Abstract
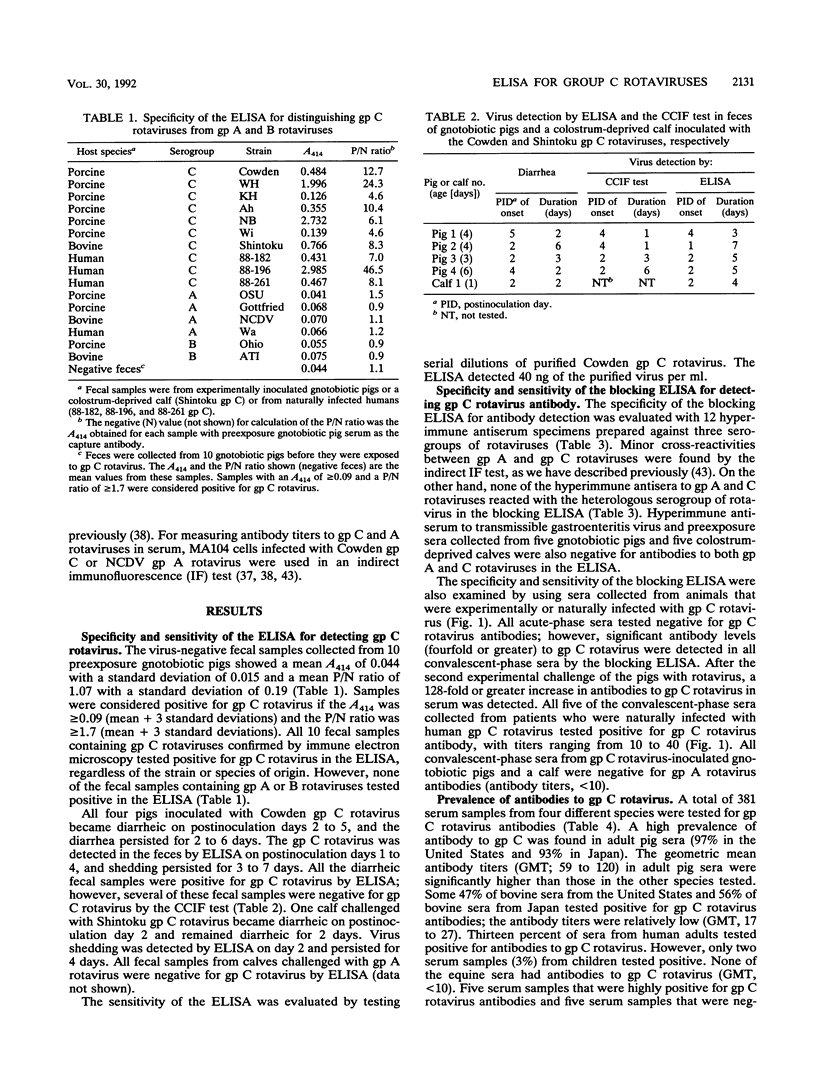
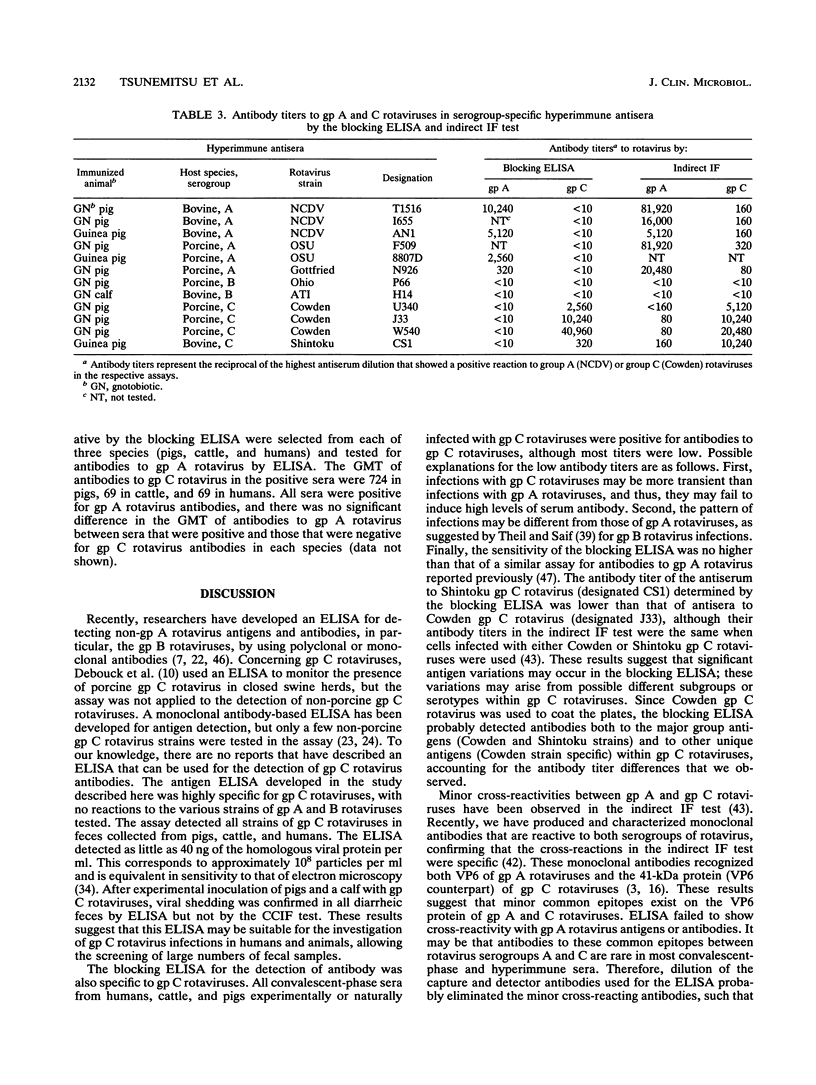
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) were developed to detect group (gp) C rotavirus antigens and antibodies. Both assays were confirmed to be specific for gp C rotavirus by using serogroup A, B, and C rotaviruses; hyperimmune antisera to these serogroups of rotaviruses; and paired serum specimens from animals infected with gp C rotaviruses. The ELISA for antigen detection reacted not only with porcine gp C rotaviruses but also with human and bovine gp C rotaviruses. Following experimental challenge of gnotobiotic pigs with porcine gp C rotavirus, the virus was found by ELISA in all diarrheic feces. A high prevalence of antibodies to gp C rotaviruses was detected in sera from adult pigs (93 to 97%) and cattle (47 to 56%) in the United States and Japan. However, no antibody to gp C rotavirus was detected in the sera (n = 20) of adult horses in the United States. In human sera from Hokkaido, Japan, 3% of children and 13% of adults possessed antibody to gp C rotaviruses. These results suggest that the ELISA that we developed may be useful for surveying gp C rotavirus infections in animals and humans. On the basis of serology, gp C rotavirus infections are common in pigs and cattle in the United States and Japan, but they occur at lower levels in humans from the Hokkaido area of Japan.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremont M., Cohen J., McCrae M. A. Analysis of the structural polypeptides of a porcine group C rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2183–2185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2183-2185.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Brown J. F. Prevalence of antibody to typical and atypical rotaviruses in pigs. Vet Rec. 1985 Jan 12;116(2):50–50. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.2.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Pedley S., McCrae M. A. Group C rotaviruses in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):760–763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.760-763.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. W., Welch S. K., Nakata S., Estes M. K. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human group B rotavirus and their use in an antigen detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):245–250. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.245-250.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caul E. O., Ashley C. R., Darville J. M., Bridger J. C. Group C rotavirus associated with fatal enteritis in a family outbreak. J Med Virol. 1990 Mar;30(3):201–205. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890300311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Davies P. Atypical rotaviruses in pigs and cattle. Vet Rec. 1984 Jan 7;114(1):16–17. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Puerto F., Soler C., González N. Characterization of a human pararotavirus. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):112–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.112-116.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke B. H., Nelson J. K., Benfield D. A., Nelson E. A. Relative prevalence of typical and atypical strains among rotaviruses from diarrheic pigs in conventional swine herds. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1990 Oct;2(4):308–311. doi: 10.1177/104063879000200410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang B. M., Qian Y., Tsunemitsu H., Green K. Y., Saif L. J. Analysis of the gene encoding the outer capsid glycoprotein (VP7) of group C rotaviruses by northern and dot blot hybridization. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90864-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang B. M., Saif L. J., Kang S. Y., Kim J. H. Biochemical characterization of the structural and nonstructural polypeptides of a porcine group C rotavirus. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3171–3178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3171-3178.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. Y., Saif L. J., Miller K. L. Reactivity of VP4-specific monoclonal antibodies to a serotype 4 porcine rotavirus with distinct serotypes of human (symptomatic and asymptomatic) and animal rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2744–2750. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2744-2750.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Hatano M., Kobayashi K., Hasegawa A., Yamazaki S., Nakata S., Chiba S., Kimura Y. An outbreak of gastroenteritis associated with acute rotaviral infection in schoolchildren. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):611–615. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Todd D., Allan G. M., McFerran J. B., Greene J. A. Epidemiology of rotavirus infection in broiler chickens: recognition of four serogroups. Arch Virol. 1984;81(1-2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01309301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagesha H. S., Hum C. P., Bridger J. C., Holmes I. H. Atypical rotaviruses in Australian pigs. Arch Virol. 1988;102(1-2):91–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01315565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Loosle R., Tao H., Wang S. H., Saif L. J., Melnick J. L. Antigenic characterization and ELISA detection of adult diarrhea rotaviruses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):448–455. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeh C. K., Jiang B. M., Tsunemitsu H., Kang S. Y., Weilnau P. A., Saif L. J. Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies to the 41-kilodalton protein of porcine group C rotavirus with homologous and heterologous rotavirus serogroups in immunofluorescence tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2051–2055. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2051-2055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeh C. K., Tsunemitsu H., Simkins R. A., Saif L. J. Development of a biotin-streptavidin-enhanced enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay which uses monoclonal antibodies for detection of group C rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1667-1673.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peñaranda M. E., Cubitt W. D., Sinarachatanant P., Taylor D. N., Likanonsakul S., Saif L., Glass R. I. Group C rotavirus infections in patients with diarrhea in Thailand, Nepal, and England. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):392–397. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Smith K. L., Theil K. W. Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Terrett L. A., Miller K. L., Cross R. F. Serial propagation of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) in a continuous cell line and characterization of the passaged virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1277–1282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1277-1282.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkins R. A., Saif L. J., Weilnau P. A. Epitope mapping and the detection of transmissible gastroenteritis viral proteins in cell culture using biotinylated monoclonal antibodies in a fixed-cell ELISA. Arch Virol. 1989;107(3-4):179–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01317915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J., Campbell I., Inglis J. M., Hargreaves F. D. Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):909–914. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J. Serial propagation of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) in primary porcine kidney cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1316–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1316-1319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Kohler E. M. Physicochemical characterization of porcine pararotavirus and detection of virus and viral antibodies using cell culture immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):268–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.268-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J. In vitro detection of porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus) and its antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):844–846. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.844-846.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemitsu H., Saif L. J., Jiang B. M., Shimizu M., Hiro M., Yamaguchi H., Ishiyama T., Hirai T. Isolation, characterization, and serial propagation of a bovine group C rotavirus in a monkey kidney cell line (MA104). J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2609–2613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2609-2613.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemitsu H., Shimizu M., Hirai T., Yonemichi H., Kudo T., Mori K., Onoe S. Protection against bovine rotaviruses in newborn calves by continuous feeding of immune colostrum. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1989 Apr;51(2):300–308. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.51.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima H., Honma H., Mukoyama A., Shinozaki T., Fujita Y., Kobayashi M., Ohseto M., Morikawa S., Kitamura T. Detection of group C rotaviruses in Tokyo. J Med Virol. 1989 Apr;27(4):299–303. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890270408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Barbour B. A., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Measurement of rotavirus antibody by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay blocking assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):283–287. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.283-287.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R., Wee S. B., Eiden J., Kinney J., Vonderfecht S. Identification of a group-reactive epitope of group B rotaviruses recognized by monoclonal antibody and application to the development of a sensitive immunoassay for viral characterization. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1853–1858. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1853-1858.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


