Abstract
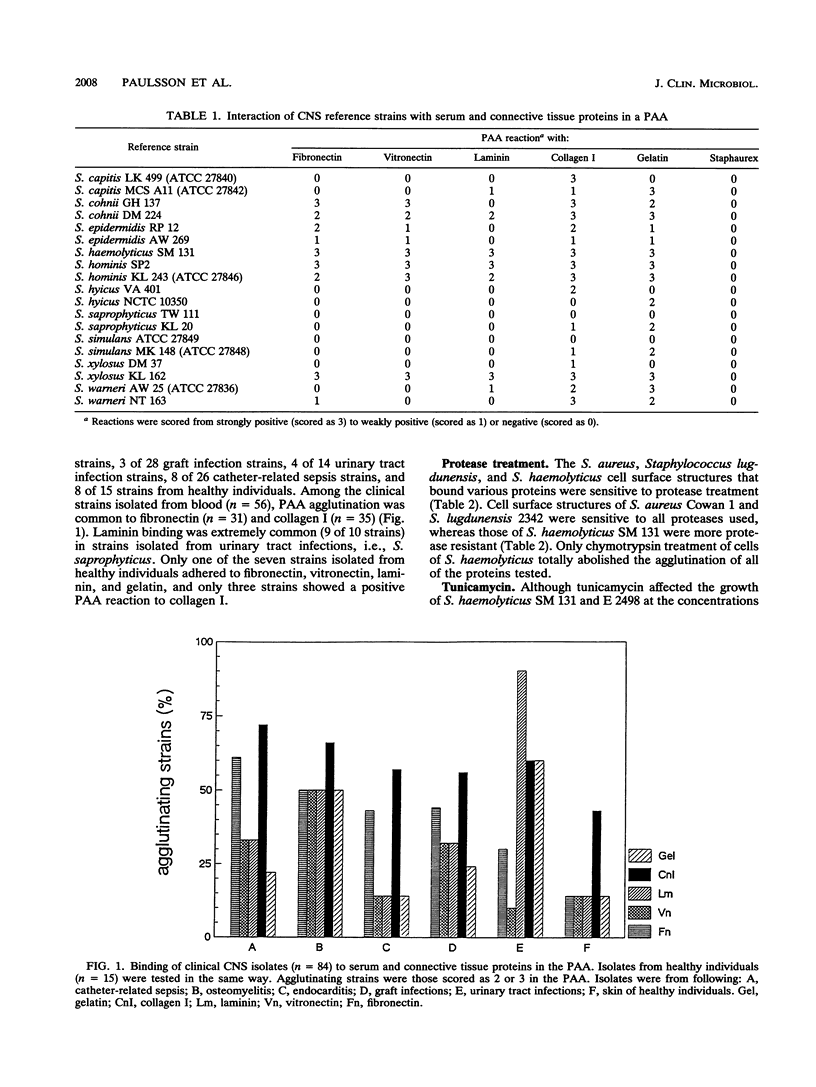
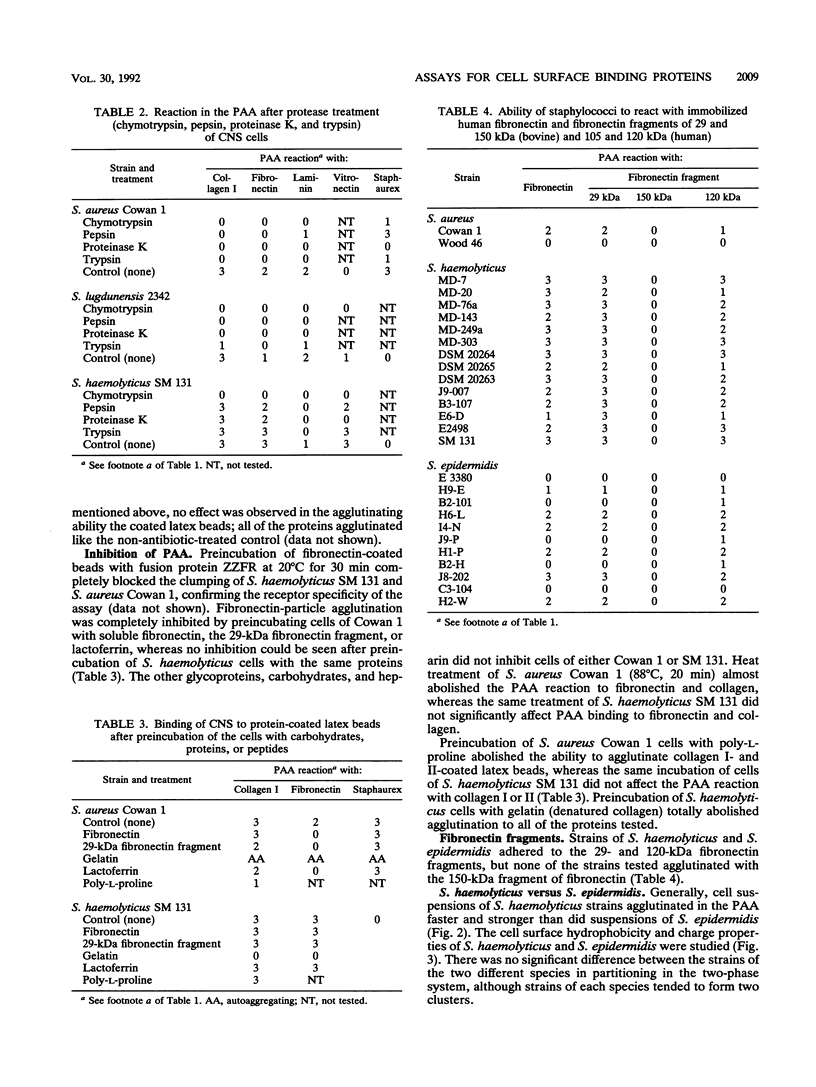
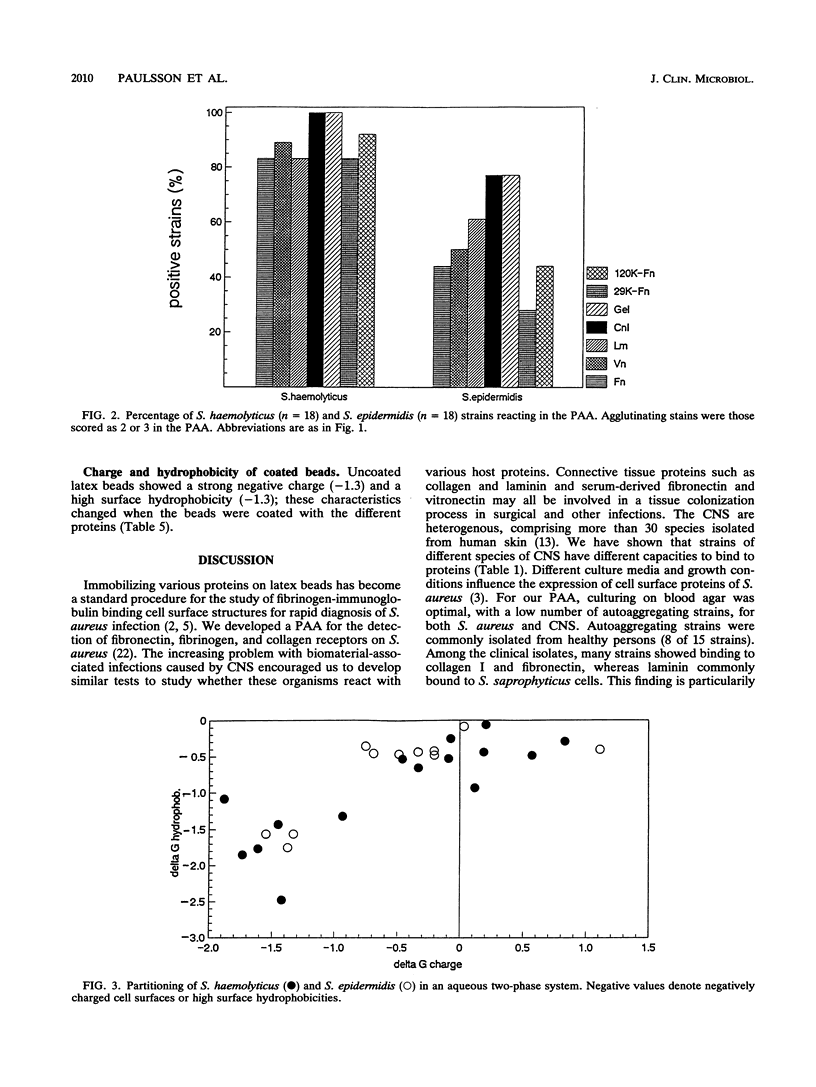
Seventeen strains of ten different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci were shown to interact with collagen, laminin, fibronectin, and vitronectin immobilized on latex beads. Different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci have different capacities to agglutinate proteins. Cells of 18 strains of Staphylococcus haemolyticus reacted more strongly than did cells of 18 Staphylococcus epidermidis strains with proteincoated latex beads, although no significant difference in cell surface hydrophobicity or charge could be shown. The cell surface receptors of S. haemolyticus were more heat and protease resistant than were Staphylococcus aureus receptors. Strains of Staphylococcus saprophyticus isolated from urinary tract infections showed a high capacity to adhere to laminin. The ability to agglutinate fibronectin and collagen was common among coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from other infections; 55% (31 of 56) and 63% (35 of 56) agglutinated fibronectin and/or collagen. S. haemolyticus and S. epidermidis bound to both N-terminal (29-kDa) and C-terminal (120-kDa) fragments of fibronectin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascencio F., Aleljung P., Wadström T. Particle agglutination assays to identify fibronectin and collagen cell surface receptors and lectins in Aeromonas and Vibrio species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1926–1931. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1926-1931.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. Comparison of a yellow latex reagent with other agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.640-642.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Fischetti V. A. Variation in the expression of cell wall proteins of Staphylococcus aureus grown on solid and liquid media. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1061-1065.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H. Specific binding of the human S protein (vitronectin) to streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1878–1883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1878-1883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essers L., Radebold K. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus by a latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):641–643. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.641-643.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuquay J. I., Loo D. T., Barnes D. W. Binding of Staphylococcus aureus by human serum spreading factor in an in vitro assay. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):714–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.714-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Vaudaux P. E., Pittet D., Auckenthaler R., Lew P. D., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Peters G., Waldvogel F. A. Fibronectin, fibrinogen, and laminin act as mediators of adherence of clinical staphylococcal isolates to foreign material. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):693–701. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Spech R. A., Ehrhart L. A. Specific binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jun;5(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A. Staphylococcus saprophyticus as a common cause of urinary tract infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):328–337. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson G. Partition of proteins and micro-organisms in aqueous biphasic systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 Oct 30;4(3):169–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01731478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Attachment of staphylococci and streptococci on fibronectin, fibronectin fragments, and fibrinogen bound to a solid phase. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. F., Schmitt D. D., Edmiston C. E., Bandyk D. F., Krepel C. J., Seabrook G. R., Towne J. B. Sequential analysis of staphylococcal colonization of body surfaces of patients undergoing vascular surgery. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):664–669. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.664-669.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to conformationally specific determinants in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2279-2285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxe I., Rydén C., Wadström T., Rubin K. Specific attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to immobilized fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):695–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.695-704.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Paulsson M., Wadström T. Particle agglutination assays for rapid detection of fibronectin, fibrinogen, and collagen receptors on Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1549–1554. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1549-1554.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Wadström T. Vitronectin and type-I collagen binding by Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1990 May;2(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer G., Beuth J., Ko H. L., Sölter J., Uhlenbruck G. Modification of glycosylation by tunicamycin treatment inhibits lectin-mediated adhesion of Streptococcus pneumoniae to various tissues. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Aug;266(1-2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of the basement membrane protein laminin to Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkonen K. H., Veijola J., Dagberg B., Uhlin B. E. Binding of basement-membrane laminin by Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2133–2141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., McCarthy J. B., Lindholm P., Peterson P. K., Jacob H. S., Furcht L. T. Extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, and type IV collagen) bind and aggregate bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vaheri A. Purification of fibronectin from human plasma by affinity chromatography under non-denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):331–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1830331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatohgo T., Izumi M., Kashiwagi H., Hayashi M. Novel purification of vitronectin from human plasma by heparin affinity chromatography. Cell Struct Funct. 1988 Aug;13(4):281–292. doi: 10.1247/csf.13.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


