by using DNA probes specific for Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1694–1697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1694-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Tasaka H., Tsukamura M., Kuze F., Asano K. Identification and partial characterization of Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare by using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.994-997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxegaard F., Baess I. Relationship between Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and "wood pigeon mycobacteria". Determinations by DNA-DNA hybridization. APMIS. 1988 Jan;96(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I., Harrington N., Rothrock A., George H. Use of a cutoff range in identifying mycobacteria by the Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.241-244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden E. A., Samagh B. S., Bundle D. R., Duncan J. R. Lipoarabinomannan and lipid-free arabinomannan antigens of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):762–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.762-770.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorel M. F. Review of the occurrence of mycobactin dependence among mycobacteria species. Ann Rech Vet. 1984;15(3):405–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoresen O. F., Saxegaard F. Gen-Probe Rapid Diagnostic System for the Mycobacterium avium complex does not distinguish between Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):625–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.625-626.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wards B. J., Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of members of the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare-M. scrofulaceum serocomplex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2309–2313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2309-2313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple D. L., Le Febvre R. B., Andrews R. E., Jr, Thiermann A. B. Isolation and analysis of restriction endonuclease digestive patterns of chromosomal DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and other Mycobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1511–1515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1511-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple D., Kapke P., Vary C. Identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2561–2564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2561-2564.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo Y., Yugi H., Merkal R. S. A method for avoiding false-positive reactions in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the diagnosis of bovine paratuberculosis. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Feb;47(1):111–119. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura H. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K., Merkal R. S. Investigation of association of mycobacteria with inflammatory bowel disease by nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.45-51.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]